Grade 12 Exam > Grade 12 Notes > Economics for Grade 12 > The (Free) Market System
The (Free) Market System | Economics for Grade 12 PDF Download
Different Economic Systems
- In order to solve the basic economic problem of scarcity, economic systems emerge or are created by different economic agents within the economy
- These agents include consumers, producers, the government, & special interest groups (e.g. environmental pressure groups or trade unions)
- Any economic system aims to allocate the scarce factors of production
- The three main economic systems are a (free) market system, mixed economy, & planned economy

How the three questions are answered determines the economic system of a country
- Economic decisions need to be made to answer three important questions
- What to produce? As resources are limited in supply, decisions carry an opportunity cost. Which goods/services should be produced e.g. better rail services or more public hospitals?
- How to produce it? Would it be better for the economy to have labour-intensive production so that more people are employed, or should goods/services be produced using machinery?
- For whom are the goods and services to be produced? Should goods/services only be made available to those who can afford them, or should they be freely available to all?
How These Questions Are Answered Determines the Economic System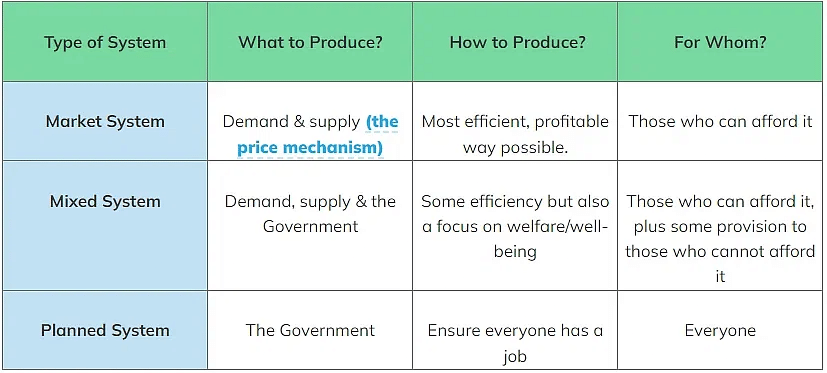
How a Market System Works
- A market system works to allocate scarce resources efficiently, purely through the forces of demand & supply (the price mechanism)
- There is no government intervention in a pure market system (no taxes or government spending)
- In reality, there is no economy which is a pure market system
- In a market system, prices for goods/services are determined by the interaction of demand & supply
- A market is any place that brings buyers & sellers together
- Markets can be physical (e.g. McDonald's) or virtual (e.g. eBay)
- The price mechanism is the interaction of demand and supply in a free market
- This interaction determines prices which are the means by which scarce resources are allocated between competing wants/needs
- The price mechanism fulfils several functions in an economy
- Prices allocate (ration) scarce resources. When resources become scarcer the price will rise further. Only those who can afford to pay for them will receive them. If there is a surplus then prices fall & more consumers can afford them
- Prices provide information to producers & consumers where resources are required (in markets where prices increase) & where they are not (in markets where prices fall)
- When prices for a good/service rise, it incentivises producers to reallocate resources from a less profitable market to this market in order to maximise their profits. Falling prices incentivise reallocation of resources to new markets
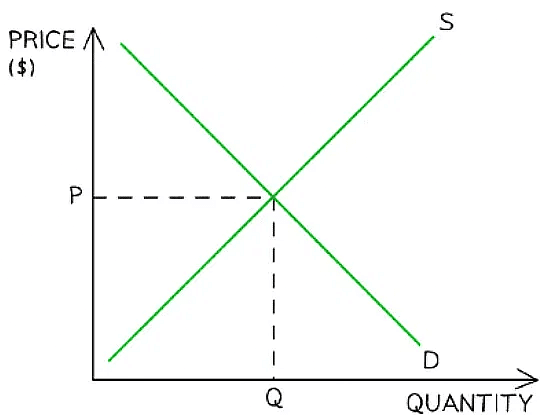
Market Equilibrium & Disequilibrium
- Equilibrium in a market occurs when demand = supply
- At this point the price is called the market clearing price
- This is the price at which sellers are clearing their stock at an acceptable rate

- This is the price at which sellers are clearing their stock at an acceptable rate
- A graph showing a market in equilibrium with a market clearing price at P and quantity at Q
- Any price above or below P creates disequilibrium in this market
- Disequilibrium occurs whenever there is excess demand or supply in a market
The document The (Free) Market System | Economics for Grade 12 is a part of the Grade 12 Course Economics for Grade 12.
All you need of Grade 12 at this link: Grade 12
|
23 videos|11 docs
|
Related Searches