Stop & Wait Protocol | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Before understanding the stop and Wait protocol, we first know about the error control mechanism. The error control mechanism is used so that the received data should be exactly same whatever sender has sent the data. The error control mechanism is divided into two categories, i.e., Stop and Wait ARQ and sliding window. The sliding window is further divided into two categories, i.e., Go Back N, and Selective Repeat. Based on the usage, the people select the error control mechanism whether it is stop and wait or sliding window.
What is Stop and Wait protocol?
- Here stop and wait means, whatever the data that sender wants to send, he sends the data to the receiver. After sending the data, he stops and waits until he receives the acknowledgment from the receiver. The stop and wait protocol is a flow control protocol where flow control is one of the services of the data link layer.
- It is a data-link layer protocol which is used for transmitting the data over the noiseless channels. It provides unidirectional data transmission which means that either sending or receiving of data will take place at a time. It provides flow-control mechanism but does not provide any error control mechanism.
- The idea behind the usage of this frame is that when the sender sends the frame then he waits for the acknowledgment before sending the next frame.
Primitives of Stop and Wait Protocol
The primitives of stop and wait protocol are:
Sender side
- Rule 1: Sender sends one data packet at a time.
- Rule 2: Sender sends the next packet only when it receives the acknowledgment of the previous packet.
Therefore, the idea of stop and wait protocol in the sender's side is very simple, i.e., send one packet at a time, and do not send another packet before receiving the acknowledgment.
Receiver side
- Rule 1: Receive and then consume the data packet.
- Rule 2: When the data packet is consumed, receiver sends the acknowledgment to the sender.
Therefore, the idea of stop and wait protocol in the receiver's side is also very simple, i.e., consume the packet, and once the packet is consumed, the acknowledgment is sent. This is known as a flow control mechanism.
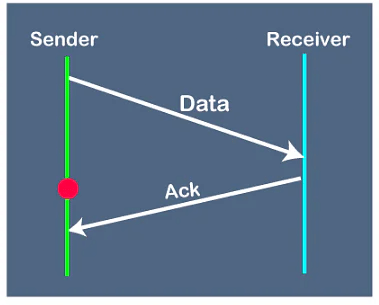
Working of Stop and Wait protocol
The above figure shows the working of the stop and wait protocol. If there is a sender and receiver, then sender sends the packet and that packet is known as a data packet. The sender will not send the second packet without receiving the acknowledgment of the first packet. The receiver sends the acknowledgment for the data packet that it has received. Once the acknowledgment is received, the sender sends the next packet. This process continues until all the packet are not sent. The main advantage of this protocol is its simplicity but it has some disadvantages also. For example, if there are 1000 data packets to be sent, then all the 1000 packets cannot be sent at a time as in Stop and Wait protocol, one packet is sent at a time.
Disadvantages of Stop and Wait protocol
The following are the problems associated with a stop and wait protocol:
1. Problems occur due to lost data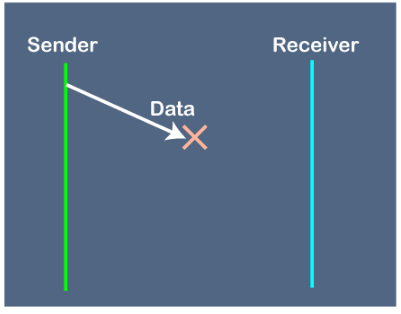
Suppose the sender sends the data and the data is lost. The receiver is waiting for the data for a long time. Since the data is not received by the receiver, so it does not send any acknowledgment. Since the sender does not receive any acknowledgment so it will not send the next packet. This problem occurs due to the lost data.
In this case, two problems occur:
- Sender waits for an infinite amount of time for an acknowledgment.
- Receiver waits for an infinite amount of time for a data.
2. Problems occur due to lost acknowledgment
 Suppose the sender sends the data and it has also been received by the receiver. On receiving the packet, the receiver sends the acknowledgment. In this case, the acknowledgment is lost in a network, so there is no chance for the sender to receive the acknowledgment. There is also no chance for the sender to send the next packet as in stop and wait protocol, the next packet cannot be sent until the acknowledgment of the previous packet is received.
Suppose the sender sends the data and it has also been received by the receiver. On receiving the packet, the receiver sends the acknowledgment. In this case, the acknowledgment is lost in a network, so there is no chance for the sender to receive the acknowledgment. There is also no chance for the sender to send the next packet as in stop and wait protocol, the next packet cannot be sent until the acknowledgment of the previous packet is received.
In this case, one problem occurs:
- Sender waits for an infinite amount of time for an acknowledgment.
3. Problem due to the delayed data or acknowledgment
Suppose the sender sends the data and it has also been received by the receiver. The receiver then sends the acknowledgment but the acknowledgment is received after the timeout period on the sender's side. As the acknowledgment is received late, so acknowledgment can be wrongly considered as the acknowledgment of some other data packet.
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|


















