Average Voltage | Network Theory (Electric Circuits) - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
In this tutorial we will look at calculating the “average” or mean voltage value of a sinusoidal waveform using both the mid-ordinate rule and the analytical rule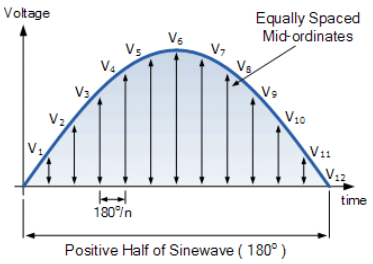
- The process used to find the Average Voltage of an alternating waveform is very similar to that for finding its RMS value, the difference this time is that the instantaneous values are not squared and we do not find the square root of the summed mean.
- The average voltage (or current) of a periodic waveform whether it is a sine wave, square wave or triangular waveform is the equivalent to the DC value of an alternating waveform. The average or mean value is defined as: “the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time“. In other words, the averaging of all the instantaneous values along time axis with time being one full period, (T).
- For a periodic waveform, the area above the horizontal axis is positive while the area below the horizontal axis is negative. The result is that the average or mean value of a symmetrical alternating quantity over the full 360o time period is therefore zero, (0).
- This is because the area above the horizontal axis (the positive half cycle) is the same as the area below the axis (the negative half cycle) and thus cancel each other out. In other words, when we do the maths of the two areas, the negative area cancels out the positive area producing a zero average value.
- Then the average or mean value of a symmetrical alternating quantity, such as a sine wave, is taken over the time period of only one half of a cycle, since as we have just stated, the average value over one complete cycle is zero regardless of the peak amplitude.
- The electrical terms Average Voltage and Mean Voltage or even average current, can be used for both AC waveforms or for DC rectification calculations. The symbols used for representing an average value are defined as: VAV or IAV.
Using The Graphical Method
- Again consider only the positive half cycle from the previous RMS voltage tutorial. The average or mean voltage of a waveform can be found again graphically with a reasonable amount of accuracy by taking equally spaced instantaneous values.
- The positive half of the waveform is divided up into any number of “n” equal portions or mid-ordinates. The width of each mid-ordinate will therefore be no degrees (or t seconds) and the height of each mid-ordinate will be equal to the instantaneous value of the waveform at that point along the x-axis of the waveform.
Average Voltage Graphical Method
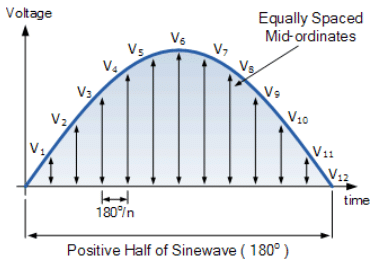
Each mid-ordinate value of the voltage waveform is added to the next and the summed total, V1 to V12 is divided by the number of mid-ordinates used to give us the “Average Voltage”. Then the average voltage (VAV) is the mean sum of mid-ordinates of the voltage waveform and is given as:
and for our simple example above, the average voltage is therefore calculated as: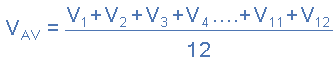
So as before lets assume again that an alternating voltage of 20 volts peak varies over one half cycle as follows: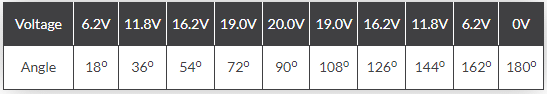
The Average voltage value is therefore calculated as: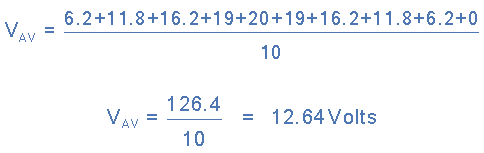
Then the Average Voltage value for one half-cycle using the graphical method is given as: 12.64 Volts.
Using The Analytical Method
- As said previously, the average voltage of a periodic waveform whose two halves are exactly similar, either sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal, will be zero over one complete cycle. Then the average value is obtained by adding the instantaneous values of voltage over one half cycle only. But in the case of an non-symmetrical or complex wave, the average voltage (or current) must be taken over the whole periodic cycle mathematically.
- The average value can be taken mathematically by taking the approximation of the area under the curve at various intervals to the distance or length of the base and this can be done using triangles or rectangles as shown.
Approximation of the Area
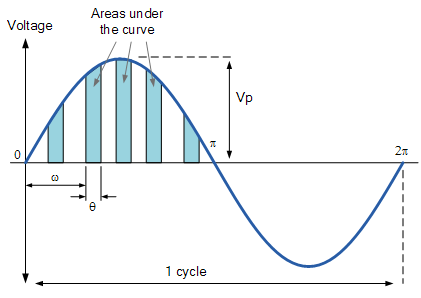
- Approximating the areas of the rectangles under the curve, we can obtain a rough idea of the actual area of each one. Thus adding together all these areas the average value can be found. If an infinite number of smaller thinner rectangles were used, the more accurate would be the final result as it approaches 2/π.
- The area under the curve can be found by various approximation methods such as the trapezoidal rule, the mid-ordinate rule or Simpson’s rule. Then the mathematical area under the positive half cycle of the periodic wave which is defined as V(t) = Vp.cos(ωt) with a period of T using integration is given as:

- Where: 0 and π are the limits of integration since we are determining the average value of voltage over one half a cycle. Then the area below the curve is finally given as Area = 2VP. Since we now know the area under the positive (or negative) half cycle, we can easily determine the average value of the positive (or negative) region of a sinusoidal waveform by integrating the sinusoidal quantity over half a cycle and dividing by half the period.
- For example, if the instantaneous voltage of a sinusoid is given as: v = Vp.sinθ and the period of a sinusoid is given as: 2π, then:
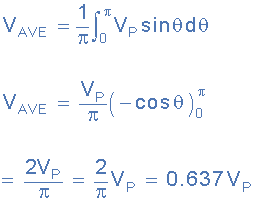
Which is therefore given as the standard equation for the Average Voltage of a sine wave as:
Average Voltage Equation
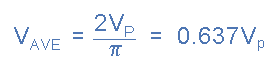
The average voltage (VAV) of a sinusoidal waveform is determined by multiplying the peak voltage value by the constant 0.637, which is two divided by pi (π). The average voltage, which can also be referred to as the mean value, depends on the magnitude of the waveform and is not a function of either the frequency or the phase angle.
Thus this average or mean value (either voltage or current) of a sinusoidal waveform can also be shown as an equivalent DC value of area and time.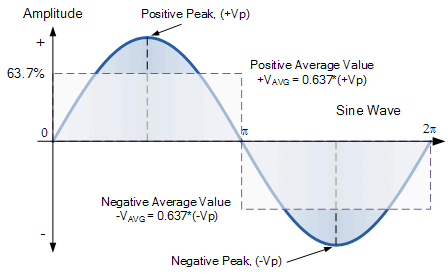
- The average value is zero over one complete cycle, as the positive average area would be cancelled by the negative average area (VAVG – (-VAVG)) in the sum of the two areas, thus resulting in zero average voltage over one complete cycle of a sinusoid.
- Referring to our graphical example above, the peak voltage, (Vpk) was given as 20 Volts. Using the analytical method the average value of the voltage is calculated as:
VAV = Vpk x 0.637 = 20 x 0.637 = 12.74 volts
Which is the same value as for the graphical method. - To find the peak value from a given average voltage value, just rearrange the formula and divide by the constant. For example, what is the sinusoidal peak value, Vpk if the average value is 65 volts.
Vpk = VAV ÷ 0.637 = 65 ÷ 0.637 = 102 volts
Note that multiplying the peak or maximum value by the constant 0.637 ONLY applies to sinusoidal waveforms.
Average Voltage Summary
- Then to summarise. When dealing with alternating voltages (or currents), the term Average value is generally taken over one complete cycle, whereas the term Mean value is used for one half of the periodic cycle.
- The average value of a whole sinusoidal waveform over one complete cycle is zero as the two halves cancel each other out, so the average value is taken over half a cycle. The average value of a sine wave of voltage or current is 0.637 times the peak value, (Vp or Ip. This mathematical relationship between the average values applies to both AC current and AC voltage.
- Sometimes it is required to be able to calculate the value of the direct voltage or current output from a rectifier or pulse type circuit such as a PWM motor circuit because the voltage or current, although not reversing, is changing continuously. Since there are no phase reversals the average value is used and the RMS (root-mean-square) value is unimportant for this type of application.
- The main differences between an RMS voltage and an average value, is that the mean value of a periodic wave is the average of all the instantaneous areas taken under the curve over a given period of the waveform, and in the case of a sinusoidal quantity, this period is taken as one-half of the cycle of the wave. For convenience the positive half cycle is generally used.
- The effective value or root-mean-square (RMS) value of the waveform is the effective heating value of the wave compared to a steady DC value and is the square root of the mean of the squares of the instantaneous values taken over one complete cycle.
- For a pure sinusoidal waveform ONLY, both the average voltage and the RMS voltage (or currents) can be easily calculated as:
Average value = 0.637 × maximum or peak value, Vpk
RMS value = 0.707 × maximum or peak value, Vpk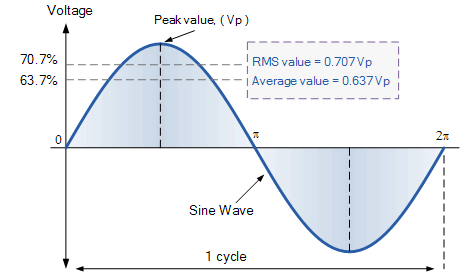
- One final comment about the average value of the voltage and its RMS value. Both values can be used to represent the “Form Factor” of a sinusoidal alternating waveform. Form factor is defined as being the shape of an AC waveform and is the RMS voltage divided by the average voltage (form factor = rms value/average value).
- So for a sinusoidal or complex waveform the form factor is given as: ( π/(2√2) ) which is approximately equal to the constant, 1.11. Form factor is a ratio and therefore has no electrical units.
- If the form factor of a sinusoidal waveform is known, then the average voltage can be found using the RMS voltage value and vice-versa as the average voltage is 0.9 times the RMS voltage value of a sine wave.
|
76 videos|152 docs|62 tests
|





















