Important Questions & Answers: Demographic Structure & Indian Society - 1 | Sociology Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Question
Q.1. What is the population structure?
By population structure we mean the distribution of the population of the country in different parts, the density of population, birth and death rate, immigration, emigration, education, sex ratio, etc. In population structure, different aspects of population and features of the population are studied.
Q.2. What is Population Density?
The ratio of a number of persons living per unit area or unit volume in a particular region or country is known as population density. It can be known only by the population living per square km of an area.
Q.3. What is Economic Density?
Economic density measures the economic resources of that area or country. It is the ratio of production capacity of all the resources and the number of people living in that particular area.
Q.4. What is meant by excessive population?
When the population of any country exceeds the highest production limit of that country then the population of that country is known as the excessive population.
Q.5. What is life expectancy?
Life expectancy is the other name of average age. The life expectancy of most of the people of living life is known as average age. It can be known on the basis of average.
Q.6. What is meant by the growth rate of the population?
The meaning of the growth rate of population is the increased rate of the population of any area of a country. It includes the difference in death rate and birth rate and the population coming in that area from another area.
Q.7. What is meant by a population explosion?
When the population of any country increases unexpectedly then it is known as the population explosion. When the population increases to a great extent then its results could become destructive. India is also facing this type of problem.
Q.8. What is Family Planning?
The meaning of family planning is to keep the family small in size. The size of the family should remain in control so that the income of the family should be more than expenditure. Giving birth to children according to one’s wish is called family planning.
Q.9. What is the biological theory of increasing-decreasing population?
According to supporters of the biological theory of increasing-decreasing population, fertility rate decreases with the increase in density of population because the power of producing children decreases with conceiving. It reduces the birth rate.
Q.10. Give two methods of population control given by Malthus.
- The First method of population control given by Malthus was preventive checks like postponing marriage or practising sexual abstinence or celibacy.
- The Second method was positive checks to population growth in the form of famines and diseases. Lots of people die due to these and thus, the population remains in control.
Q.11. What do you know about the population theory of Malthus?
According to Malthus, agricultural production grows in arithmetic progression (like 2, 4, 8, 10) but population rises in geometric progression (like 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, etc.) It means that a rise in population moves according to an increase in income or living standard.
Q.12. What do you know about the Demographic Transition theory of population?
This theory is based upon the experiences of all societies. It says that as birth rate increases and the death rate decreases, the population increases very quickly. It can be seen in modern societies where the death rate is being controlled but the birth rate is not being controlled as the death rate. It leads to a great increase in population. It is known as the demographic transition theory of population.
Q.13. How can the birth rate be reduced?
- If everyone will become literate then they will come to know about the merits of less population and demerits of more population. So they will try to keep the population in control.
- If the minimum age of marriage could be fixed then they will become mature and will come to know about the merits of less population.
Q.14. Give the main features of the National Population Policy.
- To bring down the death rate to 9 per thousand.
- To bring down the birth rate to 21 per thousand.
- To reduce the infant mortality rate to less than 60 per thousand.
- To bring down the population growth rate to 1.2% per year.
Q.15. Give the literal meaning of Demography.
Demography is the systematic study of the population. Demography is an English word which is made up of two Greek words ‘demos’ and ‘graphy which means the description of people.
Q.16. When was the first and the last census survey carried out in India?
The first census survey in India was carried out in 1872 and then it was carried out in 1881. Then, after every ten years, it is carried out. The last census survey in India was carried out in the year of 2011.
Q.17. What is a Dependent population?
That part of the population that depends upon others for their lives, for food, clothes and to live is known as a dependent population. In India, people of the age group of 0-14 years and 60+ years come in this category.
Q.18. What are Urbanism and Urbanization?
When people of villages go to urban areas and adopt the values, habits, ideals, etc. of cities then it is known as urbanism. Urbanization is a system of values in which relations of the people are full of individualism, formalism, etc.
Q.19. Give some features of cities.
- Division of labour exists in cities.
- Formal relations exist in cities.
- More industries are there in cities.
- Less dependence on agriculture.
Q.20. What is Town?
The area which is larger than a village but is smaller than the city is known as a town. Generally, that geographical area is known as a town which has a population of more than 5,000, the density of population is 400 persons per sq and more than 75% people are engaged in agricultural works.
Q.21. What is the modern village?
The village where the ideology of the people is affected by science, where scientific methods are used, where the sense of fraternity remains no more, where love, co-operation, values have very less importance and where agriculture is being done for the market is a modern village.
Q.22. What is Jajmani System? (C.B.S.E. 2011)
That system is known as the Jajmani system in which many lower or small castes used to give their services to higher castes and in lieu of which they used to get grains. One who used to take service was known as Jajmani and one who used to give service was known as Kamin.
Q.23. What is a Joint Family?
A family in which members of more than two generations live together is called a Joint Family. They live in the same house and income or expenditure are earned and spent jointly.
Q.24. What is meant by homogeneity in rural life?
When people of the same culture live in the village, their eating habits, ways of living, wearing, etc. are the same then this is known as homogeneity in rural life. People share a common culture in a village.
Q.25. Give three differences between village and city.
The population is less in villages and more in cities.
Few medical and educational services are available in villages but they are more in cities.
Most of the rural people are engaged in agricultural works but most of the urban people are engaged in non-agricultural works.
Q.26. Why are rural people moving towards urban areas?
- Educational and health services of good quality are not available in villages.
- Rural people are attracted to urban pomp and show.
- More opportunities for employment are available in urban areas.
Q.27. Tell us something about the literacy rate in India.
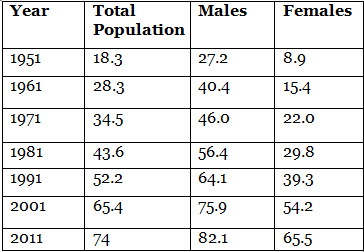
The literacy rate of India in 2011 was 74% out of which 82.1% were males and 65.5% were females. This can be seen in the given table.
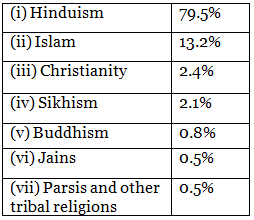
Q.28. What are the major religions of India?
Seven main religions exist in India:
|
62 videos|157 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions & Answers: Demographic Structure & Indian Society - 1 - Sociology Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the demographic structure of Indian society? |  |
| 2. How does the demographic structure affect Indian society? |  |
| 3. What are the major factors contributing to the demographic structure of Indian society? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges posed by the demographic structure of Indian society? |  |
| 5. How does the demographic structure of Indian society impact future projections? |  |