Semiconductor Memories | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Memory
- A memory is a semiconductor of magnetic device used for storage of digital data.
- A memory location is a group of storage devices that will hold one data word.
- A data word length of 8-bits is called a byte.
- Each memory location can store a different data word and has a unique address.
- Memory can hold one or more bits of information to store the Data, Instruction, and Addresses.
- Memory can be classified into the following three groups.
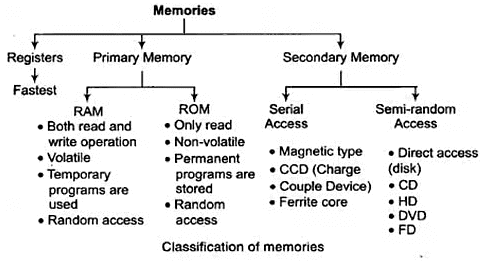
Registers: Registers are memories located within the Central Processing Unit (CPU). Various types of registers are available within CPU. Registers are small but CPU can access it quickly. Some of the registers available in the system are given below.
Instruction Register, ALU I/O registers, Status Register, Stack pointer register, Program counter, etc.
Primary Memory: It is classified into two types, namely RAM and ROM.
Secondary Memory: Disk memory is used to hold programs and data over the longer term. The contents of a disk are NOT lost if the power is turned off. Disks are much slower than Register.
Random Access Memory (RAM): The time taken to transfer information to or from any desired location is always same hence it is called Random Access Memory (RAM).
- Memory size = 2n × m, where n: address line, m: data
- RAM can be classified into two types, namely Static RAM and Dynamic RAM.
Static RAM (SRAM): In this type of RAM, data is retained as long as there is the power supply.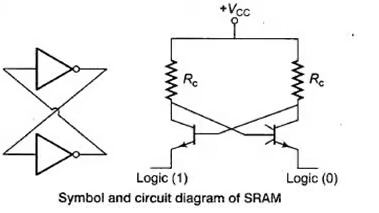
- Data is stored in flip flop like structure.
- It can be implemented with BJT or MOSFET.
- It is Faster.
- Dissipates more power.
- The memory capacity of Static RAM is less.
- It can be used as Cache memory.
- No refreshing required.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM): In this type of RAM, data is stored on capacitors and requires a periodic refreshment.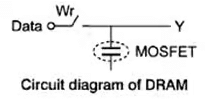
- Data is stored in MOS capacity.
- Only MOSFET is used for implementation.
- It is Slow compared to Static RAM.
- Dissipate less power.
- The memory capacity of Dynamic RAM is more.
- It can be used as Main memory.
- Refreshing is required.
Advantages of static RAM over Dynamic RAM
- The access time of SRAM is less and thus these memories are faster memories.
- As SRAM is consists of flip-flops thus, refreshing is not required.
- Less number of memory cells are required in SRAM for a unit area.
Read Only Memory (ROM): It is non-volatile memory, implemented using the combinational circuit. It is also known as masked memory.
Classification of ROM's
- Mask programmed ROM: The required contents of the memory is programmed during fabrication. Data stored this way can never be altered. It can be implemented using Fixed AND Fixed OR Circuit.
- PROM (Programmable ROM): Required content is written in a permanent way by burning out internal interconnections (fuses). It is a one-off procedure. It can be implemented using Fixed AND Programmable OR Circuit.
- EPROM (Erasable PROM): Data is stored as a charge on an isolated gate capacitor (“floating gate”). Data is removed by exposing the PROM to the ultraviolet light.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable PROM): It is also called as Flash Memory. The content can be re-programmed by applying suitable voltages to the EEPROM pins. The Flash Memories are very important data storage devices for mobile applications.
PLDs (Programmable Logic Devices): Programmable logic devices are the special type of IC’s used by the USE. Different type of logic functions can be implemented using a single programmed IC chip of PLD. PLD s can be reprogrammed because these are based on rewritable memory technologies. PLDs are divided into three types. They are PLA, PAL and FPGA. PLA (Programmable Logic Array):
- PLA is implemented using AND-OR gate arrays and programmed for specific logic functions.
- It is used where the number of don’t care conditions are excessive.
- In PLA’s both AND and OR arrays are programmable.
- The AND and OR gates are fixed for any PLA chip.
- It depends on the number of inputs and outputs of PLA.
- Combinational circuits, Sequential Circuits, Compact circuits can be implemented using PLAs.
PAL (Programmable Array Logic)
- PAL is implemented using AND gate arrays are programmable and OR gate arrays are fixed.
- Because only AND gates are programmable, the PAL is easier to program, but it is not as flexible as the PLA (programmable logic array).
PGA or FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
- It is a semiconductor device that is comprised of a different number of logic elements, interconnects, and Input/Output blocks. All these components are user-configurable.
|
76 videos|175 docs|70 tests
|





















