Short and Long Question Answers: Resource Mobilization - 2 | Entrepreneurship Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Sources of Finance
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) What is public financing?
Public Financing: The process of procuring the finance from the public, in the form of shares and debentures is known as public financing.
(ii) Define debentures as a source of finance.
Debenture is document issued by a company under its seal to acknowledge the debt that need to be paid pack after the completion of prescribed period. Debentures thus act as a source of raising long term finance from outside.
(iii) Why is Equity Share capital called “Risk Capital’?
Equity shares are the ones that are not preference shares. The company does not bear any obligation to pay them either principal amount or dividend and there by making the equity share holders the true risk bearers. Due to this reason the equity share capital is also termed as risk capital from the equity shareholder’s perspective.
(iv) From which type of capital are raw-materials purchased?
Raw materials are procured as part of the day-to-day operations of the business and hence working capital is used to purchase the raw materials.
Q.2. Answer in not more than 50 words:
(i) On the basis of duration, classify the sources of finance.
Based on the duration, the sources of finance are classified as follows:
- Long term finance: Capital financed for more than 5 years. This includes
- Debentures
- Equity Shares
- Issue of right shares
- Leasing
- Loans from financial and industrial institutions
- Medium term finance: Capital financed for a duration of more than one year and below 5 years. This includes
- Commercial banks
- Debentures
- Loans from Specialized finance institutions
- Short term finance: Capital financed for a duration of less than one year. This includes
- Advance from customers
- Bank overdraft
- Cash Credit
- Discounting bills
- Finance against bill of lading
- Installment credit
- Trade creditor open book account
(ii) What are the major sources of capital of a Public Limited Company?
The following are the major sources of finance available for a public limited company.
- Equity shares: The company issues shares to the public and provide the equity shares to them. The equity share holders become the virtual owners of the company. The company will however will be under no obligation to pay the equity share holders the principal amount or dividend.
- Preference shares: These shares will have a priority regarding
- the payment of dividend at a fixed rate before paying the dividend to the equity share holders.
- the return of the capital in case the company is wound up.
(iii) In terms of tax benefits, which of the two-preference shares or debentures will be preferred by the organization? Give reasons.
Among shares of debentures, debentures will be preferred by the organisation, in terms of tax benefits. The reason is that when the companies prefer debentures, it yields tax benefit to them. When debentures are issued, the company is liable to pay interest on the amount borrowed under debentures. This interest can be claimed under tax deduction as it fall under tax deductible expense. So, the companies prefer the debentures.
Q.3. Answer in not more than 75 words:
(i) Define ‘personal financing’. Give its sources.
Personal financing refers to the initial investment capital arranged by the entrepreneur himself/herself. Entrepreneurs use either their personal cash or they convert their assets into cash and use it.
The sources of personal finance:
Entrepreneurs use their personal resources for making the initial investment in the enterprise. They also use other options like their private assets, cash from the members of the family, near and dear relatives and friends. The friends and relatives who helped in the investment may not have any legal hold on the business. They remain as silent partners and extend their informal assistance.
All these sources of personal finance may be classified as below:
- Personal Savings: Entrepreneurs usually invest their own personal savings as these are readily available and also as they do not have to undergo any liability. The savings could be small or large and become as internal sources. These can easily meet small, short term requirements.
Friends and Relatives: Entrepreneurs can also procure finance from
- Friends
- Relatives
- Other acquaintances
This form of procurement is informal but one of the popular.- Chit Funds: Chit fund is a kind of customary source of finance. In this few members form into a club or committee or party or association. Each member contribute a monthly deposit. If someone is in sudden need of money they can claim the chit. This premature en-cashing of the deposited amount will act as a personal finance source.
- Deposits from Dealers: The enterprise can collect security deposits from the dealers selected. The security deposit collected depends on the credibility, reputation and goodwill of the enterprise. This security deposit collected becomes a short term source of financing. However, this source is applicable only for businesses which need dealers or distributors.
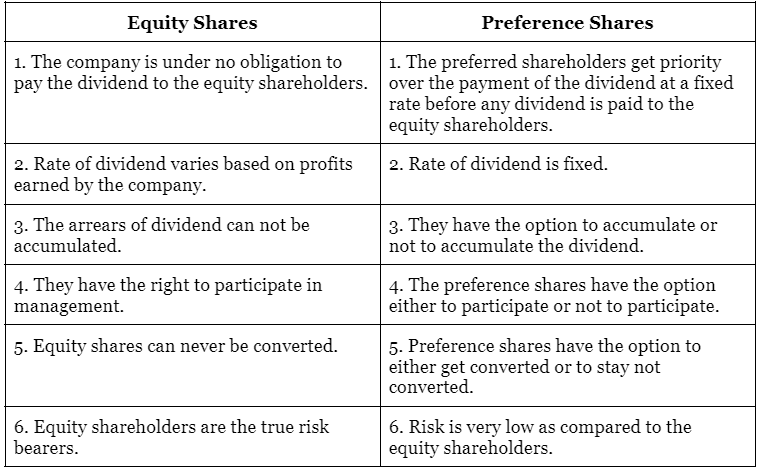
(ii) Differentiate between ‘equity shares’ and ‘preference shares’.
The following are the differences between Equity Shares and Preference Shares
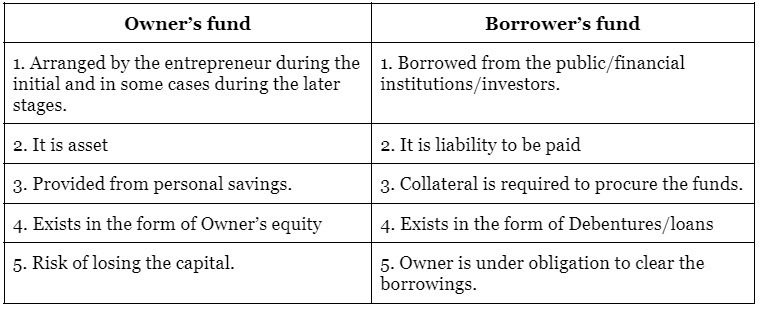
Q.3. (iii) Differentiate between “owner’s funds” and “borrowed funds”.
The following are the differences between Owner’s fund and Borrower’s fund
Q.4. Answer in not more than 150 words:
(i) Public deposits are a good source of raising medium term finance. How?
Public deposits are a good source of raising medium term finance due to the following reasons.
- The public deposits comes from the savings of the public and is readily available.
- No need to show the assets as collateral.
- As there is a constraint that the deposit should not exceed 36 months, it is ideal for medium term finance.
- As against the banks, the depositors will not have any rights in the management of the company.
- The depositors are creditors to the company and the company is not under any obligation to pay back the amount
(ii) When is it appropriate to use financial institutions as a source of financing?
It is appropriate to use financial institutions as a source of financing under the following conditions.
- To take advantage of the finance facilities provided by the government for industrial development.
- When there is a need for both owner and land capital for long and medium term requirements.
- When the other commercial banks are not available.
- When setting up the industries in backward areas.
- When there is a need to obtain technical assistance.
- Take advantage of the investment markets.
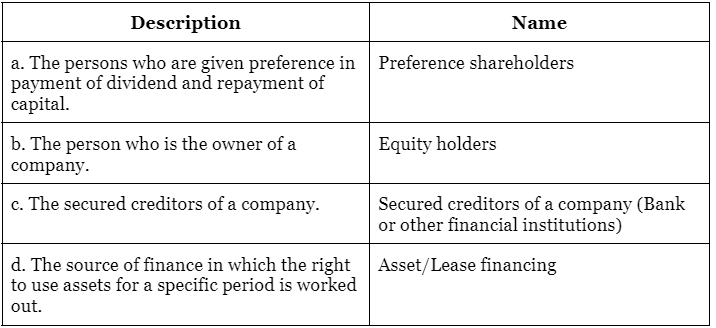
(iii) Name the following:
(a) The persons who are given preference in payment of dividend and repayment of capital.
(b) The person who are owners of a company.
(c) The secured creditors of a company.
(d) The source of finance in which the right to use assets for a specific period is worked out.
Q.5. Answer in not more than 250 words:
(i) What is ‘venture capital’? Explain the mode of raising funds?
Venture Capital: Venture capital is investment financed by a venture capitalist company in entrepreneurial ventures which are in second or third stage of development. In the event when the ventures have high potential prospects or where in high returns are expected, the venture capital can be financed as the initial equity investment too.
The following are the modes of raising finance.
- Approach them during the second or third stages of development.
- When the venture is in the area of software, biotechnology, high-potential venture, high technology venture or having high growth prospects and returns, finance can be obtained during the start up stage also.
- By sharing the equity or ownership with the venture capitalist.
- When the business is highly inclined towards profits.
- When it is difficult to procure loans from banks.
(ii) Discuss the various sources of financing capital through ownership.
The following are the various sources of financing capital through ownership.
- Retained Profits/Sloughing back of profits: Instead of distributing all the profits to the shareholders in the form of dividend, it is partly retained and reinvested into the business. This is usually used by already established enterprises that are making profits. Not possible for a new venture.
- Equity Shares: Equity shares are issued to give away part of the ownership to the equity shareholders. Equity shareholders are like virtual owners of the business. However, the business is under no obligation to pay back to them. Thus equity shareholders bear high risk. However, they possess the voting rights.
- Preference Shares: Under preference shares the shareholders gets priority to receive the dividend before any dividend is paid to the equity shareholders. There is also preference for these shareholders to regain their capital if the company is likely to wind up. These shares can be
- Cumulative or non-cumulative.
- Participating or non-participating
- Convertible or non-convertible.
- Seed Capital: Seed capital is procured for funding the initial investment to develop a prototype or to prove the feasibility of the capital. The equity/ownership finance can be procured by
- Asking banks to buy equity shares.
- Through self
- contacting specialized agencies or organizations.
(iii) Explain the term ‘debt financing’. How are Banks’ an important source of debt financing?
Debt financing: Debt financing refers to the finance procured by the entrepreneur from the bank in the form of interest-bearing instrument. This is usually in the form of loan against a collateral like a car or house etc. Due to this reason it is also known as asset-bearing finance. The payment is indirectly related to the sales and profits of the venture.
Banks act as an important source of ‘debt financing’ as described below.
Commercial banks provide short or medium term loans to firms of all sizes through the following various options and thus act as important sources of debt financing.
- Overdraft: This is a temporary provision allowing the entrepreneur to withdraw more than the amount available in his account. This works as follows:
- The entrepreneur opens a current account with the bank.
- The bank issues permission enabling the entrepreneur to withdraw amounts more than available in his account.
- The excess amount withdrawn attracts interest.
- The entrepreneur should submit an asset as security or it might be a personal security.
- Cash Credit: This is similar to overdraft. Its features are
- Entrepreneur can borrow up-to specific limits.
- The borrowed amount is credited to the entrepreneur’s account.
- The amount can be withdrawn as and when needed.
- The withdrawn amount attracts interest.
- Usually a bond or some other security should be provided to avail this facility.
- Discounting of bills/Factoring: In this mode the bank encashes customer’s bills before they become due. For providing this facility there will be nominal charges. The entrepreneur is liable to pay the amount if the bill is dishonoured. Factoring is a financial service rendered by a specialized person called as Factor. This person deals in realizing book debts, bills receivable, managing sundry debtors and sales registers of the commercial and trading firms. This person acts as an agent and charges a commission known as commercial charges or discount. Thus it is the sale of accounts receivable to the bank or finance company or others involved.
- Loans and Advances: In this case the entire loan amount is arranged to the entrepreneur either in cash or through wire-transfer. In this case
- The entrepreneur can withdraw the entire loan amount or in installments depending on his requirements.
- Irrespective of the amount withdrawn, interest is charged on the entire amount of loan.
- Usually security of certain assets is required to procure the loans.
- Term loan: These loans are granted to the entrepreneur by the bank for a fixed period to buy
- Machinery
- Trucks/scooters
- Houses
- This loan amount should be repaid in monthly/quarterly/half yearly/annual installments.
- Demand Loans: To procure these loans, the entrepreneur has to furnish security of Fixed Deposit Receipts (FDR), Government securities, Life Insurance Policies etc. The name demand loan implies that the bank has the authority to demand the loan at any time by issuing a notice to the entrepreneur.
Mentorship
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) Who is a ‘Mentor’?
A mentor is
- An adviser
- trusted guide
- wise intellectual person
who uses their mind creatively, especially in occupational settings, and advises the others to achive their goals.
(ii) Define the term ‘Business Mentor’.
A business mentor is a person who has the experience of successfully establishing and running a business and is capable and willing to offer invaluable
- advice
- guidance
- and support
to a new entrepreneur.
(iii) Give one difference between Group mentoring and Peer mentoring.
Group mentoring is the one in which the mentor mentors a group of 4 to 6 people in one go where as peer mentoring is the one where in the mentor maintains the mentoring relations with their peers either formally or informally.
Q.2. Answer in not more than 50 words:
(i) What is informal mentoring?
Informal mentoring is the type of mentoring where in
- Goals of the relationship are not specified
- Outcomes are not measured
- Depending on the basis of personal chemistry, the mentor and mentee self-reflect.
(ii) Enumerate the role played by the Mentor.
Mentors play a critical role to provide support, recognize the strengths and weaknesses of the entrepreneur and guide them to take corrective measures. Their role involves helping the entrepreneur in
- Assessing the entrepreneur’s areas of shortcomings and strengths and Provide valuable feedback to them in important areas.
- Business partner identification
- Coordinating the activities related to the assessment of funds and new technologies and provide consultation.
- Defining and understanding the current situation of the enterprise and diagnosing the order.
- Evaluate the ‘highs’ and ‘lows’ during the venture starting through their experience and create awareness in the entrepreneur to identify the threats and risks of market.
- Finding the relevant information
- Guidance and support in preparing and implementing the development activities/plans/projects so as to achieve effective business results.
- Help related to the preparation of documentation for the enterprise and enterprise support programs.
- Introducing the entrepreneur(mentee) to the relevant accountants, consultants, lawyers, suppliers, trainers etc so as to inculcate confidence in them.
- Justify the identification, procurement and utilization of the required resources.
- Knowledge, Learning, specific skill acquisition, unspoken rules essential for the success of the venture.
Q.3. Answer in not more than 75 words:
(i) What benefits do Mentors gain from their function?
Mentor gains the following benefits by mentoring others.
- Acquire insights from the mentee’s background and hist0ry which can be of help in mentor’s personal and professional growth.
- Builds an ally and there by helps in organizations well-being.
- Career of the mentor is re-energized.
- Discover more about the other areas withing the organization (especially if the mentee is from a different department or so)
- Earns personal satisfaction through sharing his expertise with others.
(ii) Explain the concept of mentoring. Give 2 examples to support your answer.
A mentor is
- An adviser
- trusted guide
- wise intellectual person
who uses their mind creatively, especially in occupational settings, and advises the others to achieve their goals. Everyone has a learning need. Learning through a mentor will play a critical role in the overall development in specific area. As mentors have already have practical knowledge, they will be able to mentor others to achieve systematic results by applying their expertise.
Mentors will usually
- Advise the mentee about specific issues.
- Builds a safe learning environment for taking risks
- Coaches the mentee in a specific skill
- Directs the mentee towards challenges and help them to go beyond their comfort zone.
- Encourages the mentee’s total development.
- Facilitates the mentee growth by sharing their networks and resources.
Examples include:
- Angel invest0rs who guides the new entrepreneurs through their knowledge and expertise, to help them realize their goals.
- A trusted friend or family member who already have vast experience in the entrepreneurial pursuit advising and guiding the entrepreneurs.
Q.4. Answer in not more than 150 words:
(i) Briefly state the different types of mentoring.
The following are the different types of mentoring.
Mode of construction: This is based on the way the mentor-ship is structured.
- Formal mentoring: In this type of mentoring
- Mentor and mentee are paired depending no the compatibility.
- The goals are pre-set before the mentor-ship is started.
- Outcomes are measured.
- Formal mentoring is further classified as
- Traditional mentoring
- Special project mentoring.
- Informal mentoring: In this type of mentoring
- Mentor and mentee are paired on depending on the personal chemistry they have
- The goals are not pre-set.
- Outcomes are not measured.
Mode of delivering: This is based on the way the mentor-ship is rendered. This is further classified as
- One to one mentoring: One mentor is paired up with one mentee.
- Group mentoring: One mentor works with 4-6 mentees at one time.
- Online mentoring: Mentoring relations through online collaboration tools.
- Peer mentoring: Maintain mentoring relations either formally or informally with the colleagues.
(ii) “Not only the entrepreneur but also the entire organization benefits from mentoring”. Explain?
Mentor-ship benefits not just the entrepreneur but the whole organization in the following ways:
- Achieve improvement in strategic business initiatives.
- Breaks down the “silo” mentality that reduces the co-operation between different departments or divisions.
- Creates a mentoring culture that help in the growth and development of the employees
- Decreases the turnover costs
- Encourages retention.
- Fosters and increases the professional development.
- Gains productivity
- Helps in linking employees who has invaluable knowledge and information with other employees who are in need of such information.
- Increase knowledge transfer from merely getting information and to retaining practical experience and knowledge gained from long-term employees.
- Justify the use of own employees rather than external consultants as internal experts from professional development.
- Keep up the creation or diverse workforce through establishing mentoring relationships among employees from various cultural backgrounds and ensure that everyone has equal access to mentoring.
Q.5. Answer in not more than 250 words:
(i) Discuss the role and importance of mentoring.
The following is the role and importance of mentoring.
Mentors play a critical role to provide support, recognize the strengths and weaknesses of the entrepreneur and guide them to take corrective measures. The role and importance of the mentoring is summarized below.
- Assessing the entrepreneur’s areas of shortcomings and strengths and Provide valuable feedback to them in important areas.
- business partner identification
- Coordinating the activities related to the assessment of funds and new technologies and provide consultation.
- Defining and understanding the current situation of the enterprise and diagnosing the order.
- Evaluate the ‘highs’ and ‘lows’ during the venture starting through their experience and create awareness in the entrepreneur to identify the threats and risks of market.
- Finding the relevant information
- Guidance and support in preparing and implementing the development activities/plans/projects so as to achieve effective business results.
- Help related to the preparation of documentation for the enterprise and enterprise support programs.
- Introducing the entrepreneur(mentee) to the relevant accountants, consultants, lawyers, suppliers, trainers etc so as to inculcate confidence in them.
- Justify the identification, procurement and utilization of the required resources.
- Knowledge, Learning, specific skill acquisition, unspoken rules essential for the success of the venture.
(ii) Explain mentoring. What are the characteristics?
Definition of Mentoring: Mentoring is the process of a person helping other person to realize their goals. Mentoring involves a mentor and a mentee. A mentor is
- An adviser
- trusted guide
- wise intellectual person
who uses their mind creatively, especially in occupational settings, and advises the others to achieve their goals. The mentor creates an informal environment where in the mentee feels comfortable to express their needs openly by confiding in the mentor. Organizations view this as a very powerful personal development and empowerment tool. The mentor provides help and support in a non-threatening manner which is received by the mentee in an appreciating and valuable pattern. Mentoring involves supporting and encouraging people so that they can manage their own learning in the most efficient manner, acquire or improve the skills, improve their performance and realize their goals.
The following are the characteristics of mentoring.
- Absolutely focuses on professional development or career growth. At times this might be outside the mentee’s area of work.
- Builds the relationships beyond job boundaries.
- Carried out outside and beyond the manager-subordinate relationship. Also it happens by the mutual consent of the mentor and the mentee.
- Develops personal relationship. As the relationship is personal the mentor will be willing to support both professionally and personally.
- Employer or the organization initiates this initiative. But the relation may be initiated by a mentor through this initiative.
- Formally it should last for nine months to one year. However, the mentor and mentee may continue the mentoring relationship informally.
Sources of Information
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) Define Census Method of collecting data.
Census Method is a method of collecting data where in all the units associated with a particular problem are studied. It is also called as Enumeration Survey Method.
(ii) Name the main producers of information.
The following are the main producers or originators of information.
- Government Agencies
- Academic Institutions
- Private Sector
- Individuals
(iii) Name the sources available to an entrepreneur at state and central level, to seek information regarding plant and machinery.
For the entrepreneur seeking information regarding plant and machinery, the following sources are available.
- SFC – State Finance Corporation
- CCIE – Chief Controller of Import and Export
Q.2. Answer in not more than 75 words:
(i) Identify any six major small scale industry groups in India.
The following are few of the major small scale industry groups in India.
- Hosiery factories in Ludhiana
- Scientific instruments making factories in Ambala
- Carpet making factories in Panipat
- Radio, TV, etc manufacturing factories in Delhi
- Garment making in Gurgaon
- Handlooms and Textiles industries in Hisar
(ii) What purpose does ‘information’ serve for an entrepreneur.
Information serves the following purposes for the entrepreneur.
- Application, Feasibility, Utility and Viability of the idea.
- Business favourable market conditions prevailing at present viz. competitors, demand, supply etc.
- Calculating the impact of prevailing environmental factors on the feasibility of the idea.
- Different types of resources required and their suppliers.
- Expected Profitability
Q.3. Answer in not more than 150 words:
(i) Identify the information resource centre at the State and Central levels available in India to the entrepreneur regarding:
(a) Product standardization and quality mark
(b) Technical know-how
(c) Selection of Project
(d) Registration
The following are the information resource centres at the State and Central levels avilable in India for the entrepreur regarding:
(a) Prodict standardization and quality mark:
- ISI – India Standards Institute.
- RT – Register of Trade Mark.
(b) Technical know-how:
- DDCA – Directorate of Drug Control Association.
- CIPET – Central Institute of Plastic and Engineer Tool.
(c) Selection of Project:
- DTC – District Industrial Centre.
- ITC – Indian Investment Centre.
- SFC – State Finance Corporation.
(d) Registration
- NSIC – National Small Industrial Corporation.
- CCIE – Chief Controller of Import and Export.
- STC – State Trading Corporation.
Q.4. Answer in not more than 250 words:
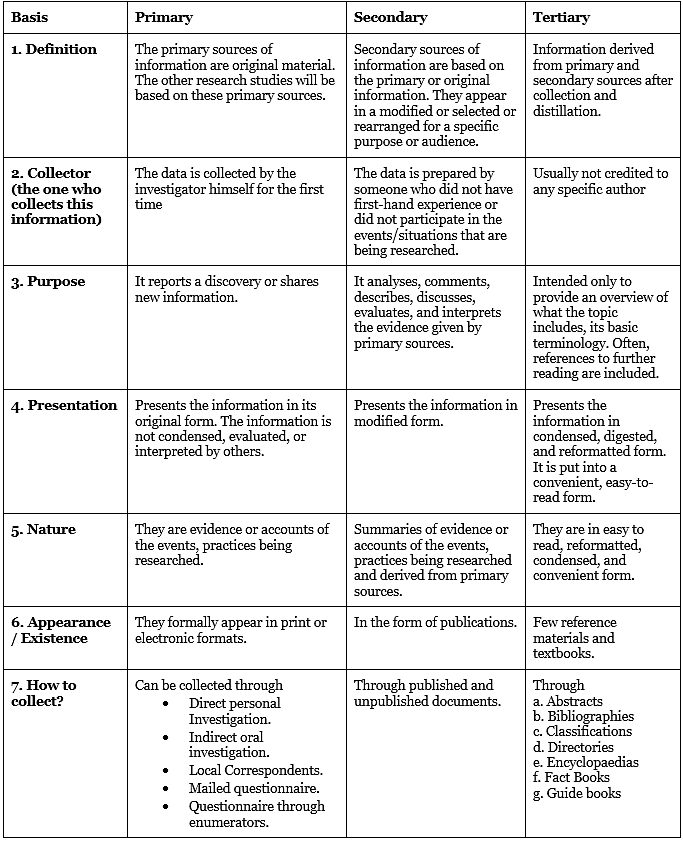
(i) Differentiate between Primary, Secondary and tertiary source of information.
The following are the differences between primary, secondary and tertiary sources of information.
(ii) What is meant by Primary source of information? Explain the method of collecting primary data.
Primary sources are original materials, usually collected by the investigator in-person, and becomes the reference for other research studies. It reports a discovery or share new information. This information is first hand accounts and is relevant to an event.
The following are the methods used in collecting primary data.
- Direct personal investigation: The investigator directly approaches the source and personally collects the information.
- Indirect oral investigation: The investigator approaches certain sources who are connected with the information directly or indirectly and personally collects the information.
- Local Correspondents: The investigator appoints local agents or correspondents in different parts of the area under investigation and collects the information through them.
- Mailed questionnaire: The investigator prepares a questionnaire with questions related to the objective of the inquiry and send it to informants by post and collects the information through them.
- Questionnaire through Enumerators: In this case the investigators appoints enumerators. The enumerators visit the informants along with the questionnaire. The informants fill the questionnaire which will be helpful to fulfill the investigators answers.
Size and Capital Based Classification of Business Enterprises
Q.1. Answer in not more than 15 words:
(i) Define a ‘Tiny enterprise.’
The Tiny enterprise is a business enterprise that falls under the tiny sector where in the total amount invested in plant and machinery does not exceed ₹ 25 lakhs at present and is likely to increase in future.
(ii) Define a Large Scale Enterprise.
The industrial units whose investment in plants and machinery exceeds ₹ 10 crores is known as large scale enterprise.
(iii) When is a unit said to be a ‘Medium Scale Enterprise’?
A medium scale enterprise is one in which the investment in plant and machinery is more than ₹ 5 crores and less than ₹ 10 crores.
Q.2. Answer in not more than 50 words:
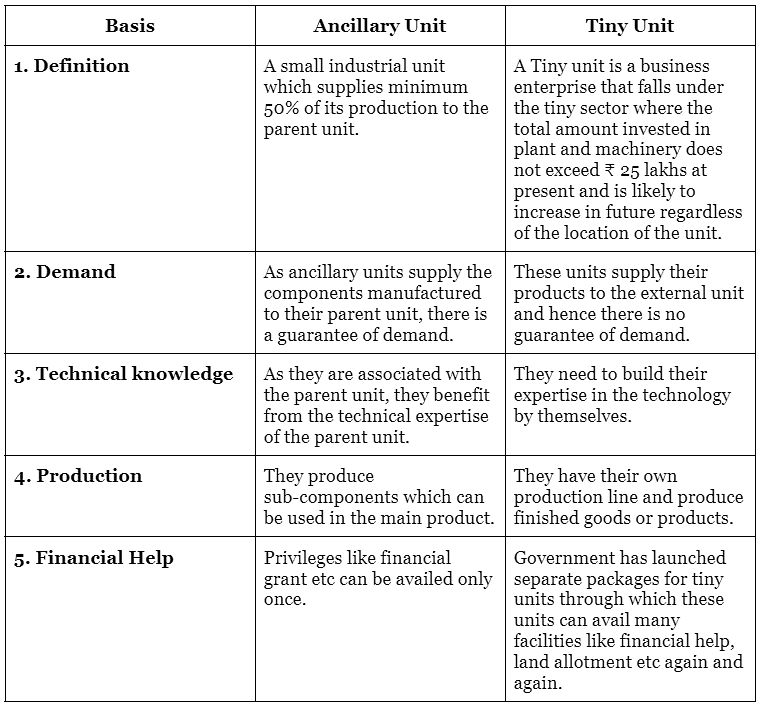
(i) How would you differentiate between an ancillary unit and a tiny unit?
The following are the differences between an ancillary unit and a tiny unit.
(iii) When is any activity referred as a ‘Business Activity’?
The pre-requisite to call any activity as business activity is that the activity should be undertaken in connection with the place of the business to the place of consumption
The basis of classification of the business activities is different in different countries.
- the activities connected with the production are known as Industry
- the activities that are connected with the distribution of the goods produced from production unit to consumers is known as commerce
In addition to the above, the business activities can also be classified base on
- Activity
- Size
- Ownership
Q.3. Answer in not more than 75 words:
(i) Classify, on the basis of size, the business enterprises.
The business enterprise is classified as follows on the basis of the size.
- Volume of capital
- Volume of output
- Value of output
- Number of employees
In India, it is adjusted on the basis of the volume of the capital invested whether the enterprise is large or small. Based on the volume, the industries are categorized as follows.
1. Small Scale: Small scale industries are the ones in which the investment in plant and machinery does not exceed ₹ 5 crores. They have the following features.
- They employ labour.
- They use machines
- They use electricity to run these machines.
- The following are the examples.
- Hosiery factories in Ludhiana
- Scientific instruments making factories in Ambala
- Carpet making factories in Panipat
- Radio, TV, etc manufacturing factories in Delhi
The following are the various types of small scale units.
- Tiny Sector
- Ancillary/Auxiliary Small Units
- Micro-business
- Small-Scale Service and Business (Industry Related) Enterprise.
- Small-Scale Industries Owned and Managed by Women Entrepreneurs.
- Export Oriented
- Cottage and rural.
2. Medium Scale: The enterprises in which the investment in plant and machinery is more than ₹ 5 crores but less than ₹ l0 crores.
3. Large Scale: The industrial units whose investment in machinery exceeds more than 10 crores.
(ii) Explain the characteristics of a Cottage and Rural industry.
The cottage industry is an industry which is run either as whole-time or part-time occupation with full or partial help of the family members. The following are the characteristics of cottage and rural industry.
- They are run by the members of the family (they do not employ labour)
- They are mainly run by artisans at their homes.
- Requires very small investment
- They often cater to the needs of surrounding localities
- They use the Machines very rarely.
- Usually traditional items like mats, shoes, pottery are made in these units. Other examples are the units where khadi and handicraft products are produced.
(iii) Discuss the enterprises which comes under the category of being an SSI units.
The following are the enterprises which fall under the category of the SSI units.
- Tiny Sector: Tine sector refers to those business enterprises whose investment in plant and machinery is less than ₹ 25 lakhs. However, this amount is likely to increase irrespective of the location of the unit. To promote these industries, the government has announced a package. This package allows these units to avail the privileges of many kinds like land allotment, electricity connection, technology etc. to continuously utilize. This package is not applicable to other small industries.
- Ancillary/Auxiliary Small Units: This is a small-scale industry unit that manufactures components for its parent unit and supplies 50% of its production to its parent unit. These units benefit from the guaranteed demand from its parent unit. They also have technical and financial help from their respective parent units.
- Micro-business: This is a business unit that has invested in plant and machinery not exceeding ₹ 25 lakhs.
- Small-Scale Service and Business (Industry Related) Enterprise: These are MSME (Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises). These are further classified as:
- Micro-enterprise: Investment in equipment is less than ₹ 10 lakhs.
- Small enterprise: Investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs and does not exceed ₹ 2 crores.
- Medium enterprise: Investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2 crores and less than ₹ 5 crores.
- Small-Scale Industries owned and Managed by Women Entrepreneurs: These are operated individually or jointly by a group of women. Their capital share is more than 51%. The government offers them concessions.
- Export Oriented: These are the units that export more than 50% of its production. The government offers them subsidies. The ministry of MSME & ARI will bring out a specific list of hi-tech and export oriented industries which would need the investment cap to be raised upto ₹ 5 crores to allow them to upgrade their technology and stay competitive.
- Cottage and Rural: The cottage industry is an industry which is run either as whole-time or part-time occupation with full or partial help of the family members. The following are the characteristics of cottage and rural industry.
- They are run by the members of the family (they do not employ labour)
- They are mainly run by artisans at their homes.
- Requires very small investment
- They often cater to the needs of surrounding localities
- They use the Machines very rarely.
- Usually traditional items like mats, shoes, pottery are made in these units. Other examples are the units where khadi and handicraft products are produced.
|
37 videos|52 docs|15 tests
|