B Com Exam > B Com Notes > Goods and Services Tax (GST) > Direct and Indirect Taxes
Direct and Indirect Taxes | Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com PDF Download
Concept of Direct and Indirect Taxes
A tax may be defined as a fee charged by a government on a product, income or an activity. It is a pecuniary burden laid upon individuals or property owners to support the Government, a payment exacted by legislative authority. A tax "is not a voluntary payment or donation, but an enforced contribution, exacted pursuant to legislative authority".
Taxes are broadly classified into direct and indirect taxes.
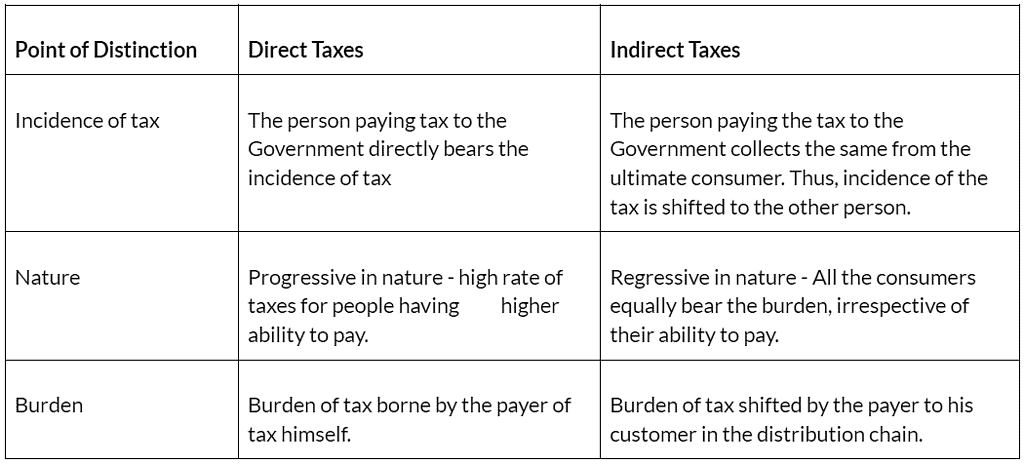
- Direct Taxes: If a tax is levied directly on or wealth an individual or an organization it is called direct tax. A direct tax is a kind of charge, which is imposed directly on the taxpayer and paid directly to the Government by the persons (juristic or natural) on whom it is imposed. An incidence of direct tax cannot be shifted by the taxpayer to someone else. The burden of such tax is borne by the payer of tax himself. An important direct tax imposed in India is income tax.
- Indirect Taxes: If tax is levied on the price of a good or service, then it is indirect tax. The person paying the indirect tax passes on the incidence of tax to some other person. He collects the tax from his customer on sale of goods and services and remits it to the government. The ultimate burden of such tax falls on the final consumer of such goods and services. If the taxpayer (such as a manufacturer or provider of service or seller of goods) is just a conduit and at every stage the taxincidence is passed on till it finally reaches the consumer, who really bears the brunt of it, such tax is indirect tax. An indirect tax is one that can be shifted by the taxpayer to someone else.
- Indirect taxes are also called consumption taxes, they are regressive in nature because they are not based on the principle of ability to pay. All the consumers, including the economically challenged bear the brunt of the indirect taxes equally.
- Indirect taxes are levied on consumption, expenditure, privilege, or right but not on income or property. Hitherto, a number of indirect taxes were levied in India, namely, excise duty, customs duty, service tax, central sales tax (CST), value added tax (VAT), entry tax, purchase tax, entertainment tax, tax on lottery, betting and gambling, luxury tax, tax on advertisements, etc.
- However, indirect taxation in India has witnessed a paradigm shift on July 01, 2017 with the introduction of a unified indirect tax regime wherein a large number of Central and State indirect taxes have been subsumed into a single tax – Goods and Services Tax (GST). The introduction of GST is a very significant step in the field of indirect tax reforms in India.
Distinction between Direct and Indirect Taxes
Features of Indirect-taxes
- A major source of revenue: Indirect taxes are an important source of tax revenue for Governments all over the world and continue to grow as more and more countries are moving to consumption oriented tax regimes. In India, indirect taxes contribute more than 50% of the total tax revenues of Central and State Governments.
- Tax on commodities and services: It is levied on commodities at the time of manufacture or purchase or sale or import/export thereof. Hence, it is also known as commodity taxation. It is also levied on provision of services.
- Shifting of burden: In the indirect taxes the tax burden is shifted by the tax payer to his customer. The tax is collected through the selling price of goods and services and remitted to the tax department of the government. Price of goods and services serves as vehicle for indirect taxes. For example, GST paid by the supplier of the goods is recovered from the buyer by including the tax in the cost of the commodity.
- No direct pinch to taxpayers: Since, value of indirect taxes are generally built in the price of the commodity or service, most of the time the tax payer pays the tax without actually knowing that he is paying tax to the Government. Thus, tax payer does not perceive a direct pinch while paying indirect taxes. Through the purchase and consumption of various goods and services in our day to day life we are regularly paying several indirect taxes to the government treasury.
- Inflationary: As indirect taxation directly affects the prices ofcommodities and services a rise in indirect taxes leads to inflationary trend.
- Wider tax base: Unlike direct taxes, the indirect taxes have a wide tax base. Majority of the products or services are subject to indirect taxes with low thresholds. Hence every person in a nation is indirect tax-payee. Therefore, it is rightly said that there are two things certain in human life namely, death and taxes.
- Promotes social welfare: High taxes are imposed on the consumption of harmful products (also known as ‘sin goods’) such as alcoholic products, tobacco products etc. This not only curtails their consumption but also enables the State to collect substantial revenue. Thus indirect taxes indirectly promote social welfare.
- Regressive in nature: Generally, the indirect taxes are regressive in nature. The rich and the poor have to pay the same rate of indirect taxes on certain commodities of mass consumption. This may lead to further increase the income disparities between the rich and the poor.
The document Direct and Indirect Taxes | Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com is a part of the B Com Course Goods and Services Tax (GST).
All you need of B Com at this link: B Com
|
130 videos|45 docs|14 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















