Johnson Counter | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
The Johnson counter is similar to the Ring counter. The only difference between the Johnson counter and the ring counter is that the outcome of the last flip flop is passed to the first flip flop as an input. But in Johnson counter, the inverted outcome Q' of the last flip flop is passed as an input. The remaining work of the Johnson counter is the same as a ring counter. The Johnson counter is also referred to as the Creeping counter.
In Johnson counter
No. of states in Johnson counter = No. of flip-flop used
Number of used states=2n
Number of unused states=2n - 2*n
Below is the diagram of the 4-bit Johnson counter. Like Ring counter, four D flip flops are used in the 4-bit Johnson counter, and the same clock pulse is passed to all the input of the flip flops.

Truth Table
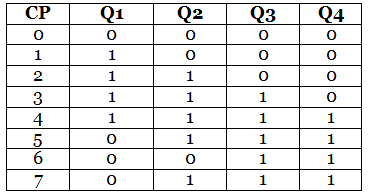
The above table state that
- The counter produces the output 0000 when there is no clock input passed(0).
- The counter produces the output 1000 when the 1st clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 1100 when the 2nd clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 1110 when the 3rd clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 1111 when the 4th clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 0111 when the 5th clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 0011 when the 6th clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
- The counter produces the output 0001 when the 7th clock pulse is passed to the flip flops.
Timing diagram

Advantages
- The number of flip flops in the Johnson counter is equal to the number of flip flops in the ring counter, and the Johnson counter counts twice the number of states the ring counter can count.
- The Johnson counter can also be designed by using D or JK flip flop.
- The data is count in a continuous loop in the Johnson ring counter.
- The circuit of the Johnson counter is self-decoding.
Disadvantages
- The Johnson counter is not able to count the states in a binary sequence.
- In the Johnson counter, the unutilized states are greater than the states being utilized.
- The number of flip flops is equal to one half of the number of timing signals.
- It is possible to design the Johnson counter for any number of timing sequences.
|
6 videos|76 docs|52 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
















