Notes: Principles of Development | Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Principles of Child Development |

|
| Educational Importance of Principles of Child Development |

|
| Factors Influencing Child Development |

|
| Child Psychology |

|
The principles of child development show how a child develops in the first few years of life! Generally, all the children pass through the same stages of development. However, the rate and the pace varies for each child.

Child development involves the scientific study of the patterns of growth, change, and stability that occur from conception through adolescence. There are many perspectives on what constitutes a child.
Some key concepts are highlighted below:
1. A Child is Unique and Special
Every child is unique, as no two children are exactly alike. Even twins, who may share physical similarities, differ in development, characteristics, personality, and behavior.
2. Childhood
Childhood is a crucial stage in life, where foundational development occurs. During this period, a child's cognitive development progresses, accumulating memory, understanding, experience, and knowledge.
3. Measured Qualitatively
Development is a qualitative process that progresses from conception through various life stages: newborn, toddler, young child, teenager, adult, and finally, death.
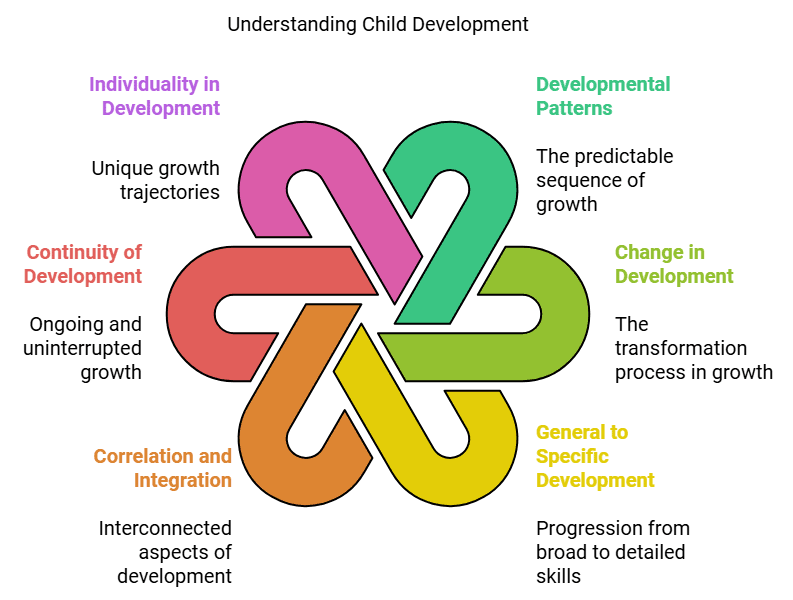
Principles of Child Development
The pattern and process of growth and development in children are characterized by several principles. These principles outline how typical development is predictable and orderly. Key principles include:
1. Development Follows a Pattern or Sequence
Although each child develops at a different rate, the overall pattern of development is similar across all human beings. Development follows a sequential pattern, which can be observed in two main directions:
(i) Cephalocaudal (Head to Toe) Sequence
According to this principle, children gain control over their bodies in a head-to-toe sequence. Initially, infants control head and face movements within the first two months after birth. In the following months, they develop the ability to lift themselves using their arms. By 6 to 12 months of age, infants typically gain leg control, enabling them to crawl, stand, or walk.
(ii) Proximodistal Sequence
This principle indicates that development proceeds from the center of the body towards the outer parts. For example, the spinal cord develops before the outer parts of the body. A child's arms develop before the hands, and the hands and feet develop before the fingers and toes. Muscles in the fingers and toes, crucial for fine motor skills, are the last to develop.
2. Development Involves Change
Human beings are never static. From conception to death, individuals undergo continuous changes. These changes include alterations in size and proportions, as well as the acquisition of new mental, motor, and behavioral skills. For instance, a child's language abilities and cognitive functions improve over time.
3. Development Proceeds from General to Specific
Throughout both prenatal and postnatal stages, a child's responses evolve from general to specific. Initially, infants grasp objects with their whole hand before learning to use the thumb and forefinger. Early motor movements are generalized and reflexive, such as waving arms or kicking, which later develop into more directed actions like reaching or crawling towards objects.
4. Development is Correlated or Integrated
All aspects of development—physical, mental, social, and emotional—are interconnected. For example, a physically healthy child is more likely to exhibit better social skills and emotional stability. Development occurs as a unified whole, with each area influencing and being influenced by others.
5. Development is a Continuous Process
Development is continuous from conception until death, occurring at a regular pace rather than in spurts. Although continuous, the rate of development varies; it is rapid during infancy and early childhood but slows down in later years.
6. Development of Individuality
Individual differences in development arise from the interaction between heredity and environment. These differences result from genetic inheritance and environmental conditions such as nutrition, medical care, psychological conditions, and learning opportunities.
7. Development Occurs at Different Rates for Different Parts of the Body
While development is continuous, different body parts grow at varying rates. For example, the brain reaches full maturity between ages 6 and 8, whereas the hands, feet, and nose reach maximum size in early adolescence. The heart, liver, and digestive system continue to grow during adolescence.
8. Development Proceeds Stage by Stage
Child development occurs in stages, each with unique characteristics. Although there are individual differences in growth rates, the age limits for these stages are approximate.
9. Early Development is More Important than Later Development
Early childhood experiences significantly impact a child's development. Factors such as nutrition, emotional support, social interactions, and cultural experiences play crucial roles during this period.
10. Development is Predictable
It is possible to predict the range within which a child's development will likely fall. However, predicting mental development with the same accuracy as physical development is more challenging.
11. Social Cognitive Theory
Formulated by N.E. Miller and J. Dollard in 1941, this theory posits that people learn by observing others. Children imitate observed actions and receive positive reinforcement, which encourages repetition of the expected behavior. Both reinforcement and punishment influence behavior and learning.
12. Development does not Proceed at the Same Pace for All (Theory of Maturation)
According to Gesell's theory, children progress through similar growth stages at their own rates. For example, while most children learn to walk around the same age, the exact timing can vary among individuals.

Educational Importance of Principles of Child Development
Children are better able to demonstrate their developmental abilities when they do so voluntarily. Clear principles linked to daily activities make it easier to achieve good educational aims. The educational importance of these principles is outlined below:
- Developing Independence and Self-Reliance:One educational aim is to cultivate children's ability to think independently, without needing to follow instructions.
- The teacher's role is to ensure children can achieve self-realization.
- Teachers should offer guidance and hints to help children when they are stuck or lose interest in their activities.
- Respecting Individual Development Pace: Education should cater to the varying developmental speeds of each child. Teachers should prepare a variety of activities so children can engage in what interests them the most and develop through those activities.
- Evaluating Development Levels: Education must assess each child's development level to decide how best to support and understand their immediate desires and thoughts.
- Widening Activities and Ideas: Education helps children expand their activities and ideas, providing an environment conducive to both physical and psychological development.

Factors Influencing Child Development
Child development is a continuous process from birth to adulthood, typically following a pattern and sequence. Each developmental step occurs at a certain age and in a usual order similar for most children. The factors influencing child development are categorized into internal and external factors.

Internal Factors
Internal factors include heredity, physical attributes, intelligence, and emotional factors.
- Heredity: Genetic factors play a significant role in a child's height, weight, and body build. These genetic materials influence growth rates and differences between male and female growth patterns.
- Physical Factors: Physical aspects can influence development in various ways. Good nutrition and consistent physical activities are crucial for proper development, minimizing obesity risks, and enhancing muscle growth.
- Intelligence: Intelligence impacts physical development, thought processes, creative thinking, information retention, and academic achievement. Intelligent children tend to grow faster physically and achieve developmental milestones quicker.
- Emotional Factors: Emotional factors affect social, mental, physical, and moral development, as well as language development. Balanced emotional development helps children respond appropriately to their own and others' emotions, facilitating easier emotional regulation.

External Factors
Child development is influenced by various external factors including family, physical environment, and socio-economic conditions. These factors are crucial in shaping a child's growth and development.
1. Family
The family plays a vital role in shaping a child's development. An affectionate bond between parents and children is essential for proper growth.
- A larger family often provides moral values, education, and support to the child, while a smaller family fosters independence.
- Children experiencing stressful family environments or coming from broken families are more likely to face learning disabilities and negative impacts on their emotional and social development.
2. Physical Environment
The environment in which a child grows up significantly affects their mental, emotional, and physical development.
- Factors such as pollution, noise levels, overcrowding, poor quality housing, and neighborhood quality play crucial roles in child development.
- Pollution adversely affects children's health. Parents in overcrowded homes tend to be less responsive to their children's needs. The quality of housing and the surrounding neighborhood greatly influence a child's behavior.
3. Socio-Economic Conditions
The socio-economic conditions in which a child grows up are fundamental to their development.
- Children from well-to-do families often have access to good schools, extracurricular activities, and vacations that provide new experiences, enhancing their cognitive, physical, and social skills.
- Children from less fortunate backgrounds may face challenges such as ill-health, depression, stress, and lack of motivation, leading to inadequate physical, cognitive, and social development.
Child Psychology
Child psychology is a comprehensive field that examines the growth of children from birth to adolescence. It seeks to understand all aspects of child development, including how children learn, think, interact, respond to their surroundings, form friendships, and comprehend emotions.
According to Mosby’s Medical Dictionary, "Child psychology is the study of the mental, emotional, and behavioural development of infants and children." This field focuses on the cognitive and intellectual growth of a child. Child psychologists aim to understand the mind and behaviour of children from prenatal development through adolescence, encompassing their physical, mental, emotional, and social development.

Importance of Child Psychology
Understanding child psychology is crucial for parents, teachers, and caregivers to help children adapt to various life situations. The importance of child psychology includes the following:
- Understanding the Child: It helps in comprehending the development and behaviour of a child.
- Identifying Psychological Issues: It aids in recognizing problems faced by children that have psychological origins.
- Effective Communication: It establishes effective communication with the child.
- Creating a Conducive Learning Environment: It produces a comfortable environment for efficient and effective teaching and learning processes.
- Building Confidence: It helps gain the confidence of both the child and the parents, ensuring a better understanding of the child's growth environment.
- Recognizing Individual Differences: It assists teachers in delivering content in a way that acknowledges individual learning differences, providing proper direction for skill development.
- Understanding Behaviour Causes: It explains specific child behaviours and their causes, aiding in appropriate interventions.
- Studying Personality Traits: It involves the study of a child's personality traits, helping to predict future behaviour and guiding the child's development accordingly.
|
68 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Principles of Development - Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the key principles of child development? |  |
| 2. Why is understanding the principles of child development important in education? |  |
| 3. What are some factors that influence child development? |  |
| 4. How does child psychology relate to child development? |  |
| 5. What are some common developmental milestones in children? |  |
|
68 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CTET & State TET exam
|

|



















