Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Science Class 5 > The Earth and its Natural Satellites
The Earth and its Natural Satellites | Science Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Earth |

|
| The Moon |

|
| Phases of the Moon |

|
| What are Artificial Satellites? |

|
Introduction
- Have you ever looked up at the sky and thought about what might be up there?
- In this topic, we will explore the Earth by going deep into its hidden layers.
- We will also travel to the Moon to see how its shape changes throughout the month.
- Additionally, we will learn about the interesting devices humans have sent into space, known as satellites!
- These satellites enable us to do incredible things such as:
-Watching TV
-Predicting the weather
-Calling friends - Get ready for an exciting journey through our planet and beyond!
The Earth
- About 5 billion years ago, scientists believe the solar system started as a spinning cloud made of hot gas and dust.
- At the center of this cloud, the Sun formed, collecting most of the material from the cloud.
- The planets also formed from materials coming together in different parts of the cloud.
- One of these planets is Earth.
- As the Earth cooled down, its surface developed a layer called the crust.
- The thickness of the crust on land is about 70 kilometres, while the crust on the ocean floor is only about 5 kilometres thick.
The Earth has four layers. Let's discuss them in detail:
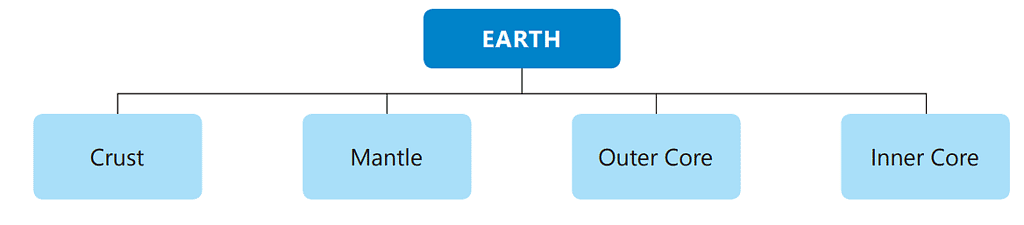
Crust
- The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth made of rocks.
- Its thickness varies from 5 km under the ocean floor to 70 km under the continents.
- All continents and oceans lie on this layer.
Mantle
- It lies below the crust. It is about 2900 km thick.
- The upper part of the mantle consists of hard rocks and the lower part consists of hot molten rocks.
- When a volcano erupts, magma comes out from this layer.
- This layer contains iron, magnesium and aluminium.
Question for The Earth and its Natural SatellitesTry yourself: What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?View Solution
Core
- It is the innermost layer of the Earth.
- It has two parts – the outer core and the inner core.
- The outer core is about 2300 km thick and the inner core is about 1200 km thick. The outer core contains molten iron and nickel. The inner core is a solid ball made up of iron.

The Moon
- The moon is the natural satellite of the Earth.
- A natural satellite is a natural object in space that orbits around a planet. Natural satellites can be large or small, and they help scientists learn more about the planets they orbit.
- It is also spherical in shape like the sun and eight planets.

- The moon is made of rocks. There is no air on the moon. Thus, there is no atmosphere on the moon.
- So the side that receives sunlight is very hot and the other side away from the sun is very cold. No sound can be heard on the moon due to the absence of air.
- It is about 3,84,400 km away from the Earth.
- It does not have its light. It shines because it reflects the sunlight that falls on it.
- The surface of the moon is covered with craters, mountains and valleys.
 Outer Surface of Moon
Outer Surface of Moon
- Craters are big, round hollows that are formed when pieces of rocks called meteorites crash into the surface of the moon.
- The diameter of the moon is about 3500 km.
 Craters on the Moon's Surface
Craters on the Moon's Surface
- The moon’s gravity is one-sixth of the Earth’s gravity. You can easily lift objects on the moon, that would be too heavy for you to lift on the Earth.
- If your weight is 36kg on the Earth, then it will be just 6kg on the moon.
Phases of the Moon
- The moon takes around one month to complete its orbit around the Earth.
- As the moon moves in its orbit, it also rotates slowly on its axis.
- It takes the moon about one month to make one full rotation.
- Because the moon revolves and rotates at the same rate, the same side of the moon always faces the Earth.
 The Earth rotates around the Sun and the Moon rotates around The Earth
The Earth rotates around the Sun and the Moon rotates around The Earth
- The moon does not give out its own light.
- It only reflects the light of the sun to us.
- Depending on the position of the sun, different areas reflect light.
- The moon appears to change its shape every day.
- The different shapes of the moon are called its phases.
 Phases of the Moon
Phases of the Moon
- The day when we cannot see the moon in the sky is called the New Moon day. The moon is not visible as the side of the Moon facing us gets no sunlight at all.
- In the next couple of days, a small portion of the side of the moon facing us gets sunlight and is visible to us. This is the Crescent Moon.
- In a week, the first quarter moon is visible.
- In the next three days from then, three-quarters of the Moon is visible to us. This is the waxing gibbous Moon.
- On the fourteenth day, the entire side facing us gets sunlight and we can see the Full Moon.
- In the next fourteen days, the moon progressively decreases in size, and the phases reverse.
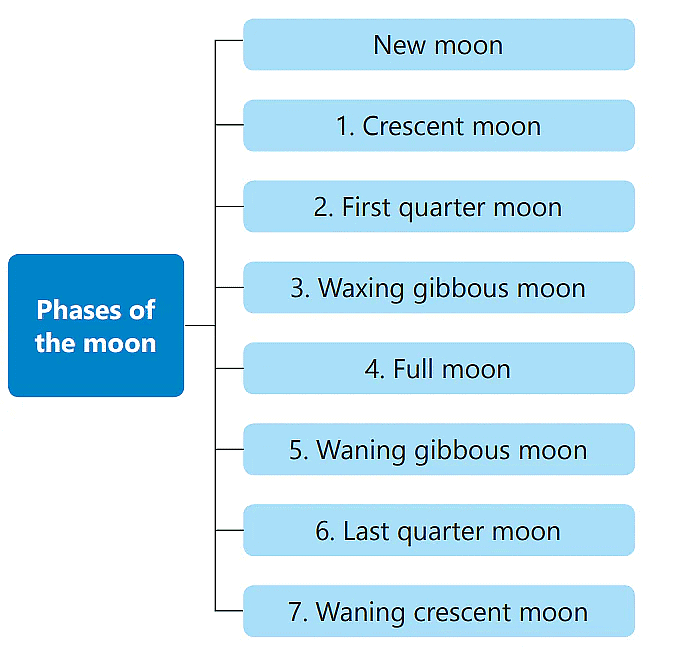
After the full moon is seen the waning gibbous moon, then the last quarter moon, the waning crescent moon and finally the new moon.
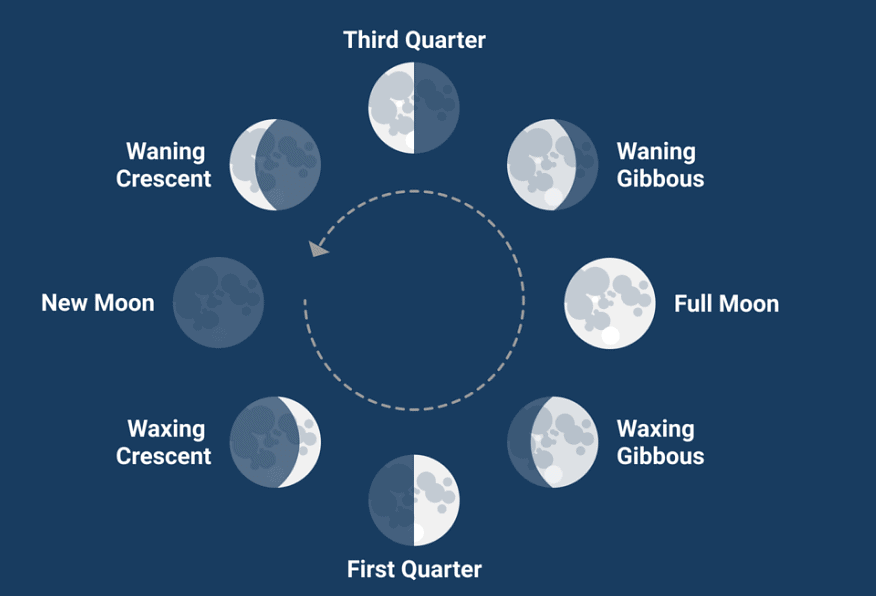 Moon's Phases
Moon's Phases
What are Artificial Satellites?
An artificial satellite is a human-made spacecraft which revolves around the earth. Aryabhata was India’s first satellite launched in the year 1975. Bhaskara, Rohini, INSAT-2A and CARTOSAT are some other Indian satellites.
- Artificial satellites are used for forecasting weather, transmitting signals of mobile or television programmes, etc.
- The first artificial satellite was Sputnik 1, launched by Russia on 4 October 1957.
 Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1
- Since then hundreds of artificial satellites have been launched. India has also launched several satellites.
- The GSAT-15 was launched on 11 November 2015. Satellites are extremely useful to us.
 GSAT-15 Satellite
GSAT-15 Satellite - Some are communication satellites (e.g. GSAT-15) which are used to send telephone conversations and television programmes around the world.
- Weather satellites are used to forecast the weather. You may have seen satellite pictures of clouds over our country shown on TV. Such pictures not only help us to forecast the weather but also to give early warning of dangerous storms and cyclones.
- Some satellites, called remote sensing satellites take photographs of the earth to study the features of the earth’s surface.
- Cartosat-2 is a remote sensing satellite launched by India on 12 January 2018.
 Cartosat-2
Cartosat-2 - India launched the world’s first educational satellite called EDUSAT in September 2004. It is used to send educational programmes all over India, even to remote villages.

- Satellites are also used to study outer space. They have helped to increase our knowledge of the planets and stars.
The document The Earth and its Natural Satellites | Science Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Science Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on The Earth and its Natural Satellites - Science Class 5
| 1. What is the Earth made of? |  |
Ans.The Earth is made up of several layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the outermost layer where we live, composed of solid rocks and minerals. Below that, the mantle is made of semi-solid rock that flows slowly. The outer core is liquid and composed mainly of iron and nickel, while the inner core is solid and also made of iron and nickel.
| 2. How does the Moon affect the Earth? |  |
Ans.The Moon affects the Earth primarily through its gravitational pull, which causes ocean tides. The gravitational interaction between the Earth and the Moon creates high and low tides in the oceans. Additionally, the Moon stabilizes the Earth's axial tilt, which helps maintain a stable climate over long periods.
| 3. What are the phases of the Moon? |  |
Ans.The phases of the Moon refer to the different appearances of the Moon as seen from Earth, caused by the changing positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun. The main phases include the New Moon, First Quarter, Full Moon, and Last Quarter. Each phase occurs as the Moon orbits the Earth, taking about 29.5 days to complete a full cycle.
| 4. What are artificial satellites? |  |
Ans.Artificial satellites are human-made objects that are intentionally placed in orbit around the Earth or other celestial bodies. They are used for various purposes, including communication, weather monitoring, navigation, and scientific research. Examples include GPS satellites, weather satellites, and the International Space Station.
| 5. Why is the Moon considered a natural satellite of the Earth? |  |
Ans.The Moon is considered a natural satellite of the Earth because it orbits around the Earth due to gravitational attraction. Unlike artificial satellites, which are built and launched by humans, natural satellites like the Moon are formed through natural processes. The Moon is the largest and closest natural satellite to Earth, playing a significant role in various natural phenomena.

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches






















