Important Questions and Answers: International Business | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q.1. Explain the importance and advantages of foreign trade.
Importance of External Trade:
Due to the unequal distribution of natural resources and skills across different countries, foreign trade serves as a crucial solution. It allows nations to specialize in the production of goods for which they possess abundant resources and facilities, enabling them to export surplus production to other countries while simultaneously importing goods that are not produced domestically. This exchange not only makes goods available to consumers in countries where they are not produced but also enhances the standard of living for individuals.
Foreign trade is vital for the economic development of a nation, as it allows for the importation of capital equipment and scarce raw materials. Additionally, surplus commodities can be exported, generating foreign exchange that can be reinvested into the economy.
Advantages of Foreign Trade:
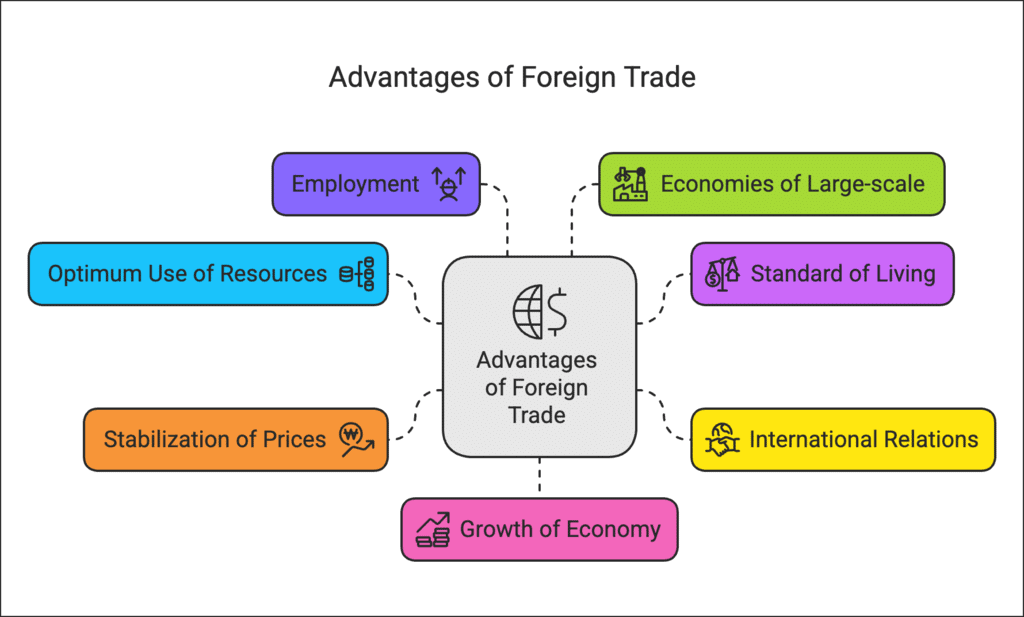
The advantages of foreign trade are discussed below –
- Optimum use of Resources: Foreign trade leads to the international division of labour and specialisation. It reduces wastage of resources resulting from the production of uneconomic goods. The resources are also used efficiently.
- Standard of Living: International trade helps the people living in different countries to raise their standard of living by providing goods and services which cannot be produced economically in a particular country.
- International Relations: Foreign trade makes different countries dependent upon each other. A country having surplus products can sell its surplus stock to the deficient countries and a country having a deficiency of a product can import it from another country. This promotes goodwill and cordial relations among the nations of the world.
- Stabilisation of Prices: Foreign trade leads to stabilisation of prices of commodities throughout the world by adjusting demand and supply. This would not have been possible in the absence of foreign trade.
- Employment: Foreign trade helps in increasing employment opportunities in the export-oriented industries.
- Economies of Large-scale: Foreign trade facilitates the specialisation of a country in the production of certain goods. This will help to carry on the production of some commodities not only for home consumption but also for external consumption. This will lead to several economies of large scale production. The resources will also be utilised in a better way.
- Growth of Economy: Under-developed and developing countries can exploit their unutilised natural resources with the import of technical know-how, machinery and equipment from the advanced countries.
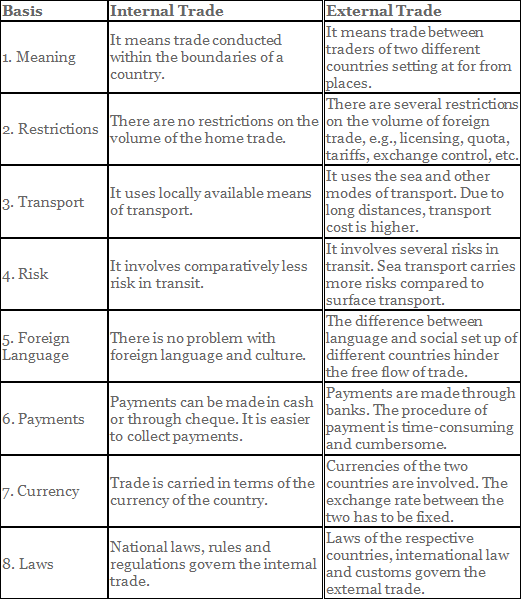
Q.2. Differentiate between Internal (Home) Trade and Foreign (external) Trade.
Difference between Home Trade and Foreign Trade:
Q.3. Explain the various terms used in foreign trade.
Terms used in external trade:
Some of the important terms used in export trade are given below –
- Free on Board (FOB): The importer has to bear all costs and risks of loss or damage from the port of shipment.
- Cost and Freight (C&F): Under this contract, the exporter is expected to deliver the goods at the port of shipment. The freight charges are payable by the exporter. The importer bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods after this destination. C&F price consists of the FOB price plus freight charges.
- Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF): Under CIF contract, the exporter bears the costs and freight for bringing the goods to the port of destination. It includes charges of insurance against the risks of loss or damage to the goods during transit.
Other relevant terms in international trade include:- Joint Ventures: A business arrangement where two or more parties agree to pool their resources for a specific goal, often involving shared ownership and profits.
- Wholly Owned Subsidiaries: A company that is completely owned by another company, where the parent company holds 100% of the subsidiary's stock.
- Export Processing Zones (EPZ): Designated areas in a country where goods can be landed, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured, and re-exported without the intervention of customs authorities.
- Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme (EPCG): A scheme that allows import of capital goods at zero customs duty for the purpose of enhancing export competitiveness.
- Customs Appraiser: An official responsible for assessing the value of goods being imported or exported to determine the appropriate duties and taxes.
- Bank Certificate of Receipt: A document issued by a bank confirming that it has received goods or documents related to a shipment.
- Duty Drawback: A refund of customs duties paid on imported goods that are subsequently exported, aimed at encouraging exports.
- Export Finance: Financial assistance provided to exporters to help them cover the costs associated with exporting goods, including production and shipping.
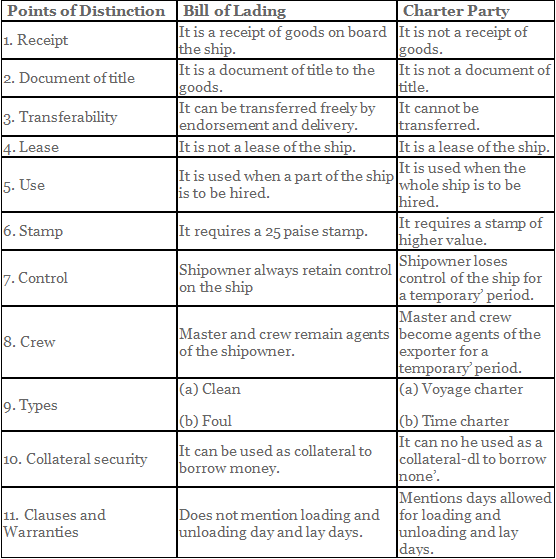
Q.4. Differentiate between the Bill of Lading and Charter Party.
The distinction between Bill of Lading and Charter Party:
Q.5. Explain the various methods of payment in External Trade.
External Trade payment can be made through various methods. The important methods for payment of international trade are as follows:
- Advance Payment
- Open Account
- Documentary Bills
- Letter of Credit
- Direct Remittance
- International Credit Card.
Advance Payment:
Advance payment means the payment made along with the order by the importer as the exporter is always interested in advance payment of the goods exported. The importer can send payment to the exporter by means of:
(a) Bank Draft.
(b) International Money Order.
(c) Telegraphic/Mail Transfer.
(d) Electronic Transfer.Payment against Open Account:
Exporter generally ship the goods and send the shipping documents to the importer and make debit his account for the payment due on goods sent. The importer may make periodic payments against his account. This is convenient for both the exporter and the importer. The exporter is relieved of the botheration of drawing and discounting the bills of exchange. The importer is relieved of the botheration of accepting bills of exchange or getting letters of credit in favour of the exporter.Documentary Bill:
The exporter draws a bill of exchange on the importer. The bill may be
- Sight Bill, or
- Usance Bill.
In case of a sight bill, the importer has to make the payment immediately and obtain the shipping documents/ This mode is known as Documents against Payment (D/P). In case of a usance bill, the exporter is given some time to make the payment. However, documents are passed on to him against acceptance of the bill. It is known as Documents against Acceptance (D/A) bill.
The exporter draws a bill of exchange on the importer and attaches to it shipping documents such as a bill of lading, insurance policy, invoice, consular invoice, certificate of origin, and certificate of quality. Such a bill is known as a documentary bill. It is sent through the exporter’s bank which will present it to the importer through his bank or agent. Documentary bills may be of two types:
- D/A Bill: In case of documents against acceptance, the bank will hand over the shipping documents to the importer when the latter gives acceptance on the bill of exchange.
- D/P Bill: In case of documents against payment bill, the documents are to be released by the bank only on the payment of the bill either at the time of presentation or within a specified period of time.
Letter of Credit:
The exporter can request the importer to open a letter of credit with his bank in favour of the exporter. When such an arrangement is made, the importer’s bank will accept the bill of exchange drawn by the exporter under the terms of the letter of credit. After acceptance, the bill is returned to the exporter who can get it discounted with his bank. He can also wait till the period of maturity and instruct his bank to collect payment on its maturity from the importer’s bank.Direct Remittance:
Under this method, the exporter sends the goods to the importer and also passes on the shipping documents to him. After receipt of documents, the importer can remit the payment to the exporter through the banking channel or telegraphically. This method involves risk for the exporter as the importer may not send the payment in time.The modes of direct remittance are as follows –
- Bank Draft: Bank draft is a popular method of making payment in respect of foreign transactions. A bank draft is issued in favour of the exporter by a commercial bank on receipt of the necessary amount.
In fact, a bank draft is a sort of cheque drawn by a bank on its foreign branch, directing the foreign branch to pay the specified amount of money in a particular currency to the person named in the bank draft. The bank charges a nominal commission for providing this service.- Telegraphic Transfer: Under this method, there is a transfer by the telegraph or cable of bank deposits from one country to another. As in case of bank draft, the money is deposited with the importer’s bank which will in return send a telegram to its bank in the exporter’s country to pay a specified amount either to the exporter or his bank.
This method of making the transfer is adopted only when the traders are in a hurry to settle accounts. This method is costlier as compared to other methods. That is why it is not commonly used.International Credit Card:
Multinational banks issue international credit cards to importers whose financial position are very sound. They make payment through these cards to the exporter for the goods shipped.
Q.6. What are Special Economic Zones (SEZs)? Explain their benefits in brief.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) have been established to encourage free trade and promote exports. These zones act as duty-free enclaves and are considered foreign territories for trade operations, duties, and tariffs. Goods going to an SEZ are treated as “deemed exports,” while goods entering the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) from an SEZ are considered imported goods.Structure & Establishment
SEZs can be set up by the public sector, private sector, joint ventures, or state governments, as per government notifications.
Existing Export Processing Zones (EPZs) are being converted into SEZs.
The key difference between EPZs and SEZs is that EPZs require customs permission for moving raw materials, while SEZs do not.
Functions & Activities
SEZs facilitate various operations, including:
Manufacturing of goods.
Service rendering and processing.
Trading, assembling, repairing, remarking, reconditioning, and re-engineering of products.
Jewellery made from gold, silver, and platinum.
Key Exemptions & Benefits
No predetermined value additions, export obligations, or input/output wastage norms.
Exempt from duties and tariffs within the SEZ.
Income tax benefits under the Export-Import (EXIM) Policy 2002-2007, ensure full tax concession periods.
Offshore banking access, allows SEZ units to secure funds at international rates, reducing the cost for exporters.
Freedom for SEZ units to:
Hedge in commodities.
Make overseas investments from export earnings.
Borrow funds internationally.
Banking & Financial Reforms in SEZs
Overseas Banking Units (OBUs) have been introduced in SEZs, allowing exporters to raise American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) and Global Depositary Receipts (GDRs) without travelling abroad.
SEZ-based bank branches are treated as overseas branches and are exempt from the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), and priority sector lending requirements.
Indian banks can set up OBUs, permitting:
Exporters and developers to hold dollar accounts.
Transactions in multiple currencies.
Financing at international cost rates.
Foreign banks registered in India to establish OBUs in SEZs.
Benefits Available to SEZ Units
Duty-free import of goods.
Reimbursement of central sales tax.
Exemption from central excise duty on eligible goods.
Reimbursement of excise duty on bulk tea procured by SEZ units (as long as the levy remains in force).
Reimbursement of duty on fuels and goods procured from DTA, as per the Directorate General of Foreign Trade’s (DGFT) notified rates.
Q.7. Explain the various agreements of WTO.
WTO Agreements As against GATT which covered only rules relating to trade in goods, the WTO agreements cover trade in goods, services as well as intellectual property. WTO Agreements make the government responsible to formulate the policies and procedure and make them transparent in order to avoid disputes among the nations. Major WTO agreements are discussed below:
- Agreements Forming Part of GATT: The erstwhile General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) after its substantial modification in 1994 (effected as part of the Uruguay Round of negotiations) is very much part of the WTO agreements. Besides the general principles of trade liberalisation, GATT also includes certain special agreements evolved to deal with specific non-tariff barriers. Some of the specific agreements contained in the GATT are listed in the bank on GATT 1994 major agreements.
- Agreement on Textile and Clothing (ATC): This agreement was evolved under WTO to phase out the quote restrictions as imposed by the developed countries on exports of textiles and clothing from the developing countries. The developed countries were imposing various ends of quota restrictions under the Multi-Fibre Arrangement (MFA) that itself was a major departure from the GATT’s basic principle of free trade in goods. Under the ATC, the developed countries agreed to remove quota restrictions in a phased manner during a period of ten years starting from 1995. ATC is considered a landmark achievement of the WTO. It is due to the ATC that the world trade in textile and clothing has become virtually quota-free since 1st January 2005, thus, benefiting immensely the developing countries to expand their textiles and clothing exports.
- Agreement on Agriculture (AoA):It is an agreement to ensure free and fair trade in agriculture. Though original GATT rules were applicable to trade in agriculture, these suffered from certain loopholes such as exemption to member countries to use some non-tariff measures such as customs tariffs, import quotas and subsidies to protect interests of the farmers in the home country. Trade-in agriculture became highly distorted especially due to the use of subsidies by some of the developed countries. AoA is a significant step towards an orderly and fair trade in agricultural products. The developed countries have agreed to lower down the customs duties on their imports and subsidies to the exports of agricultural products. Due to their higher dependence on agriculture, the developing countries have been exempted from making similar reciprocal offers.
- General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS): Agreements are applicable to services also like on goods or merchandise, although services are intangible and cannot be toughed like commodities. GATS is regarded as a landmark achievement of the Uruguay Rbiind as it extends the multilateral rules and disciplines to services. It is because of GATS that the basic rules governing ‘trade in goods’ have become applicable to trade in services.
- Three major provisions of GATS governing trade in services are as follows –
- All member countries are required to remove restrictions on trade in services in a phased manner. The developing countries, however, have been given greater freedom to decide about the period by which they would liberalise and also the services they would like to liberalise by that period.
- GATS provides that trade in services is governed by ‘Most Favoured Nations’ (MFN) obligation that prevents countries from discriminating among foreign suppliers and services.
- Each member country shall promptly publish all its relevant laws
and regulations pertaining to services including international agreements pertaining to trade and services to which member is a signatory.,
Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property’ Rights (TRIPS): The WTO’s agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) was negotiated in 1986-1994. It was the Uruguay Round of GATT negotiations where for the first time the rules relating to intellectual property rights were discussed and introduced as part of the multilateral trading system. Intellectual property means information with commercial values such as ideas, inventions, creative expression and others. The agreement sets out the minimum standards of protection to be adopted by the parties in respect of seven intellectual properties, viz., copyrights and related rights, trademarks, geographical indication, industrial designs, patents, layout design of integrated circuits, and undisclosed information (trade secrets).
|
39 videos|272 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions and Answers: International Business - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is international business commerce? |  |
| 2. What are the benefits of international business commerce? |  |
| 3. What are the challenges of international business commerce? |  |
| 4. How does international business commerce impact the global economy? |  |
| 5. What skills are required for a successful career in international business commerce? |  |