Tips for General Training Writing Task 1 | Writing for General Training IELTS PDF Download
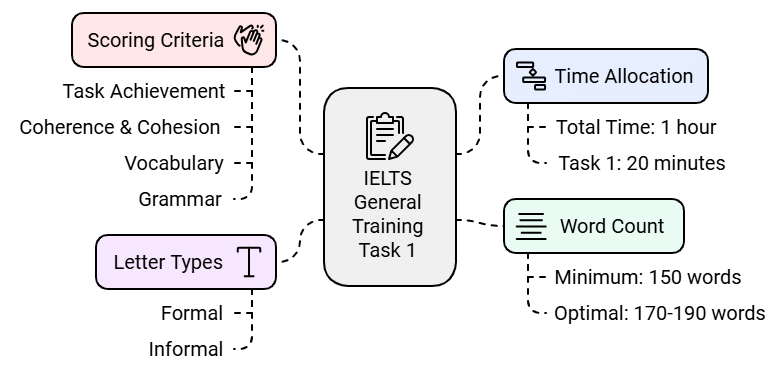
Overview of IELTS General Training Task 1
- Time Allocation: You have a total of one hour for both Writing Task 1 and Task 2. However, it is recommended to spend no more than 20 minutes on Task 1.
- Word Count: The instructions specify "Write at least 150 words," which means your letter should be over 150 words. Aim for a range of 170 to 190 words to provide enough detail for a high score.
- Letter Types: General Training letters can vary in aim, style, and tone, such as formal or informal. Understanding the type of letter required is crucial.
- Scoring: Writing Task 1 accounts for about 33% of your writing marks. There are four criteria, each worth 25%:
- Task Achievement: Completing the letter and meeting its objectives.
- Coherence & Cohesion: The structure, organization, and linking of information in your letter.
- Vocabulary: The range and appropriateness of your word choice.
- Grammar: The accuracy and variety of your grammatical structures.
Tips For IELTS General Task 1
Tip 1: Time Management for Task 1
- Allocate 20 minutes for writing the letter.
- Spend the first 3-5 minutes planning your response.
- Use the remaining time for writing, but ensure you leave 2 minutes at the end to check for spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Since you need a full 40 minutes for Task 2, it's important not to exceed 20 minutes for Task 1.
- It's your responsibility to manage your time effectively during the writing test, so keep an eye on the clock.
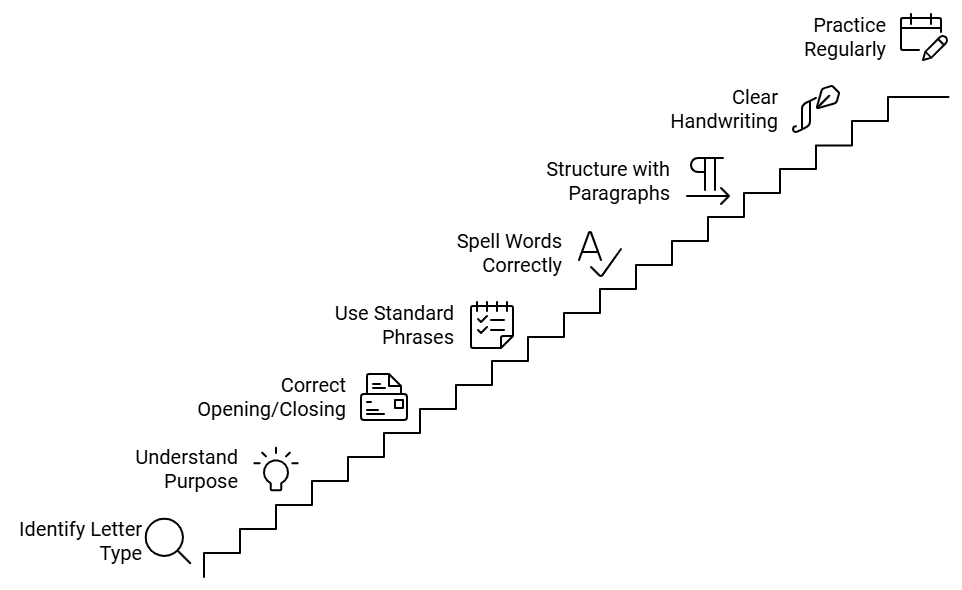
Tip 2: Identify the type of letter you are being asked to write.
- Formal
- Semi-formal
- Informal
Tip 3: Identify the purpose of the letter.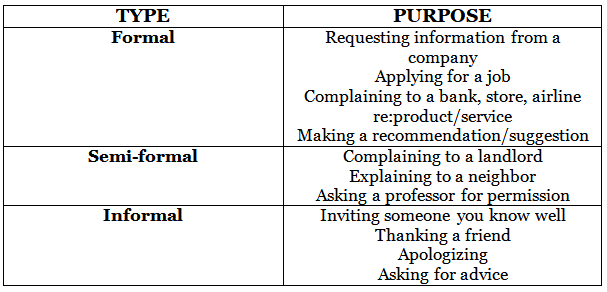 Read lots of sample questions. Decide whether the question requires a formal, semi-formal, or informal response. Steps 1 & 2 will help you choose the right language, style, and tone for your letter.
Read lots of sample questions. Decide whether the question requires a formal, semi-formal, or informal response. Steps 1 & 2 will help you choose the right language, style, and tone for your letter.
Tip 4: Open and close the letter correctly. Do this based on the type and purpose of the letter.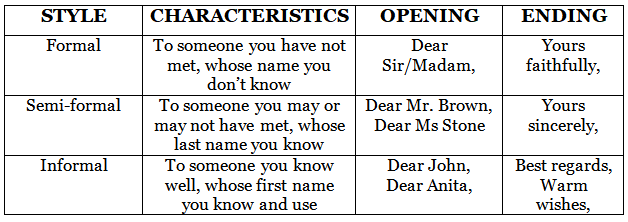
Tip 5: Start the letter appropriately.
(a) Open a formal and semi-formal letter with a formal sentence and paragraph. Get down to business and say why you are writing. Don’t try to be friendly, as you do not know the person you are writing to.
Formal:
- Dear Sir/Madam,
- I am writing to inquire about…
- I am writing in connection with…
Semi-formal:
- Dear Mr. Johnson,
- I am writing to inform you that…
- I am writing to…
(b) Open an informal letter with a general, friendly paragraph. Acknowledge your friendship first, before explaining the reason for your letter. In fact, the first paragraph could include just friendly small talk, unrelated to the reason for your writing.
Dear Susan
I hope you and your family are all well! It was so wonderful to spend time with all of you last month. It felt great to catch up with you and Bob, get to know your children, and have fun together after so long. You have always been dear friends of mine, and always will be.
Anyway, the reason I’m writing is that I have some good news: I am getting married in September…
Tip 6: Learn and use standard written phrases.
In English letter writing, we use a number of standard expressions and phrases. These not only save time and effort, but also make it easier for the reader to understand our meaning. You can add on the specific information you wish to communicate to these standard phrases. See the list of Useful Expressions below.
Tip 7: Spell commonly used words correctly. Learn and practice the correct spelling of words you are likely to use on the exam. Examples are: “sincerely”, “faithfully”, “in connection with”, “apologize”, and so on. This is an easy way to boost your score.
Tip 8: Divide your letter into paragraphs. Usually you need four paragraphs:
- Introduction
- Problem / Situation
- Solution / Action
- Conclusion
Make sure to signal the start of a new paragraph in one of two ways:
Indenting: Do NOT leave a line space between paragraphs. Start writing a little to the right of the left margin.
Skipping a line: Leave a line space between paragraphs. Start writing directly from the left margin.
Tip 9: Use clear handwriting. Make sure your writing is neat and legible, so your words can be read easily and do not appear to have spelling mistakes. Get feedback from a teacher on your handwriting. Pay special attention to how you form and connect letters such as a, e, i, u, n, r, and w.
Tip 10: Write at least 150 words. Practice writing letters till you know what 150 words feels like and looks like. You will lose marks if you write less. You will not lose marks if you write more.
Tip 11: Include all three bulleted points. If you exclude even one of the points given to you in the question prompt, you will get a lower grade. Answer all the points.
In your letter:
- explain the problem
- describe why it disturbs you
- suggest a solution
Tip 12: Finish in time.
The IELTS General Task I letter is worth about 30% of your writing score, so make sure you complete the whole letter. Though you have to make up a story to explain the situation, keep it simple so you don’t run out of time. Make sure to keep 40 minutes to complete the essay in Task 2, which is worth much more in terms of points.
Tip 13: Read model letters but don’t memorize them. Instead, read the letters to get an idea of the overall flow and to pick up new vocabulary and expressions. Make sure to consult only reliable sources, such as Good Luck IELTS, for model answers.
Tip 14: Understand the scoring criteria. Learn how to get a high score by knowing what examiners look for and how they award or deduct points.
IELTS General Task 1 Grading Criteria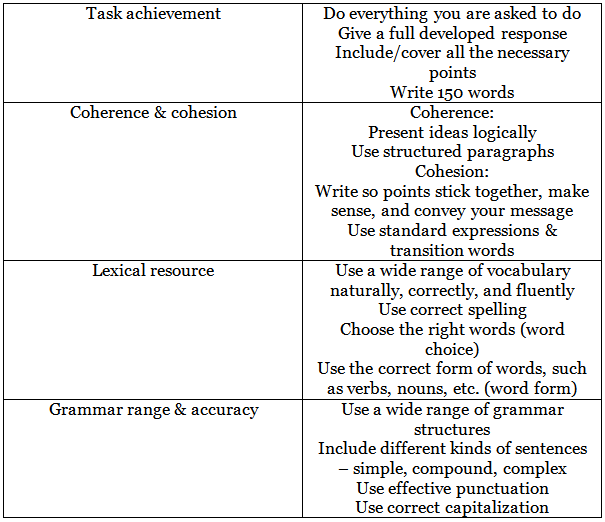
Tip 15: Practice writing letters regularly and get them checked by an IELTS trainer. Not every English teacher understands the demands of this particular exam, so find someone who has IELTS teaching experience, if possible. Practice writing answers to sample questions every day in order to improve your skills, your speed, your confidence, and your score!
|
33 videos|170 docs
|
FAQs on Tips for General Training Writing Task 1 - Writing for General Training IELTS
| 1. What is the structure of a General Training Writing Task 1 letter in the IELTS exam? |  |
| 2. How should I address the recipient in my IELTS General Training letter? |  |
| 3. How much time should I spend on Writing Task 1 of the General Training IELTS? |  |
| 4. What types of letters can I expect in the General Training Writing Task 1? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my score in the General Training Writing Task 1? |  |

















