Mole Concept | Chemistry for JAMB PDF Download
Mole concept is the method used to express the amount of substance. This has been experimentally proving that one gram atom of any element, as well as one gram molecule of any substance, contains the same amount of entities. The experimentally decided number is found to be 6.022137 × 1023. After the discovery of the mole concept, the problem of finding absolute atomic masses of atoms was solved. It was so because the mole concept helps to count the number of atoms or molecules in a definite amount of the given substance.
What is a Mole Concept?
Mole concept is known as the method used to express the amount of substance. A mole is defined as the amount of substance containing the same number of different entities (such as atoms, ions, and molecules) as the number of atoms in a sample of pure 12C weighing precisely 12 g. Even a gram of any pure element contains a high amount of atoms. The mole connects a simple macroscopic feature (bulk mass) to a genuinely significant fundamental trait (number of atoms, molecules, etc.). One mole is also defined as the amount of a substance that contains as many entities as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of the 12C isotope. It was found that the mass of one atom of carbon-12 element is equal to 1.992648 × 10-23 g as measured by the mass spectrometer. Since one mole of Carbon-12 atom weighs 12 g, therefore, the number of atoms in it equals 12 g mol-1 / 1.992648 × 1023 g atom-1 = 6.0221367 × 1023 atoms mol-1. The following formula may be used to calculate the number of moles of a chemical in a given pure sample:
n = N/NA
Where n represents the number of moles of the chemical, N denotes the average number of fundamental units in the sample, and NA represents the Avogadro constant.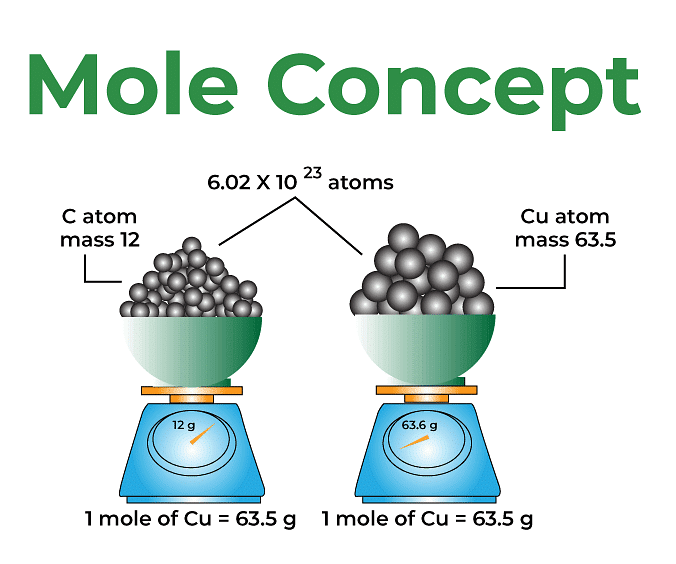
Avogadro’s Number (NA)
Avogadro’s number is 6.0221367 × 1023. It is named Avogadro’s constant or number in honor of Amedeo Avagadro, a great pioneer in this field. It is denoted by NA. We can also say that 1 mole is the collection of 6.0221367 × 1023 units of a substance. Here, the substance is atoms, molecules, or ions. The number of units that make up a mole has been established empirically to be 6.0221367 × 1023. This is known as the fundamental constant, also known as Avogadro’s number (NA) or the Avogadro constant. This constant is appropriately stated in chemistry using an explicit unit termed per mole. No matter what the given substance may be, one mole of it is always equal to NA.
Mole Concept Formulas
Mole concept is a method where we identify the mass of chemical substances as per requirement. The entire mole concept revolves around 12 g (0.012 kg) of the 12C isotope. In the SI system, the unit of the fundamental quantity ‘the amount of substance’ is the mole. The symbol of the mole is “mol”. Below are the quantities related to the mole concept:
Atomic Mass and Molecular Mass
Atomic mass of an element is the mass of its one atom. The unit of atomic mass is a.m.u. The atomic mass is roughly the sum of protons and neutrons present in the atom. One atomic mass unit (a.m.u.) is said to be exactly equal to one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Therefore, the value of one a.m.u. is 1 g / NA = 1.66056 × 10-24 g. In the present era, the atomic mass unit is known as a unified mass unit. Hence, a.m.u. has been replaced by u.
For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 amu since carbon mostly contains carbon-12 isotope. Carbon-13 is 1.1%, and very few traces of carbon-13. The atomic mass of these isotopes is different.
Molecular Mass is the sum of the masses of the atoms present in a given molecule. The unit of molecular mass is a.m.u. However, if the molecular mass of a mole of a substance is asked, then the unit used is grams despite the fact that the SI unit is kilograms. The molecular mass of a molecule is defined as the relative mass of its molecule when compared to the mass of a 12C atom divided into 12 units. In layman’s words, it denotes the number of times a molecule of the relevant material is heavier than an atom.
For example, the molecular mass of water (H2O) is 18.015 amu, the atomic mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.007 amu and the atomic mass of oxygen is 15.99 amu.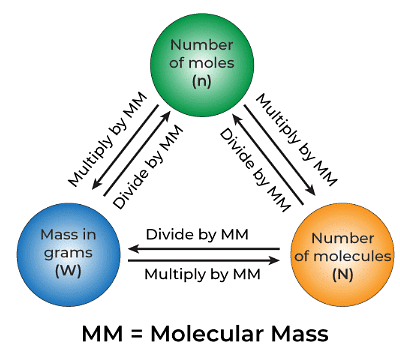
What is Molar Mass?
Molar mass is defined as the total mass of one mole of the substance. It is frequently expressed in terms of ‘grams per mole’ (g/mol). The SI unit for this amount, however, is kg/mol. The following formula may be used to calculate molar mass:
Molar mass of a Substance = (Mass of the substance in grams)/(Number of Moles)
The molar mass of water, for example, is roughly 18.015 g/mol, which is the mass of NA number of water molecules.
Gram Atomic Mass and Gram Molecular Mass
Gram atomic mass is the mass of one mole of an atom. Gram molecular mass is the mass of one mole of a molecular substance expressed in grams. It is also known as molar mass. It is also defined as the mass of one mole of molecules. This is the difference between gram atomic and gram molecular mass. This amount of a substance is also called one gram molecule.
- How to Find Gram Molecular Mass?
A substance’s gram molecular mass is its molecular mass measured in grams. e.g., the molecular mass of O2 is 32 grams; this is the relative molecular mass given in grams. Remember that relative atomic mass is always expressed as a ratio and has no units. - Gram Molecular Volume
The volume occupied by one gram mole of a substance in a vapor state or gaseous state at STP is called as gram molecular volume. The standard temperature to obtain GMV is 273K, and the standard pressure is 1 atm. The ideal gas equation is utilized to get gram molar volume (GMV = 22.4L). - Relative Molecular Mass (RMM)
Relative molecular mass is the molecular weight of an element or molecule; it is expressed as RMM. It is the number of times a single molecule of a substance remains heavier than one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom (12C).
Number of Electrons in a Mole of Hydrogen Molecule
One mole of H2 contains 6.023 × 1023 molecules, and each molecule of hydrogen contains two electrons. 1 mole = 6.023 × 1023
Hence, the total number of electrons in 1 mole of H2 is 12.046 × 1023.
|
213 videos|201 docs|162 tests
|





















