Short and Long Question Answers: Resource Mobilization - 1 | Entrepreneurship Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Mobilization of Resources
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) Define the term ‘resources’.
Any tangible or non-tangible means essential to carry out the activities of an enterprise so that the enterprise is able to realize its goal are called as resources.
(ii) Why do entrepreneurs need resources?
Entrepreneurs need resources as the resources primarily act as the life blood of the enterprise. The success of the organization directly depends on
(iii) What do you mean by ‘mobilisation of resources’?
Resource mobilization refers to the process of procuring the required resources from the resource provider, through different means. The resources thus procured are optimally utilized to realize the organization’s goals. These resources should be acquired at the right time, right prices and should be of right type.
(iv) Name two state level organisations, which provide information about the infrastructural facilities.
The following are the state level organisations which provide information about the infrastructural facilties
- District Industries Center (DIC)
Electricity Board (EB)
Local Authorities (LA)
(v) How can an entrepreneur procure professional assistance.
An entrepreneur can procure professional assistance through the following chaneels
- Captive Unit arrangement
- Contractual arrangement
- Lease basis
- Part time arrangement
- Regular basis
- Third party arrangements
Q.2. Answer in not more than 50 words:
(i) What are physical resources? Give two examples.
The resources which are made by humans by putting their skills and abilities are known as physical resources. These physical resources are influenced by the place where the enterprise is established.
The following are the examples of the physical resources.
- Building
- Machinery
- Plant
(ii) What factors help in determining the resources required?
The factors that help in determining the resources required are as follows:
- Nature or type of the activity
- Nature or type of the business
- Size of the activity
- Product specification
(iii) What basic resources are required to commence any enterprise?
The resources which are primarily required for setting up an enterprise are as below.
- Capital
- Labour
- Land
(iv) Enlist any four expert professional assistance required to start a school.
The following is the list of expert professional assistance required to start a school.
- A marketing survey expert to assist in the market survey regarding what kind of school can be started in premises (Nursery, Boarding, Montessori, Curriculum etc).
- A lawyer to look into the legal work required.
- A financial expert to prepare the budget plan (both operational budget and capital budget).
- An architect/builder to look into the building plan etc.
- A marketing expert to promote or advertise about the school.
(v) Name any four factors to be kept in mind while selecting physical resources.
The following are the factors that should be kept in mind while selecting physical resources.
- Access to market to procure raw materials as well as to sell finished goods.
- Affordability of manpower.
- Availability of other resources
- Availability of water fuel, gas and other required utilities.
- Capital Cost.
- Communication and transportation expenses.
- Cost of production.
- Regulations related to the pollution.
Q.3. Answer in not more than 75 words:
(i) Why does an Entrepreneur need expert professional services?
An entrepreneur needs expert professional services as they help in the following ways:
- Availing quality service in stipulated time and at lower cost.
- Better focus on the areas that need attention.
- Cost, Energy and time saving.
- Explore new markets and grow in the existing markets.
- Efficient and expert quality of service available at disposable.
- Growth of business as additional expertise is available.
- Reduced risk
- Reduced infrastructural requirements as the professionals will already have their own infrastructure
- Reduced wastage.
(ii) What is said to be an ‘efficient utilization of human resources’?
When we consider the following factors it is said to be an ‘efficient utilization of human resources’?
- Managerial Staff: The managerial staff forms the core of the enterprise. They formulate the goals, objects and policies to be implemented in the enterprise and get the work done through the workers.
- Non-managerial staff: They are the workers who help in converting the raw materials into the finished goods. Depending on the type of work their quality and quantity varies.
- Trained Technical staff: These are technical experts who help in
- Selection of machinery
- Installation of machinery
- Supervision of work
- Operations
- Administrative staff: They provide support services to all the above namely the managerial, non-managerial and technical staff. They’re not directly involved in production. They role is to help and maintain the business operations..
- Professional staff: They are professionals like
- Auditors
- Bankers
- Chartered Accountants
- Lawyers
- Other professionals
who are available for consultation. As these professional services are expensive, they are only consulted if required and may not be part of regular staff. As the enterprise comprise all the above staff, the efficient utilization of the human resources is possible only if
- The organization is able to estimate the total amount of work to be done.
- The right type fo personnel who can perform the required job.
- Put the right person for the right job.
(iii) Why should entrepreneurs ensure that there is a “right individual at the right job”?
Entrepreneurs should ensure that there is a “right individual at the right job” due to the following reasons:
Human resources are the most important assets of any organization because they are the ones who put all the non-living resources(tools, machinery, digital equipment etc) into best use. The quality and quantity of the human resources has a significant direct impact on the performance and productivity of any enterprise. Having a Right human resource working on the right job at the right time helps in benefiting from
- Advantage of specialization
- Low wastage of resources
- Lowered absenteeism
- Lowered inefficiencies
- Lowered labour turnover ratio
- Reduced cost of production
Due to these reasons the entrepreneurs strive to put the Right person in the right job at the right time.
Q.4. Answer in not more than 150 words:
(i) Define ‘intangible resources’. What do they generally comprise of?
Definition of Intangible resources: The resources that are neither seen nor felt nor can be touched nor can be preserved but at the same time for a strong base for the existence of an enterprise are known as intangible resources. These resources help the business to gain profits in addition to the normal profits earned by any other similar enterprise. These are critical resources of an organization.
The intangible resources generally comprise of the following:
- Brands: The success or failure of a business depends on how strong is the brand it is associated with. The worth of the brand need to be computed. A strong brand often brings in higher margins easily.
- Intellectual Property: Intellectual property comprises the critical commercial rights protected by trademarks and patents. These are very important and should be given due consideration.
- Goodwill: The value of the business will be much more than the total value of all the tangible assets it possesses. In other-words when someone want to buy a business they will be willing to pay more than the total value of the tangible assets. This additional value is known as the goodwill. A startup enterprise may not have earned any goodwill yet. But if an entrepreneur is acquiring an already existing enterprise or forming a partnership or a joint alliance, the he will be able to earn the goodwill.
- Reputation: Reputation is associated when the strategic objectives of a business are continually met. A reputed business have the advantage of gathering the necessary support from the employees and the suppliers.
(ii) With reference to utilization of resources, state any four moral responsibilities of the entrepreneur.
With reference to utilization of resources, the entrepreneurs should ensure that they follow the following moral responsibilities.
- Avoid over consumption of resources, especially when they are scarce.
- Basic resources like air, water, fuel etc are used only to the extent required. Especially when they are scarce and need to be shared with the living beings in that area.
- Careful use of the resources so that they do not cause any pollution and damage the environment.
- Do not cross the legal permissions in procuring and utilization of the resources.
- Ensure proper facilities are provided to the human resources and they are not over worked. In other-words they should abide by the labour laws.
- Financial resources are not overt-utilized and all the stakeholders are paid properly, especially the ones who have provided the fundings.
Q.5. Answer in not more than 250 words:
(i) What are material resources? While planning state the important decisions to be made by the entrepreneur.
Definition of material resources: The materials required to arrive at the final product or service offered by an organization are called as material resources. The raw materials, machines, tools, power, processing and assembling need to be combined to perform the essential operations to arrive at the finished product or service. These are known as material resources. In short any material that is found in nature and can be utilized in the product or manufacturing process is known as raw material.
While planning, the important decisions to be made by the entrepreneur are as follows:
- Availability of the spare parts and support services (after sales service)
- Basic raw materials required and their types.
- Capacity required for installation and the size of the unit.
- Details of the machinery required and the technical insight of the machinery (like how to operate how to repair etc)
- Estimation of the technical training required.
- Future maintenance costs
- Gathering of the quality controls systems needed.
- Identification of supplies of the raw materials, the quantity required and their location.
- Job and type of technical staff required.
- Kind of wear and tear and the rate at which the wear and tear of the assets take place.
(ii) Procurement of physical resources is not easy. Giving reasons, state what is required to be planned for this procurement.
Procurement of physical resources is not easy due to the reasons specified below:
Acquiring the physical resources is a difficult task as it requires the following issues to be minimized by a very careful selection of the place. If the place is not properly selected these issues will be intensified.
The issues that are likely to be taken into consideration are
- Access to market for procuring the raw materials.
- Access to market for selling the finished goods.
- Access to other resources.
- Availability of manpower and the associated cost.
- Availability of utilities like electricity, fuel, gas, water etc.
- Capital cost.
- Cost of manufacturing or production.
- Cost of Communication.
- Cost of Transportation.
- Concerns related to pollution etc.
- Degree of the legal requirements like taxes, procuring permissions etc
The following aspects need to be planned for procuring the physical resources.
- Asset durability and utility(to what extent they will be useful) expected.
- Basic size of the market to be covered. Depending on the size of the market the size or capacity of the manufacturing unit will be decided.
- Cost associated with the short and long term duration of the project.
- Decide the range of products to be introduced and which technology to adopt by assessing the market needs.
- Ease and feasibility of transfer of technology. Whether or not the technology/technique can be acquired and implemented
- Feasibility of facilitating the training the staff in the new technology.
- Growth potential in the future.
- Handling the quality concerns.
Estimating Financial Requirement
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) Define ‘Capitalisation’.
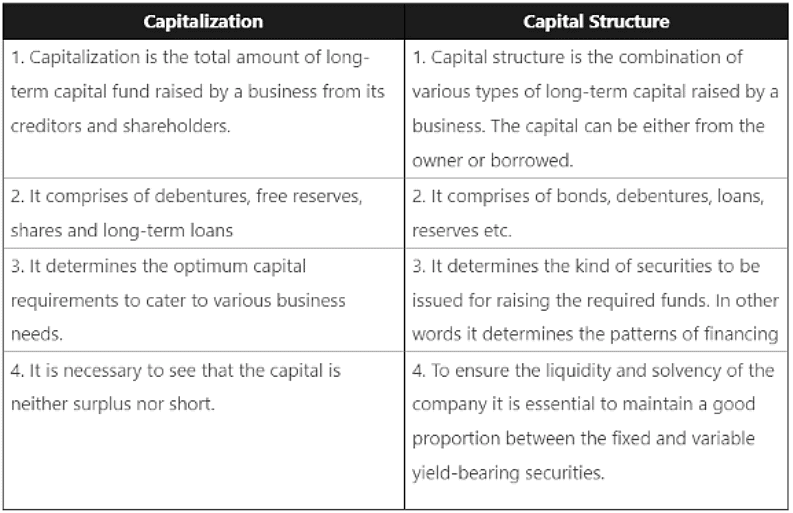
Definition of Capitalisation: The long-term funds contributed by the shareholders and creditors to a business is called as capitalization.
The funds are invested in the form of
- Debentures
- Free reserves
- Long term loans
- Shares
(ii) Define the term “Business Finance”.
Business finance refers to the process where in the capital funds are acquired and utilized so that the financial requirements are met and the overall business objectives are attained.
(iii) What is meant by ‘Capital Structure’?
Capital structure refers to the long term funds that include different types of funds like
- Bonds
- Debentures
- Loans
- Reserves
- Share Capital
These funds are borrowed or invested by the entrepreneur himself/herself
(iv) Name the plan that shows the inflows and utilization of funds.
Financial plan is the one that depicts that flow of funds into the business and their efficient utilization to meet the goals of the organization.
Q.2. Answer in not more than 50 words:
(i) Why is finance required for business?
Finance is required for the business as it plays critical role to bring the various resources like human resources, machinery, raw material, methods and processes, land etc to realize the business goal. It is due to this critical role played by the finance that the following proverbs came into place.
- Finance is the lubricant to the production process.
- Finance is the lifeblood of the business.
- Whoever has the gold makes the rule.
(ii) Enlist the major areas of financial decision-making by the entrepreneur.
The following is the list of the major areas of financial decision-making by the entrepreneur.
Amount of finance needed: The finance raised should neither be excessive nor it should be insufficient.
Term: The term could be
- Short term: upto a period of 1 year to meet the working capital.
- Medium term: From 1 to 5 years to proceed with the modernization needs.
- Long term: More than 5 years to
- Procuring fixed assets
- To carry out research operations.
- To execute expansion or diversification plans.
Sources from where finance is procured: The various funds are:
- Owner’s fund: This is entrepreneur’s own fund such as equity, preference, margin/seed capitals.
- Borrowed funds: Outside sources include:
- Issue debentures
- Loan from Banks
- Loan from financial institutes
- Loan from private lenders
Again depending on the collateral security demanded by the lender the loans can be secured or unsecured.
(iii) The nature of business affects the requirement of fixed capital. Give two examples to support this observations.
The nature of business like whether it is trading or manufacturing or services affects the requirement of fixed capital required.
For example in case of a manufacturing business like car manufacturing, huge investment is required to procure the land, building, equipment, hiring highly skilled technical human resources etc. Thus the investment required would be more.
Another example is a trading business where in the finished goods are brought purchased from the suppliers and sold to the customers or retailers. In this case there is no need of huge land, building, equipment or highly skilled human resources. And hence the investment required would be less.
Q.3. Answer in not more than 75 words:
How is “Capitalisation” different from “Capital Structure”?
Defferentiation of “Capitalisation” from “Capital Structure” is as follows:
Q.4. Answer in not more than 150 words:
(i) What are the objectives of financial planning?
The following are the objectives of the financial planning.
- Allocate the funds among the different departments so as to achieve the objectives set.
- Build a reserve of funds for meeting future contingencies.
- Capitalization to assess the various types of financial requirements and segregating them into short, medium and long term.
- Decide the capital structure so as to procure the funds from the appropriate resources. While doing this the principles of convenience, economy, financial commitments and ownership are taken into consideration.
- Establish an effective control over financial status.
- Fund raising to an optimum level to accumulate the working capital of the business.
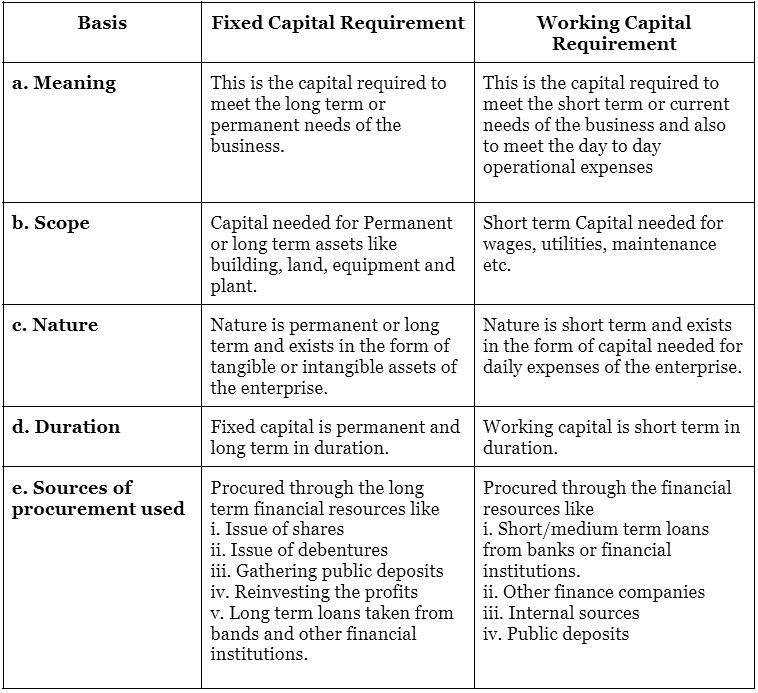
(ii) Differentiate between the Fixed Capital Requirement and Working Capital Requirement on the following basis:
(a) Meaning and scope
(b) Nature
(c) Duration
(d) Sources of procurement used.
The following is the differentiation between the fixed capital requirement and working capital requirement on the basis of parameters given.
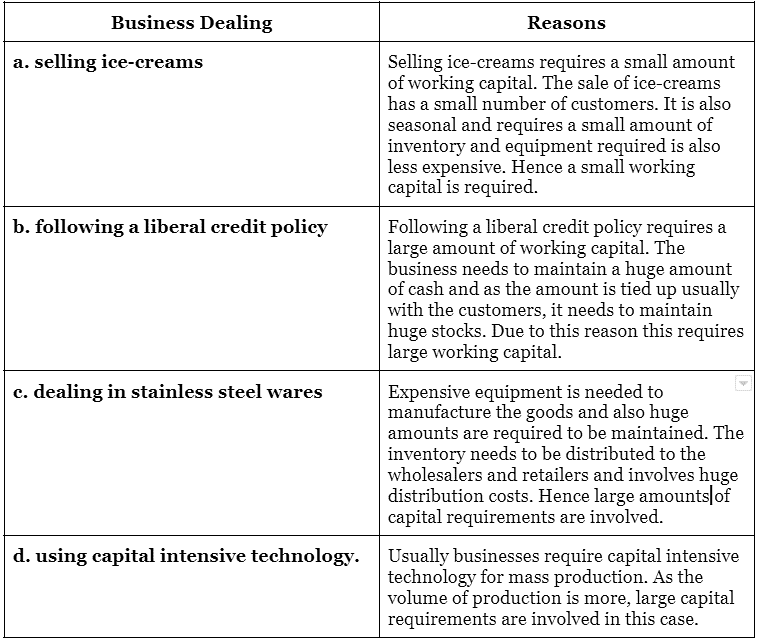
(iii) State whether the following require small or large working capital. Answer should be supported by a valid reason:
(a) selling ice-creams
(b) following a liberal credit policy
(c) dealing in stainless steel wares
(d) using capital intensive technology.
Q.5. Answer in not more than 250 words:
(i) Discuss the factors that determine the amount of working capital required by an enterprise.
Working capital is that part of the capital which is needed for running working or current requirement of the enterprises and also for taking care of the day-to-day operational expenses. It varies among different enterprises. The following factors determine the amount of working capital required by an enterprise.
- Nature and size of business: A business that has a production process requires more working capital compared to a business that deals with the trade services. Also, large scale units require large working capital and small scale units require small working capital.
- Business Cycle: When the demand for the business varies, the business needs more working capital during the boom period and less working capital during depression.
- Gestation Period: When there is large time gap between the beginning and ending of a manufacturing process, more working capital is required. A smaller gestation period requires comparatively small working capital.
- Volume and procurement of raw material: If the nature of the business is such that more capital need to be invested on the raw materials, it requires huge capital amount. When the cost of raw material is low, it requires small amount of working capital.
- Manual v/s Automation: Compared to an automated business, a business where in more man power is needed requires more working capital.
- Need to stock up inventories: When the nature of the business requires more amount of raw materials/stock to be maintained in inventory, it requires more working capital. If the inventory is low, the working capital is also low.
- Turnover of working capital: When the turn over is more, the working capital is recovered at a faster rate from the sale of finished goods. So, it requires less working capital compared to the business where in the turnover is less.
- Terms of Credit: When the business has to sell the goods on credit, the investments are locked up in the form credit with the buyers(clients or customers). Hence it requires more working capital compared to a business that sells on cash.
(ii) Explain the term ‘Fixed Capital Requirement’. Discuss the factors to be kept in mind while planning for fixed capital.
Definition of Fixed Capital Requirement: Fixed capital refers to the capital that is required for meeting the permanent or long term needs of the business. Fixed capital exists in the form of investment made in fixed assets like land, building, plant and machinery etc.
The following are the factors that should be kept in mind while planning for fixed capital.
- Nature of the business: The amount of fixed capital depends on whether the business is trading or manufacturing or service oriented.
- Size of the business: Large business requires large fixed capital and small business requires small fixed capital.
- Technology used in the production: The more the sophisticated the technology, the more the requirement for the fixed capital. On the otherhand if the business is labour intensive, then the amount of fixed capital required might be less.
- Range of production: If the business deals with diversified range of products (the number of products is more), then more fixed capital is needed. On the otherhand if the business deals with a single or less number of products, less fixed capital is needed.
- Type of product manufactured: If the product is more complex (like a car or computer), it requires more complicated machinery and hence more is the fixed cost. On the otherhand, if the product manufacture is simple (like a mobile phone case), the fixed capital required is less.
- Method of acquisition of fixed assets: When the business decides to buy the fixed assets, the fixed capital required is more. On the other hand, if the business decides to hire or lease the fixed assets, the fixed capital requirement is comparatively lesser.
(iii) ‘An ideal capital structure is the result of great, planning and team work’. What factors are required to be planned and paid attention at this time.
The following are the factors that are required to be planned and paid attention for an ideal capital structure.
- The total amount of finance needed to implement the business plan.
- The forms and proportion of various securities that should be used to raise the capital.
- The policies of using and administering the capital requirement.
The financial planning entails the policies and procedures for proper coordination between the various functional areas of business, requiring effective allocation of resources across the different departments. It enables smooth functioning of the enterprise. So, we can conclude that an ideal capital structure is the result of great planning and team work.
(iv) Explain the meaning of ‘Working Capital’. Briefly state any four factors that help determining the working capital requirement of a company.
Working capital is that part of the capital which is needed for running working or current requirement of the enterprises and also for taking care of the day-to-day operational expenses. It varies among different enterprises.
The following factors help in determining the working capital required of a company.
- Nature and size of business: A business that has a production process requires more working capital compared to a business that deals with the trade services. Also, large scale units require large working capital and small scale units require small working capital.
- Business Cycle: When the demand for the business varies, the business needs more working capital during the boom period and less working capital during depression.
- Gestation Period: When there is large time gap between the beginning and ending of a manufacturing process, more working capital is required. A smaller gestation period requires comparatively small working capital.
- Volume and procurement of raw material: If the nature of the business is such that more capital need to be invested on the raw materials, it requires huge capital amount. When the cost of raw material is low, it requires small amount of working capital.
- Manual v/s Automation: Compared to an automated business, a business where in more man power is needed requires more working capital.
- Need to stock up inventories: When the nature of the business requires more amount of raw materials/stock to be maintained in inventory, it requires more working capital. If the inventory is low, the working capital is also low.
- urnover of working capital: When the turn over is more, the working capital is recovered at a faster rate from the sale of finished goods. So, it requires less working capital compared to the business where in the turnover is less.
- Terms of Credit: When the business has to sell the goods on credit, the investments are locked up in the form credit with the buyers(clients or customers). Hence it requires more working capital compared to a business that sells on cash.
|
37 videos|52 docs|15 tests
|