Electronic Waste - People, Development and Environment Notes
Waste Pollution
Waste is any substance that constitutes scrap material, effluent, or other unwanted surplus substance resulting from the application of any process.
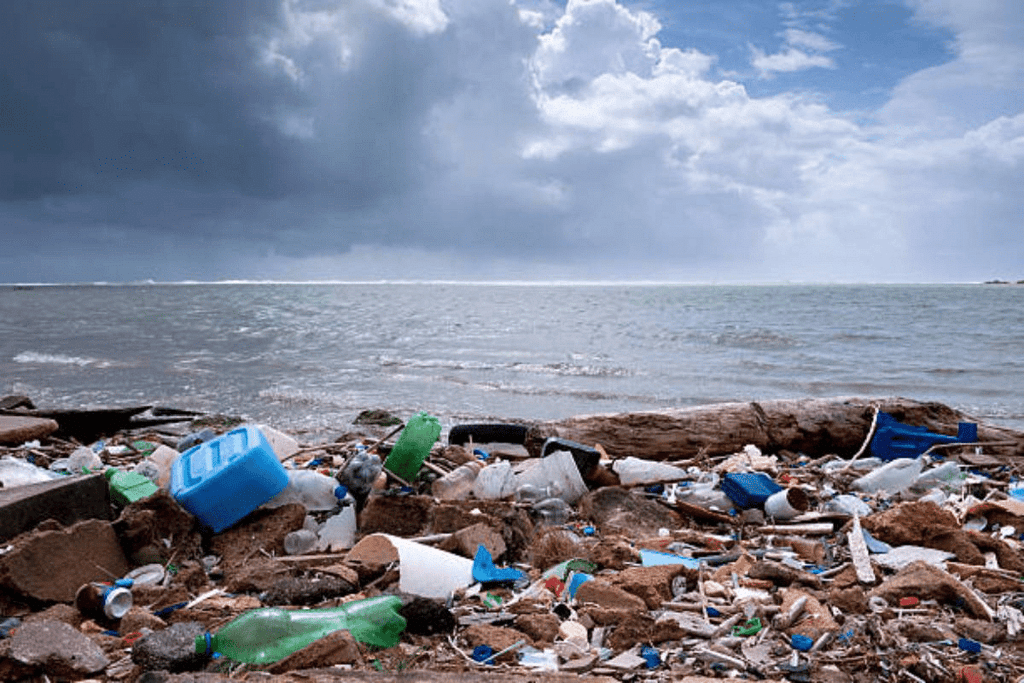

Depending on its properties, waste can be classified as inert, toxic, or inflammable. If these wastes are not treated, they lead to pollution of air, water, soil, and solid waste. Waste can exist in solid, liquid, and gaseous forms.
Types of Waste
1. Solid Waste
Solid waste includes municipal wastes, industrial wastes, and hazardous wastes. It primarily consists of man-made waste, often plastic litter, discarded in the environment and found in seas, along coastlines, either floating or submerged.
- Municipal Waste: Arises from domestic activities.
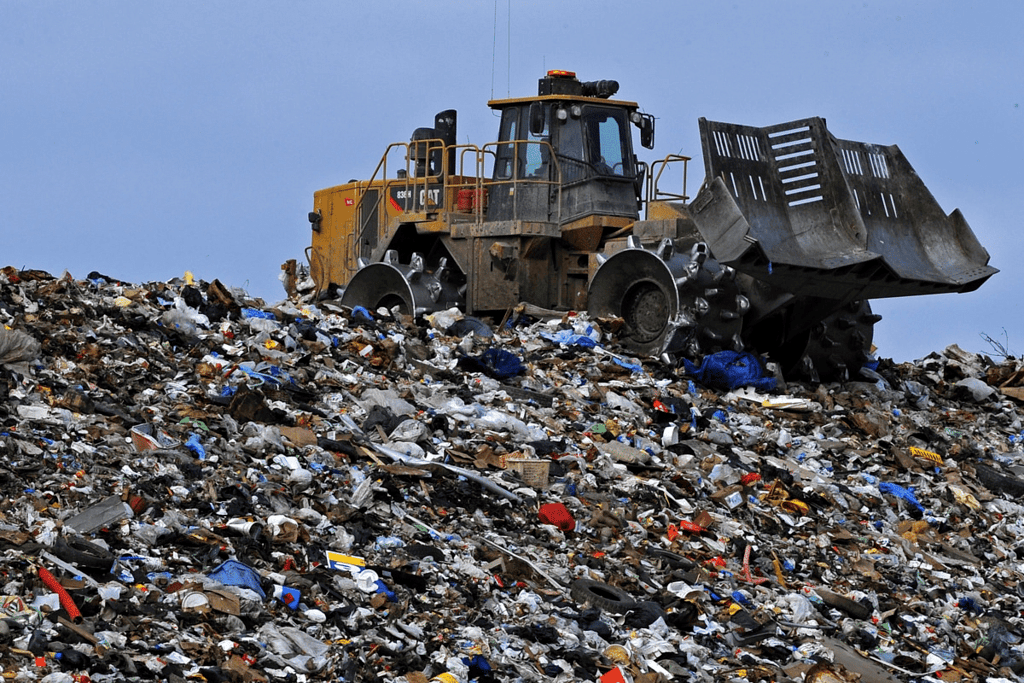

- Industrial Waste: Results from industrial activities.
- Hazardous Waste: Includes substances harmful to plants, animals, and humans, such as radioactive substances, chemicals, biological wastes, flammable wastes, and explosives.
Solid Waste Management
Different methods are used to manage solid wastes based on land area availability and disposal costs.
Disposal
- Sanitary Landfills: Waste is dumped in a scientifically designed area, spread in thin layers, and covered with soil daily. Methane is produced due to anaerobic decomposition of organic matter.
- Incineration: Burning municipal solid waste in a properly designed furnace under suitable temperature and conditions, reducing waste volume by about 90% and weight by 75%.
Composting: Bacterial decomposition of organic components of municipal waste forms humus or compost, valuable as manure for crops. This process is also known as biodegradation.
Pyrolysis: Thermal degradation of waste in the absence of air, using an external heat source. It recovers chemical constituents and energy from organic wastes, splitting them into gaseous and liquid fractions like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, tar, and methane.
Recycling: Reusing some components of waste that have economic value.
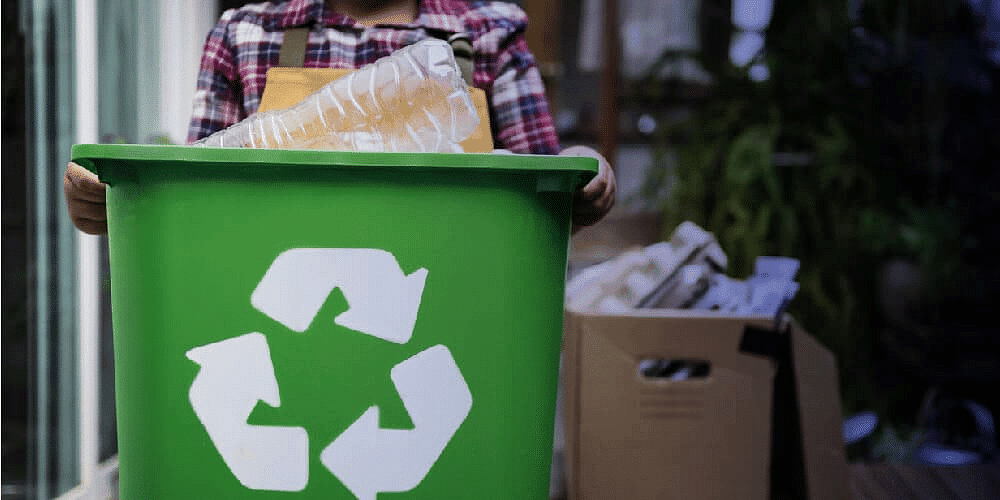 It conserves resources, reduces energy used during manufacture, and reduces pollution.
It conserves resources, reduces energy used during manufacture, and reduces pollution.Source Reduction: Reducing waste by using less material when making products, reusing products, and designing packaging to reduce quantity.
Land Treatment: Applying solid waste, such as sludge, onto or into the soil surface.
Impacts of Solid Waste
- Degrades water and soil quality.
- Causes chemical poisoning through inhalation.
- Chokes drains, leading to waterlogging and the spread of diseases like malaria and plague.
- Pollutes the atmosphere with noxious fumes when burnt.
2. Liquid Waste
Liquid waste includes wastewater, fats, oils, grease (FOG), used oil, liquids, solids, gases, sludge, and hazardous household liquids.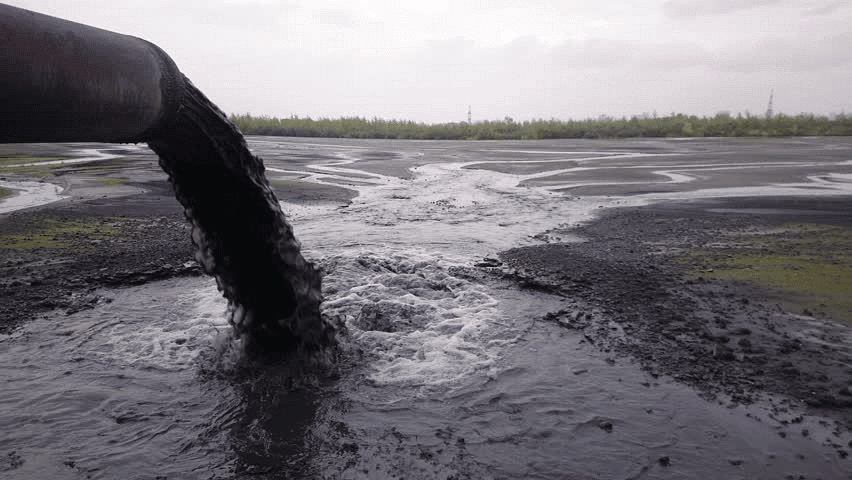  These liquids can be harmful to human health and the environment.
These liquids can be harmful to human health and the environment.
Sources of Liquid Waste
- Household Wastewater: Contains pollutants hazardous to humans and the environment.
- Industrial Wastewater: Water used in industries for cooling and cleaning, containing large amounts of chemicals.
- Inorganic and Organic Wastewater.
- Oil and Water Mixtures.
Effects of Liquid Waste Pollution
- Badly affects water bodies, land, and the environment.
- Ultimately impacts human health.
Management of Liquid Waste
- Primary or Physical Treatment: Mechanically removing solid materials through metal screening, removing 60% of floating solid materials.
- Secondary or Biological Treatment: Biological oxidation of organic matter, breaking down complex compounds into water, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia.
- Tertiary or Chemical Treatment: Advanced chemical and physical processes, such as precipitation, filtration with carbon, and passage through a membrane to remove dissolved organic and inorganic materials.
3. Biomedical Waste
Biomedical waste is any waste generated during the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals, or in research activities and production or testing of biologicals.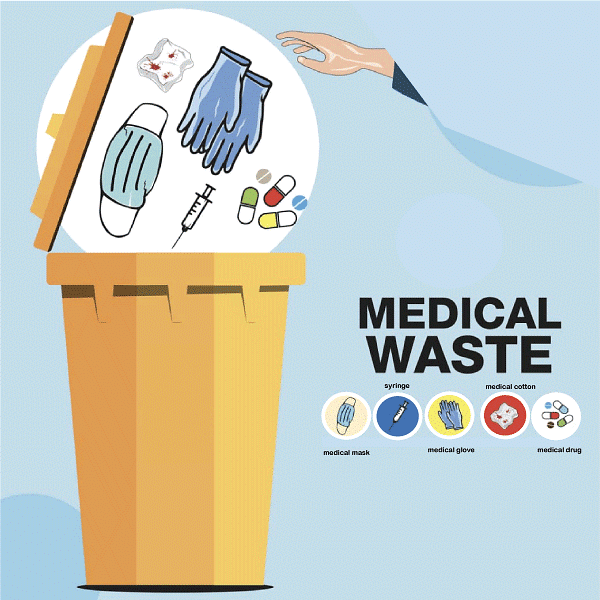
Sources of Biomedical Waste
- Discarded blood, sharps, microbiological cultures, identifiable body parts, used bandages and dressings, discarded gloves, and laboratory waste.
- Waste sharps include potentially contaminated needles, scalpels, lancets, and other devices capable of penetrating the skin.
Biomedical Waste Management
- Segregation: Primary division of different categories of waste generated.
- Storage and Accumulation: Done between the point of waste generation and the location of waste treatment and disposal.
- Eco-friendly Biodegradable Plastics: Needed for managing biomedical waste.
- Periodic Monitoring: Recommended for safe management of healthcare waste systems.
4. Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste poses potential threats to human health and the environment. It includes any solid waste that is reactive, toxic, explosive, corrosive, or otherwise dangerous.
Sources of Hazardous Waste
- Batteries
- Pesticides
- Equipment containing mercury
- Lamps containing mercury
- Paints and solvents
- Automotive wastes
- Electronics (computers, televisions, cell phones)
- Aerosols/Propane cylinders
- Caustics/Cleaning agents
- Refrigerant-containing appliances
- Special batteries
- Ammunition
5. e-Waste (Electronic Waste)
e-Waste refers to discarded electrical or electronic devices. It includes used electronics destined for reuse, resale, salvage, recycling, or disposal.
It includes used electronics destined for reuse, resale, salvage, recycling, or disposal.
Sources of e-Waste
- Products used for data processing, such as computers and peripherals.
- Electronic devices used for entertainment, like TVs and DVD players.
- Communication devices, like phones and fax machines.
- Household appliances, like vacuum cleaners and washing machines.
- Audio-visual components, like VCRs and stereo equipment.
Effects of e-Waste
- Liquid and atmospheric release of toxins affects water bodies, soil, and air, causing harmful infections.
- Increased levels of carcinogens in water bodies.
- Heavy metals in road dust cause skin cancer and respiratory diseases.
- Prenatal exposure to e-waste leads to adverse birth outcomes like stillbirth and low birth weight.
e-Waste Control
- Basel Convention (1992): First effort to control e-waste, with provisions for recycling 60% of e-waste in developed countries.
- e-Waste Management Rule (2016): Replaced the 2011 rules, covering producers, consumers, collection centers, dismantlers, recyclers, manufacturers, dealers, refurbishers, and Producer Responsibility Organizations (PROs). Applies to various electronic equipment and components.
e-Waste Microfactory
In April 2018, an Indian-origin scientist developed the world’s first microfactory to transform components of electronic waste into valuable materials for reuse.
|
25 videos|43 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Electronic Waste - People, Development and Environment Notes
| 1. What are the different types of waste pollution? |  |
| 2. How does waste pollution impact the environment? |  |
| 3. What are some ways to reduce waste pollution? |  |
| 4. How does waste pollution contribute to climate change? |  |
| 5. What are the regulations in place to control waste pollution? |  |
















