Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Science Class 6 > NCERT Summary: Getting to Know Plants
NCERT Summary: Getting to Know Plants | Science Class 6 PDF Download

Introduction
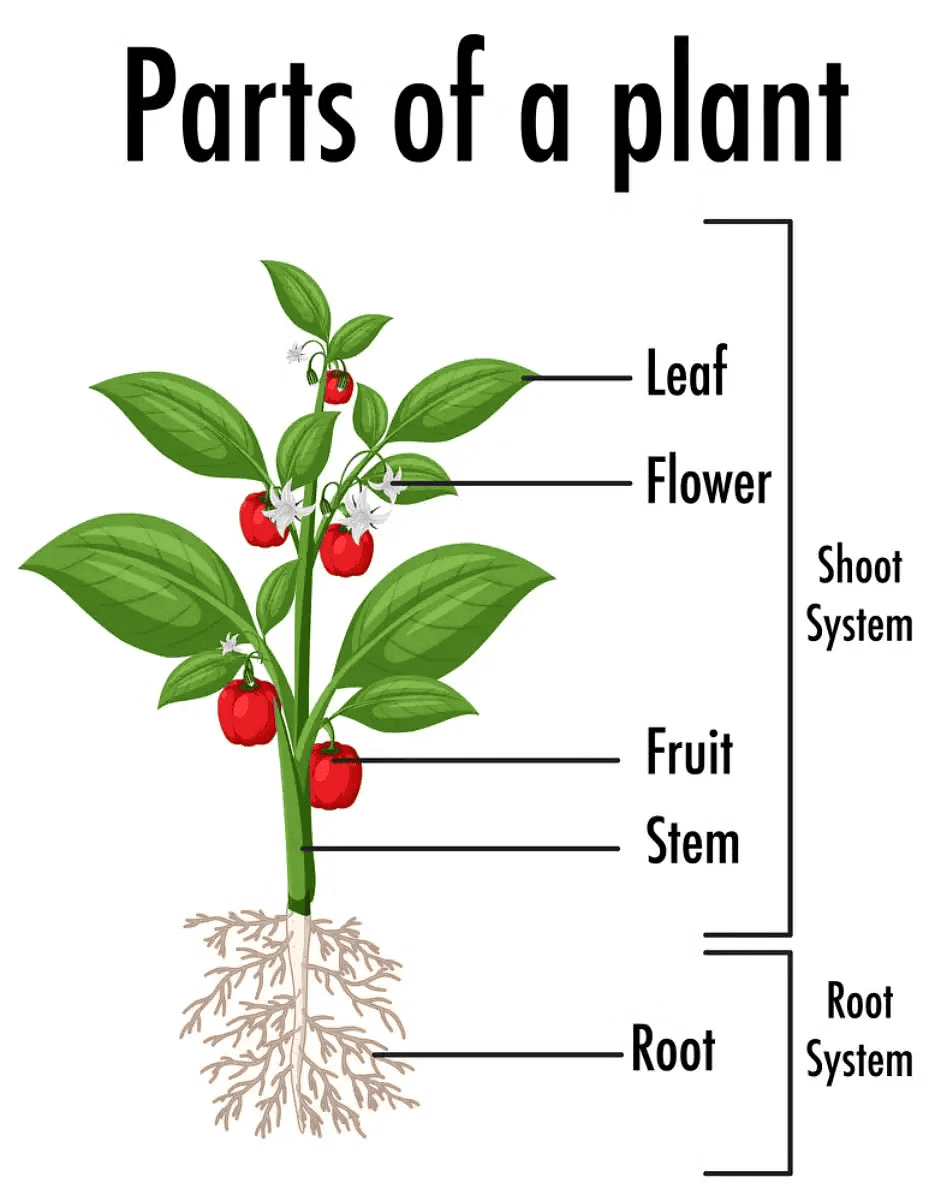
There are various plants around us, differing in size, colour, leaf shape, and the presence or absence of flowers.The main parts of a plant are:
- Root: Absorbs water and nutrients.
- Stem: Supports the plant and transports materials.
- Branch: Holds leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Leaf: Performs photosynthesis.
- Flower: Reproductive part.
- Fruit: Develops from the ovary and contains seeds.
Classification of Plants
The plants are classified into five types based on growth habits:
- Herbs
- Shrubs
- Trees
- Climbers
- Creepers

Herbs
- These plants have green, tender stems and are usually short with few branches.
- They do not develop a hard, woody structure and are often used in cooking or medicine.
- Example: Basil.
Shrubs
- Shrubs have harder stems but are not as thick as trees.
- Their branches grow near the base of the stem, making them bushy and medium-sized.
- Example: Rose Bush.
Trees
- Trees are very tall with hard, thick stems and branches that grow high up on the trunk.
- They have a woody structure and provide shade.
- Example: Oak Tree.
Creepers
- Creepers have weak stems that spread on the ground and do not stand upright.
- They often cover the ground and can spread over large areas.
- Example: Pumpkin Plant.
Climbers
- Climbers have stems that need support to grow upwards.
- They attach themselves to structures or other plants and climb to reach sunlight.
- Example: Bean Plant.
Parts of a Plant

Stem
- The stem is the main part of the plant.
- It gives structural support and helps in transportation of the water, minerals and food.
- The leaves and branches originate from the stem.
Leaf

Leaf Structure:
- Petiole: The stalk that attaches the leaf to the stem.
- Lamina: The broad, flat part of the leaf.
Leaf Patterns:
- Veins: The lines on a leaf that transport nutrients and water.
- Midrib: The central vein running through the leaf.
- Reticulate Venation: A net-like pattern of veins.
- Parallel Venation: Veins run parallel to each other.
Functions of Leaves:
- Transpiration: The process where water evaporates from leaves into the air.
- Photosynthesis: The process where leaves use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce food and release oxygen. Leaves contain starch, which is produced during photosynthesis.

Roots
Functions of Roots:
- Roots anchor the plant securely in the soil.
- Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil and transport them to other parts of the plant.
Types of Roots:
- Tap Roots: Have a main root with smaller lateral roots branching off (e.g., carrot, radish).
- Fibrous Roots: Do not have a main root; instead, they consist of many similar-sized roots that spread out (e.g., grass, maize).

Characteristics of Roots:
- Root Systems can be classified into tap root systems or fibrous root systems.
- Roots can vary in appearance and structure depending on the type of plant.

Flowers
- A flower is the reproductive organ of a plant.
- Flowers get developed into fruits and the fruits contain seeds with them for the next generation.

Parts
- Petals: Colorful parts that attract pollinators; vary in color and number.
- Sepals: Green, leaf-like structures that protect the flower bud; may be joined or separated.
- Stamens: Male part of the flower, includes:
Anthers: Produce pollen.
Filaments: Support the anthers. - Pistil: Female part of the flower, includes:
Stigma: Where pollen lands.
Style: Connects stigma to ovary.
Ovary: Contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization. - Ovules: Small bead-like structures inside the ovary, develop into seeds.
Structure
- Petal Arrangement: Petals can be separated or fused together.
- Sepal Arrangement: Sepals can be joined or separated, and this affects the overall appearance of the flower.
- Stamen and Pistil Count: The number of stamens and pistils can vary, and some flowers may have different numbers of these parts compared to petals.
The document NCERT Summary: Getting to Know Plants | Science Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Science Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Getting to Know Plants - Science Class 6
| 1. What are the main parts of a plant? |  |
Ans. The main parts of a plant are roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Roots anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients. Stems support the plant and transport fluids between roots and leaves. Leaves are the sites of photosynthesis, where plants make their food. Flowers are involved in reproduction, and fruits contain seeds.
| 2. What is photosynthesis and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make their own food in the form of glucose. It is important because it provides energy for the plant and releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
| 3. How do plants reproduce? |  |
Ans. Plants can reproduce in two main ways: sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction involves the formation of seeds through the fertilization of flowers, while asexual reproduction can occur through methods such as cuttings, runners, and tubers, where new plants grow from parts of the parent plant.
| 4. What are the different types of plants based on their habitat? |  |
Ans. Plants can be classified based on their habitat into aquatic plants, terrestrial plants, and aerial plants. Aquatic plants grow in water, terrestrial plants grow on land, and aerial plants, like some orchids, grow on other plants or surfaces without harming them.
| 5. Why are plants important for the environment? |  |
Ans. Plants are crucial for the environment as they produce oxygen, improve air quality, provide food and habitat for many organisms, prevent soil erosion, and contribute to the water cycle. They also play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















