Logic Gates & Truth Tables | Digital Logic - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
These are important digital devices that are mainly based on the Boolean function. Logic gates are used to carry out logical operations on single or multiple binary inputs and give one binary output. In simple terms, logic gates are the electronic circuits in a digital system.
Types of Basic Logic Gates
There are several basic logic gates used in performing operations in digital systems. The common ones are;
- OR Gate
- AND Gate
- NOT Gate
- XOR Gate
Additionally, these gates can also be found in a combination of one or two. Therefore we get other gates such as NAND Gate, NOR Gate, EXOR Gate, and EXNOR Gate.
OR Gate
In an OR gate, the output of an OR gate attains state 1 if one or more inputs attain state 1.
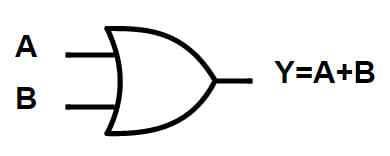
The Boolean expression of the OR gate is Y = A + B, read as Y equals A ‘OR’ B.
The truth table of a two-input OR basic gate is given as;
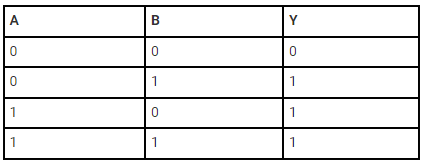
AND Gate
In the AND gate, the output of an AND gate attains state 1 if and only if all the inputs are in state 1.
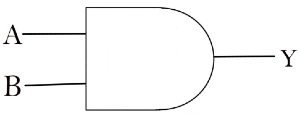
The Boolean expression of AND gate is Y = A.B
The truth table of a two-input AND basic gate is given as;
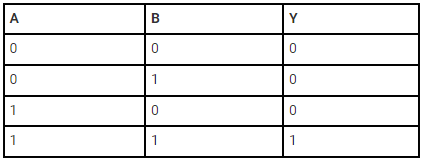
NOT Gate
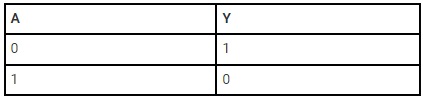
In a NOT gate, the output of a NOT gate attains state 1 if and only if the input does not attain state 1.
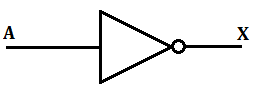
The Boolean expression is:
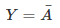
It is read as Y equals NOT A.
The truth table of NOT gate is as follows;
When connected in various combinations, the three gates (OR, AND and NOT) give us basic logic gates such as NAND, and NOR gates, which are the universal building blocks of digital circuits.
NAND Gate
This basic logic gate is the combination of AND and NOT gates.
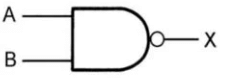
The Boolean expression of the NAND gate is:
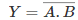
The truth table of a NAND gate is given as;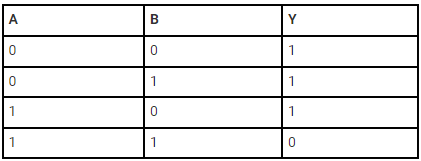
NOR Gate
This gate is the combination of OR and NOT gate.
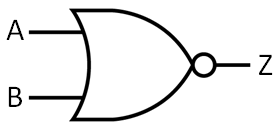
The Boolean expression of NOR gate is: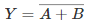
The truth table of a NOR gate is as follows;
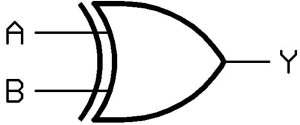
Exclusive-OR gate (XOR Gate)
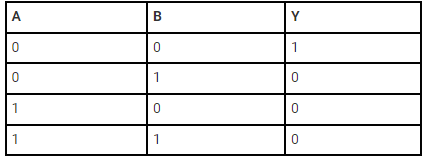
In an XOR gate, the output of a two-input XOR gate attains state 1 if one adds only input attains state 1.
The Boolean expression of the XOR gate is: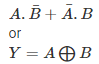
The truth table of an XOR gate is;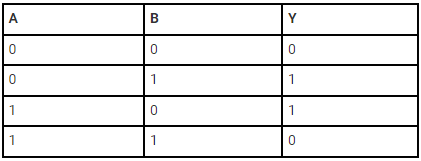
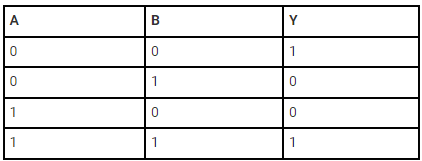
Exclusive-NOR Gate (XNOR Gate)
In the XNOR gate, the output is in state 1 when both inputs are the same, that is, both 0 or both 1.
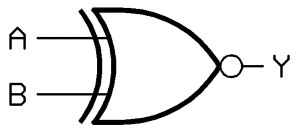
The Boolean expression of the XNOR gate
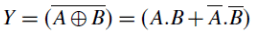
The truth table of an XNOR gate is given below;
Application Of Logic Gates
Logic gates have a lot of applications, but they are mainly based upon their mode of operations or their truth table. Basic logic gates are often found in circuits such as safety thermostats, push-button locks, automatic watering systems, light-activated burglar alarms and many other electronic devices.
One of the primary benefits is that basic logic gates can be used in various combinations if the operations are advanced. Besides, there is no limit to the number of gates that can be used in a single device. However, it can be restricted due to the given physical space in the device. In digital integrated circuits (ICs), we will find an array of the logic gate area unit.
De Morgan’s Theorem
First theorem – It states that the NAND gate is equivalent to a bubbled OR gate.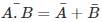
Second theorem – It states that the NOR gate is equivalent to a bubbled AND gate.
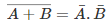
Important Conversions
(1) The ‘NAND’ gate: From ‘AND’ and ‘NOT’ gate
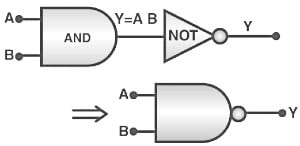
Boolean expression and truth table:
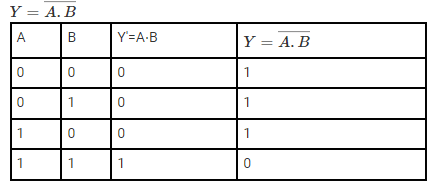
(2) The ‘NOR’ gate: From ‘OR’ and ‘NOT’ gate
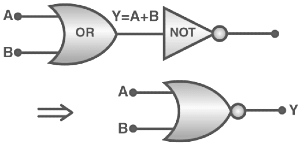
Boolean expression and truth table: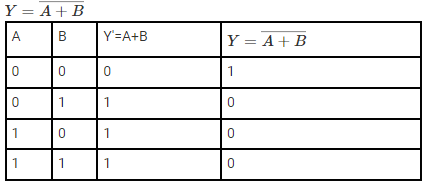
(3) The ‘XOR’ gate: From ‘NOT’, ‘AND’ and ‘OR’ gate.
The logic gate, which gives a high output (i.e., 1) if either input A or input B but not both are high (i.e. 1), is called the exclusive OR gate or the XOR gate. It may be noted that if both the inputs of the XOR gate are high, then the output is low (i.e., 0).
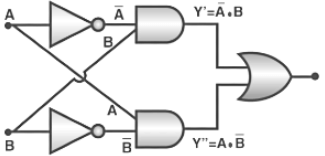
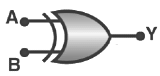
Boolean expression and truth table: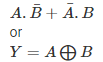
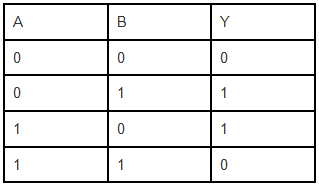
(4) The Exclusive nor (XNOR) gate XOR + NOT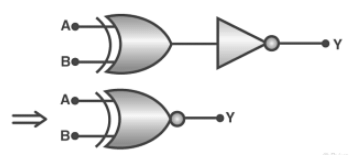
Boolean expression: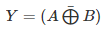
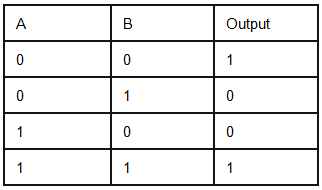
|
53 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Logic Gates & Truth Tables - Digital Logic - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are logic gates and truth tables in computer science engineering? |  |
| 2. How many types of logic gates are there? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of logic gates in computer science engineering? |  |
| 4. How do logic gates work? |  |
| 5. Can logic gates be combined together? |  |






















