BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Notes > Bihar Geography
Bihar Geography - BPSC (Bihar) PDF Download
Introduction to Bihar
Geographically, Bihar is located in the eastern region of India. It is a land-locked state having boundaries with three Indian states namely Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand and West-Bengal. Bihar shares its border with Nepal in the north, Uttar Pradesh in the west, Jharkhand in the south and West Bengal in the east.Bihar Location and Extent
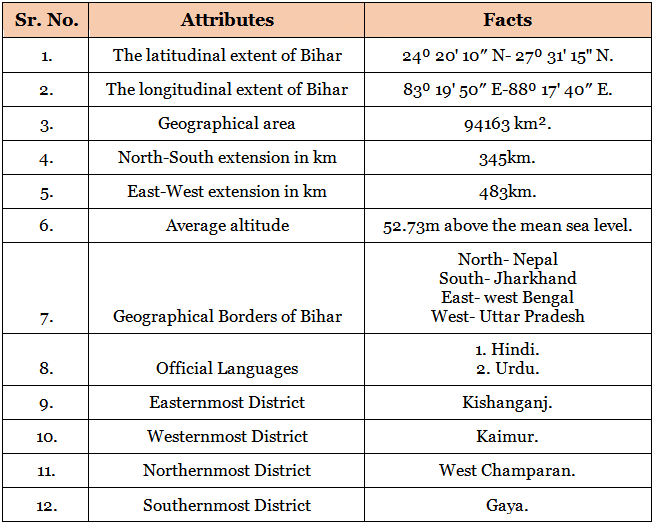
Important Facts of Bihar
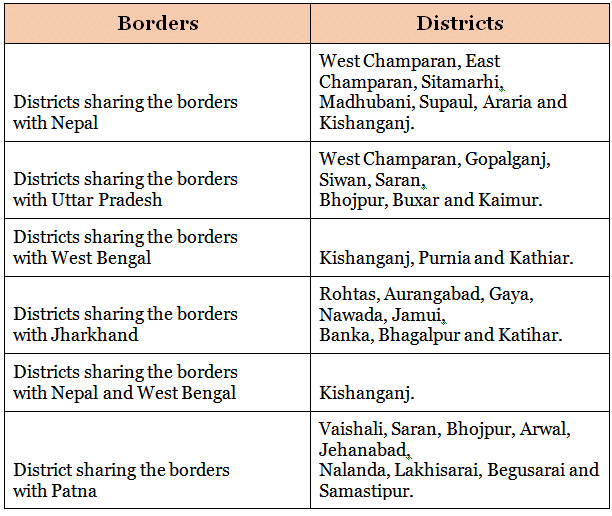
Borders of Bihar

Administrative divisions of Bihar
Question for Bihar GeographyTry yourself: Which states share their border with Bihar?View Solution
Physiographic division of Bihar
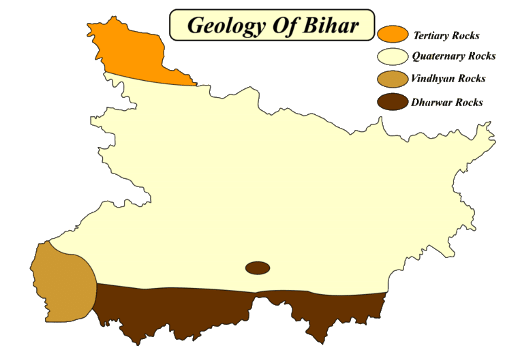
Geologically, Bihar consists of both the younger and older formation of rocks ranges from the Tertiary Period to Pre-Cambrian Period. The plains of Bihar have come into existence by the sediments deposited by the rivers. Geographically, Bihar is bounded by the Himalayan foothills, the Indo-Gangetic plains, the Vindhyan plateau and the Gondwana Basin. Based on the physical and structural conditions, Bihar is divided into three physiographical units.- The Shivalik Ranges or Shiwalik Ranges.
- The Bihar plains.
- Southern Plateau regions.
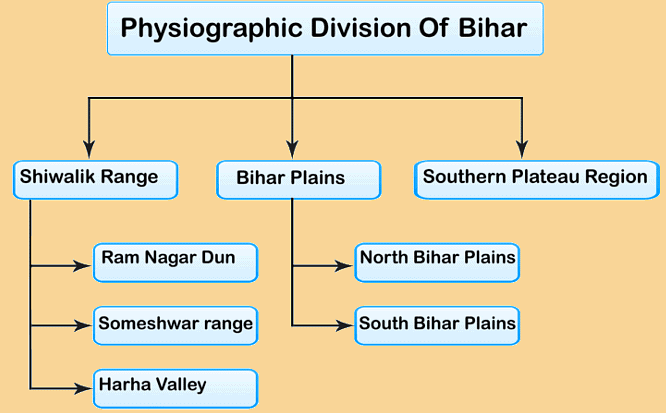
Question for Bihar GeographyTry yourself: Which physiographic unit of Bihar is characterized by the presence of the Shivalik Ranges?View Solution
The Shiwalik Range in Bihar
- The Shiwalik range is located in the north-western part of West Champaran.
- It spreads over an area of 32km in length and 6-8km in width.
- Based on the local variations of topography, it can be further divided into the following parts.
Someshwar Range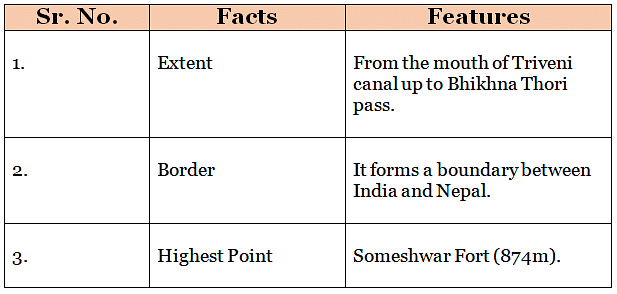
Ramnagar Dun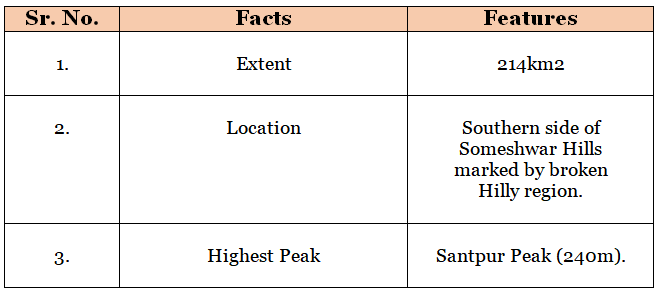
Harha valley
Bihar Plains
The Ganga river flows from west to east in Bihar, dividing the state into two unequal halves namely North Bihar plains and South Bihar plains. The plains of Bihar are formed by the silt carried by the Ganga and its tributaries. They are spread on an area of 45000km2.The North Ganga plains
The north Bihar consists of the plains of alluvium north of Ganga, falling between the Ganga and Indo-Nepal border. Generally, the slope of north Bihar is from north-west to south-east. Also, this region has been drained by the rivers of north Bihar.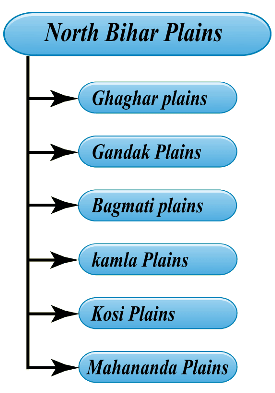

The South Ganga Plains
- In terms of the geographical area of Bihar, the South Bihar is spread over 40,070km2. In terms of percentage, it accounts for 42.7% of the total area of Bihar. Demographically, it supports 36.5% of the state’s population. Also, this area is administered under the Magadh, Patna, parts of Munger and Bhagalpur administrative divisions.
- The eastern portion of the alluvial plains of South Bihar is interrupted by the Kharagpur Hills. The south plains of Bihar are wider in the west and narrower in the east. Moreover, the western portion of this alluvial plain slopes from southwest to northeast. On the other hand, central and eastern parts of the plain slopes from south to north. The hills of Rajgir have an elevation of 445m. While the Kharagpur range has an elevation of 300m above the mean sea level.


South Hilly region of Bihar
- The south Hilly regions of Bihar is marked by hills and ridges.
- Geographically, it extends from Kaimur district in the west to Banka district in the east.
- Geologically, this region is made up of hard rocks of Genesis, Schist and Granite.
- The important hills of this region are Pretshila, Jethian, Ramshila etc.
Soils of Bihar
Being an agriculture dominant state, the people of Bihar obtain their livelihood from agriculture. Based on the composition, regional distribution and its features, the soils in Bihar are divided into the soils of North Bihar Plains and South Bihar Plains.Soils of North Bihar
- Piedmont Swamp Soil.
- Terai Soil.
- Recent Alluvium Soil- Khadar and Bhangar.
Soils of South Bihar
- Old Alluvium Soil.
- Tal Soil.
- Balthar Soil.
- Red Sandy Soil.
Climate in Bihar
The climate of Bihar is characterised by humid and subtropical climate. There are three distinct seasons in Bihar (Summer season, Winter Season and Rainy Season). Annual average temperature ranges between 8C in cold winters during December- February to 38C in the hot summer month during April- June.Agro-Climatic zones of Bihar
The following are the agro-climatic zones of Bihar.- North-West zone, consisting 13 districts with an annual rainfall of 1040mm-1450mm.
- North-East zone, covering 8 districts having annual rainfall of 1200mm to 1700mm and loam or clay-loam soil.
- South Zone covering, 17 districts, having soil of sandy loam, loamy, clayey or clay-loam and rainfall of 990mm to 1300mm.
The document Bihar Geography - BPSC (Bihar) is a part of BPSC (Bihar) category.
All you need of BPSC (Bihar) at this link: BPSC (Bihar)
FAQs on Bihar Geography - BPSC (Bihar)
| 1. What is the geographical location of Bihar? |  |
Ans. Bihar is located in the eastern part of India, bordered by Nepal to the north, West Bengal to the east, Jharkhand to the south, and Uttar Pradesh to the west.
| 2. What are some major geographical features of Bihar? |  |
Ans. Bihar is known for its fertile plains, with the Ganges River flowing through the state. The state also has a diverse landscape, including hills, forests, and rivers.
| 3. How does the geography of Bihar influence its agriculture? |  |
Ans. The fertile plains of Bihar, along with the presence of rivers like the Ganges, make the state suitable for agriculture. The geography provides ample water supply for irrigation, leading to the cultivation of crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
| 4. What are some key geographical challenges faced by Bihar? |  |
Ans. Bihar faces challenges such as floods due to its proximity to rivers like the Ganges. The state also experiences soil erosion and waterlogging in certain areas, impacting agriculture.
| 5. How does the geography of Bihar contribute to its cultural heritage? |  |
Ans. The diverse geography of Bihar has influenced its cultural heritage, with traditional art forms, music, and dance reflecting the state's agricultural roots. The Ganges River is also considered sacred in Hinduism, leading to the development of religious sites along its banks in Bihar.
Related Searches



















