NEET Exam Classwise Biology Syllabus 2026 PDF Download
Securing a good rank in the NEET examination requires a deep knowledge of the topics from the Botany and Zoology syllabus of classes 11 and 12. Learning the definitions and terminology related to Biology is essential, and regular practice is required to gain success. The syllabus for the NEET exam largely follows the concepts taught in the NCERT Biology textbooks, and hence thorough revision of the textbooks for class 11 and class 12 is crucial for candidates aspiring to do well in the NEET UG Exam 2023.
NEET Class-wise Biology Syllabus: Key Highlights
In this EduRev document, we will see the Biology class-wise syllabus in detail.The table below outlines the five units of Biology Class 11 and Biology Class 12, along with the chapters that each unit covers.
Detailed Class-wise NEET Biology Syllabus
Biology Class 11 Syllabus
The NEET Biology syllabus includes both Zoology and Botany, making it more important since it is so extensive and comprises the major portion in NEET Exam (100 questions out of 200 in which 10 questions are optional). Given below is the detailed syllabus covered in the NEET Biology syllabus.
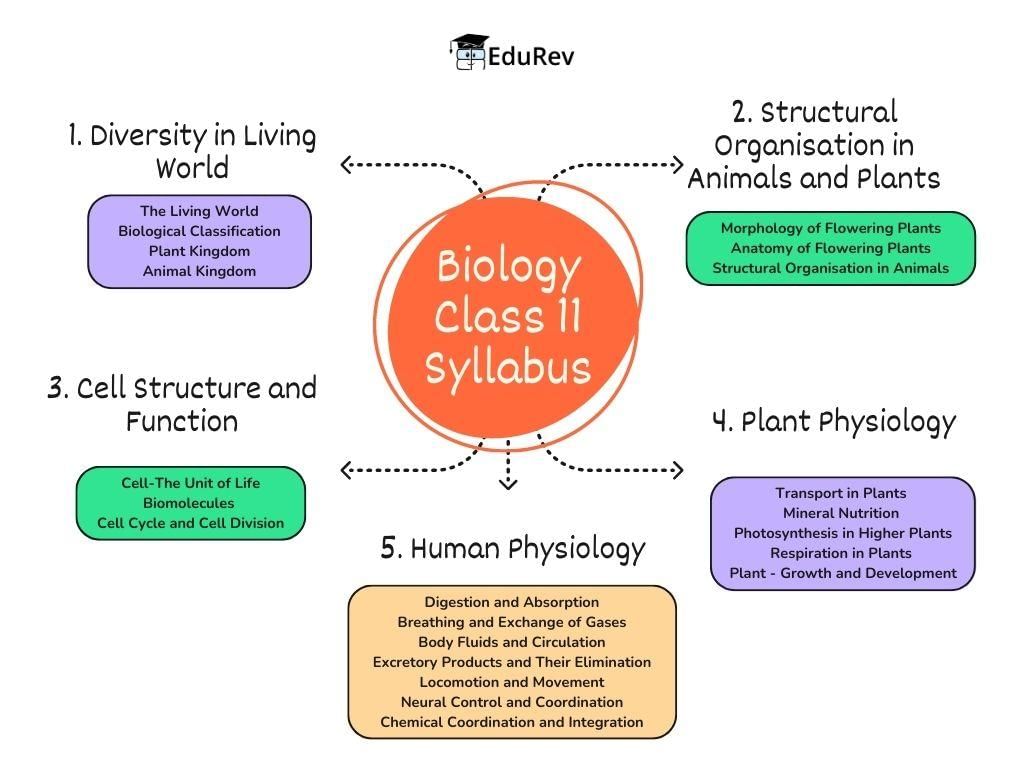
Unit 1: Diversity in Living World
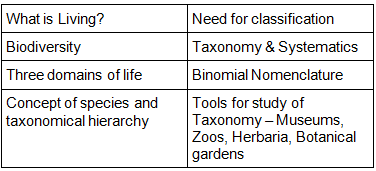
Chapter 1: The Living World
- What is living?; Biodiversity; Need for classification; Three domains of life; Taxonomy & Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature; Tools for study of Taxonomy – Museums, Zoos, Herbaria, Botanical gardens
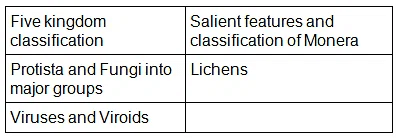
Chapter 2: Biological Classification
- Five kingdom classification; salient features and classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens; Viruses and Viroids
Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom
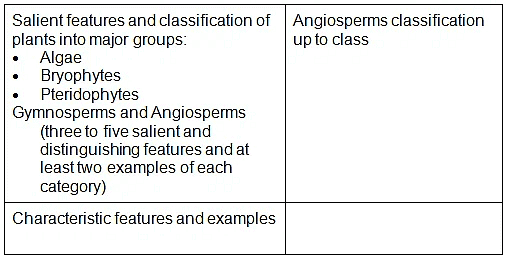
- Salient features and classification of plants into major groups-Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category); Angiosperms classification up to class, characteristic features and examples)
Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom
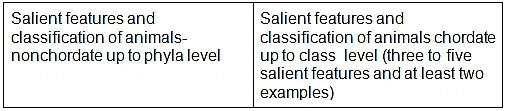
- Salient features and classification of animals-nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to class level (three to five salient features and at least two examples)
Unit 2: Structural Organization in Plants and Animals
Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Morphology and modifications; Tissues

Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and recemose, flower, fruit and seed (To be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus)

Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals
- Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (cockroach). (Brief account only)

Unit 3: Cell Structure and Function
Chapter 8: Cell-The Unit of Life
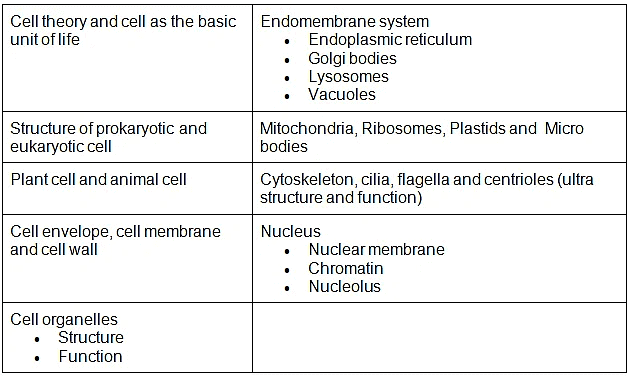
- Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles-structure and function; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, micro bodies; Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultra structure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus
Chapter 9: Biomolecules
- Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids; Enzymes-types, properties, enzyme action

Chapter 10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance

Unit 4: Plant Physiology
Chapter 11: Transport in Plants
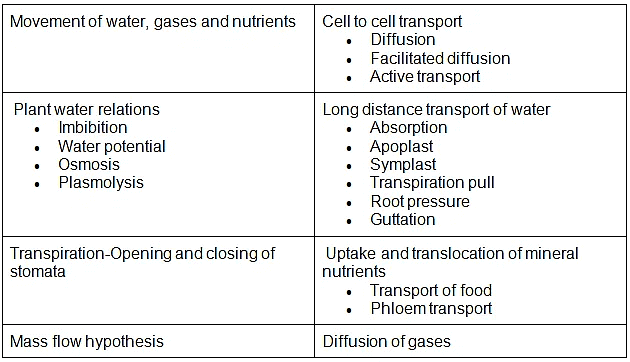
- Movement of water, gases and nutrients; Cell to cell transport-Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; Plant – water relations – Imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; Long distance transport of water – Absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation; Transpiration-Opening and closing of stomata; Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients-Transport of food, phloem transport, Mass flow hypothesis; Diffusion of gases (brief mention)
Chapter 12: Mineral Nutrition
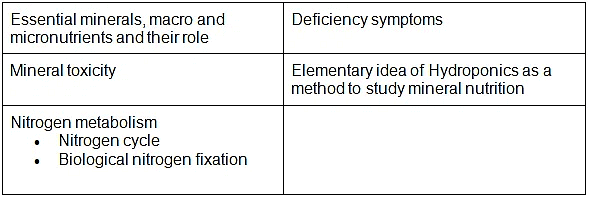
- Essential minerals, macro and micronutrients and their role; Deficiency symptoms; Mineral toxicity; Elementary idea of Hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; Nitrogen metabolism-Nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation
Chapter 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
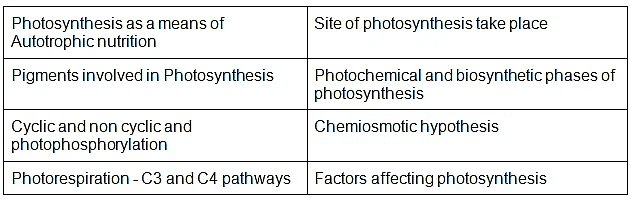
- Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non cyclic and photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways; Factors affecting photosynthesis
Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants
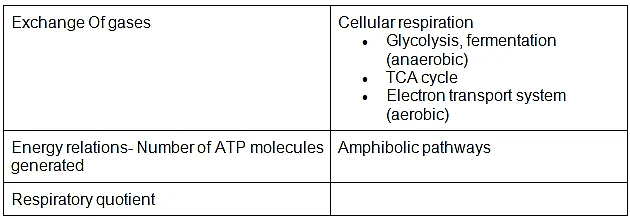
- Exchange gases; Cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); Energy relations- Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient
Chapter 15: Plant - Growth and Development
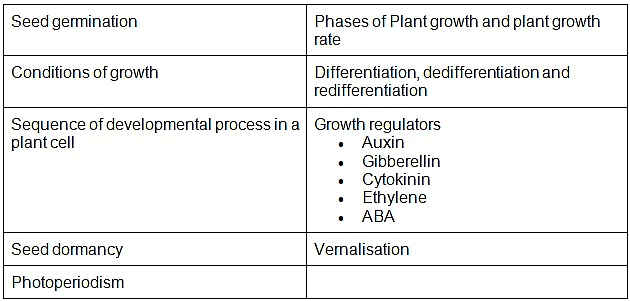
- Seed germination; Phases of Plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth; Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; Sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; Seed dormancy; Vernalisation; Photoperiodism
Unit 5: Human Physiology
Chapter 16: Digestion and Absorption
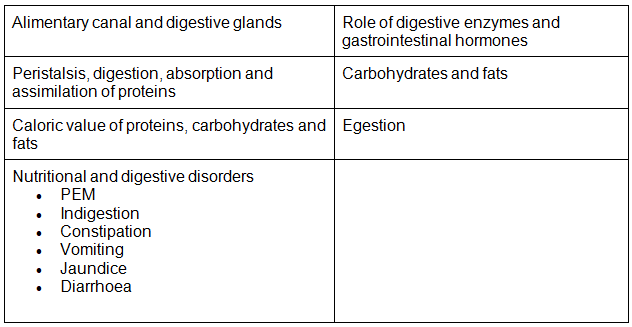
- Alimentary canal and digestive glands; Role of digestive enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Caloric value of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Egestion; Nutritional and digestive disorders – PEM, indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhea
Chapter 17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
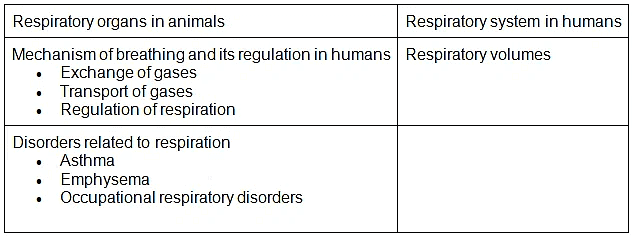
- Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Respiratory system in humans; Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-Exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration Respiratory volumes; Disorders related to respiration-Asthma, Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders
Chapter 18: Body Fluids and Circulation
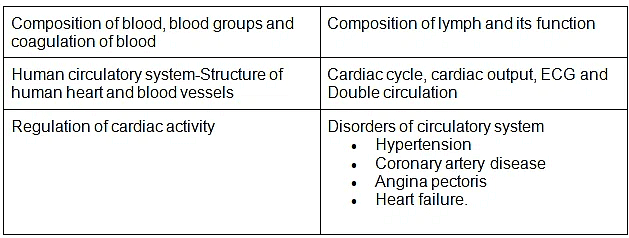
- Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Composition of lymph and its function; Human circulatory system-Structure of human heart and blood vessels; Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure
Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
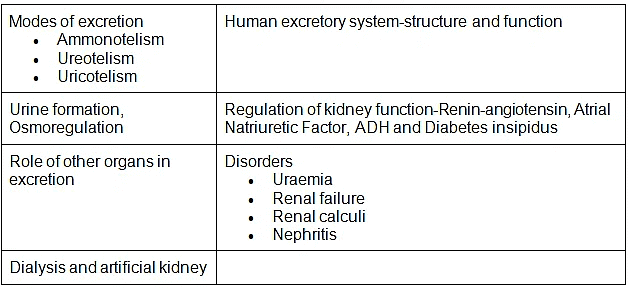
- Modes of excretion- Ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory system-structure and function; Urine formation, Osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin, Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders; Uraemia, Renal failure, Renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney
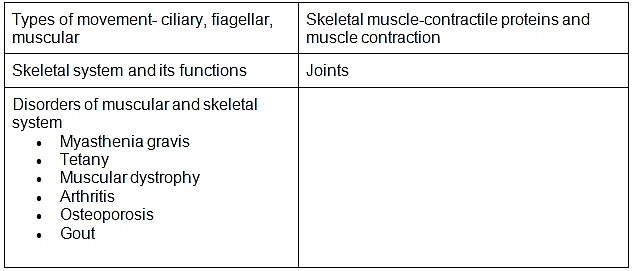
Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement
- Types of movement- ciliary, fiagellar, muscular; Skeletal muscle-contractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions (To be dealt with the relevant practical of Practical syllabus); Joints; Disorders of muscular and skeletal system. Myasthenia gravis, Tetany, Muscular dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout
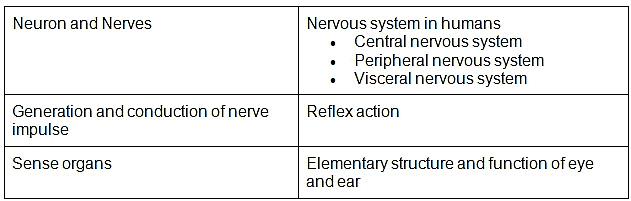
Chapter 21: Neural Control and Coordination
- Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse; Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear
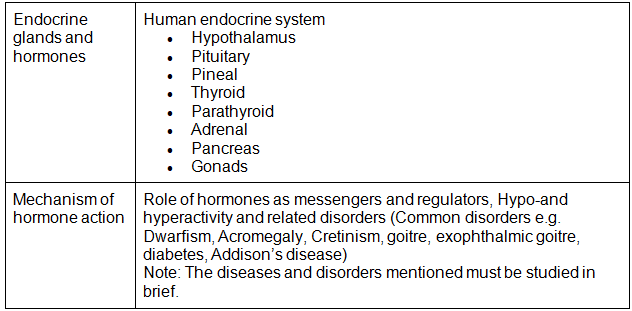
Chapter 22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine systemHypothalamus, Pituitary, Pineal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders (Common disorders e.g. Dwarfism, Acromegaly, Cretinism, goiter, exopthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addison’s disease)
Biology Class 12 Syllabus
Unit 1 : Reproduction
Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organisms
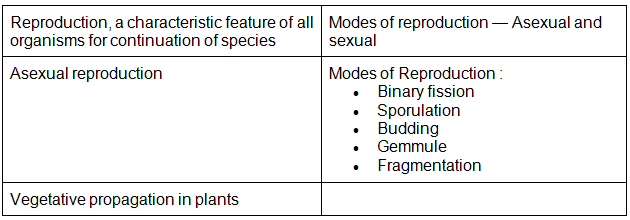
- Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; Modes of reproduction – Asexual and sexual; Asexual reproduction; Modes-Binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants
Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
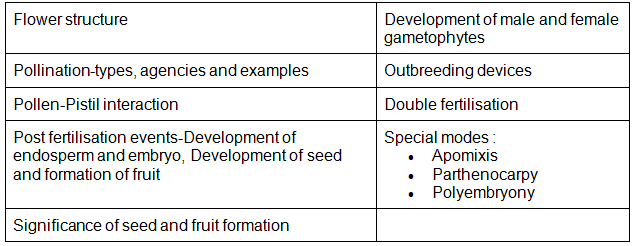
- Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Pollination-types, agencies and examples; Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Double fertilization; Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed and formation of fruit; Special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation
Chapter 3: Human Reproduction
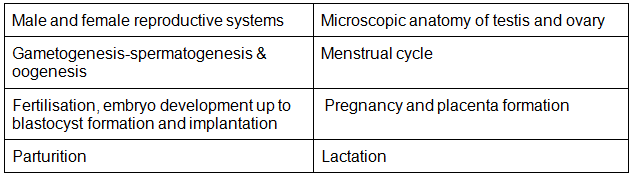
- Male and female reproductive systems; Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Gametogenesis-spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Menstrual cycle; Fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Lactation (Elementary idea)
Chapter 4: Reproductive Health
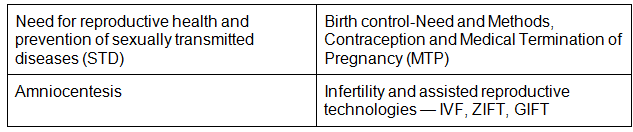
- Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); Birth control-Need and Methods, Contraception and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP); Amniocentesis; Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness)
Unit 2 : Genetics and Evolution
Chapter 5: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
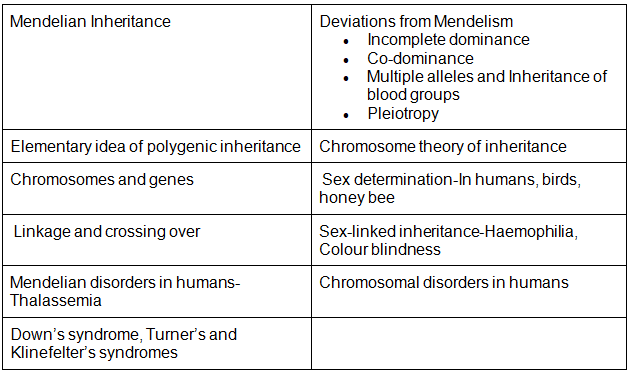
- Mendelian Inheritance; Deviations from Mendelism- Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, Multiple alleles and Inheritance of blood groups, Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Chromosome theory of inheritance; Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination-In humans, birds, honey bee; Linkage and crossing over; Sex linked inheritance-Haemophilia, Colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia; Chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes
Chapter 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
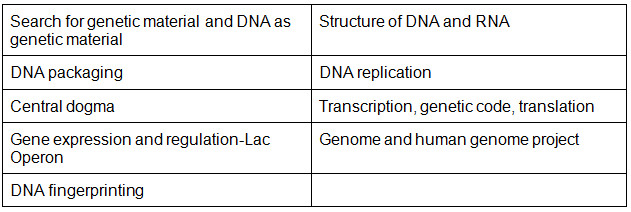
- Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma; Transcription, genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation- Lac Operon; Genome and human genome project; DNA fingerprinting
Chapter 7: Evolution
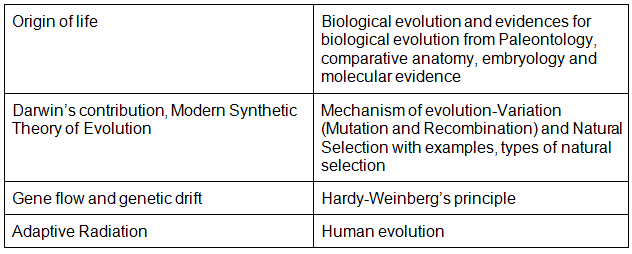
- Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Darwin’s contribution, Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution; Mechanism of evolution-Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; Adaptive Radiation; Human evolution
Unit 3 : Biology and Human Welfare
Chapter 8: Human Health and Diseases
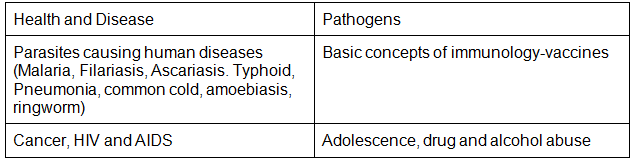
- Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ringworm); Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines; Cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse
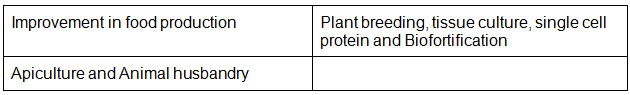
Chapter 9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry
Chapter 10: Microbes in Human Welfare
- In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers

Unit 4 : Biotechnology and Its Applications
Chapter 11: Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology)

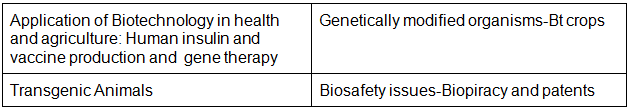
Chapter 12: Biotechnology and its Application
- Application of Biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy; Genetically modified organisms-Bt crops; Transgenic Animals; Biosafety issues – Biopiracy and patents
Unit 5 : Ecology and Environment
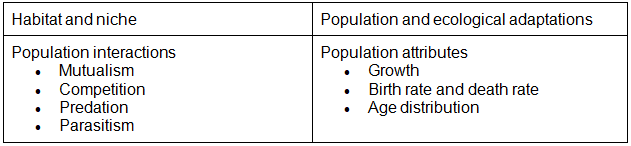
Chapter 13: Organisms and Populations
- Habitat and niche; Population and ecological adaptations; Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; Population attributes-growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution
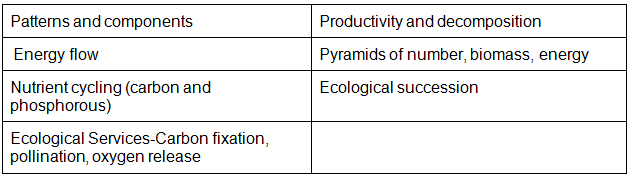
Chapter 14: Ecosystem
- Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; Energy flow; Pyramids of number, biomass, energy; Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorous); Ecological succession; Ecological Services-Carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release
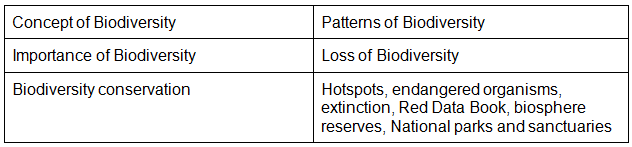
Chapter 15: Biodiversity and its Conservation
- Concept of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity; Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity; Biodiversity conservation; Hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries
Chapter 16: Environmental Issues
- Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals and their effects; Solid waste management; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warming; Ozone depletion; Deforestation; Any three case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues

NEET Biology 2023 Chapter-wise Weightage
Chapters | Approximate Weightage |
Diversity of Living Organisms | 12% |
Structural Organization in Plants & Animals | 9% |
Cell: Structure and Function | 8% |
Plant Physiology | 8% |
Human Physiology | 16% |
Reproduction | 11% |
Genetics and Evolution | 13% |
Biology and Human Welfare | 9% |
Biotechnology and its Applications | 4% |
Ecology and Environment | 10% |
NEET Exam Pattern
The syllabus for the NEET exam has remained consistent over time, but there have been changes to the exam's structure in the last two years. Before delving into the specifics of the NEET UG syllabus for 2023, let's examine the exam pattern in detail. Each subject has two sections: Section A contains 35 questions, while Section B has 15 questions. Candidates are free to attempt any 10 questions out of the 15 in Section B. Consequently, the total number of questions has remained the same. The exam's duration has been extended by 20 minutes, and the overall duration is now 200 minutes or 3 hours and 20 minutes. The table below will assist candidates in gaining a better understanding.
Sections | Number of Questions | Total Marks |
Physics Section A | 35 | 140 |
Physics Section B | 15 | 40 |
Chemistry Section A | 35 | 140 |
Chemistry Section B | 15 | 40 |
Botany Section A | 35 | 140 |
Botany Section B | 15 | 40 |
Zoology Section A | 35 | 140 |
Zoology Section B | 15 | 40 |
NEET Preparation 2023 Related Links
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to NEET Class-wise NEET Biology Syllabus
What is the change in syllabus of NEET 2023?
The syllabus for NEET 2023 remains the same as the previous years, with no major changes.
Who can take the NEET 2023 exam?
All candidates must be at least 17 years old as of December 31, 2023 in order to be eligible for the NEET undergraduate exam. There is no upper age limit for taking the NEET exam.
Will NEET 2023 be held in May 2023?
The NEET-UG 2023 exam is scheduled to take place on 7th May 2023.
How many chapters are included in the NEET syllabus for 2023?
The syllabus for NEET 2023 consists of 98 chapters covering Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology.
What is the total number of marks available in the NEET exam?
The NEET exam consists of 180 questions to be answered out of 200 questions, with a total of 720 marks.
How can I prepare for NEET 2023?
A candidate can keep in mind below topics to prepare for NEET 2023 exam :-
- Become familiar with the NEET Exam pattern 2023 by utilising sample papers from past exams.
- Make sure to have a digital or printed version of the syllabus, question papers and other relevant documents easily accessible for preparation.
- Construct a suitable plan to guide your study.
- Draft comprehensive notes to regularly refer back to.
- Focus on obtaining a strong understanding of the material.
- Take mock tests to become comfortable with the examination layout.
- Set achievable goals on a daily basis and meet them. Eventually you will develop the ability to study for long periods with more concentration.
- Complete as many questions as possible each day to map your progress and obtain good results in NEET 2023.
- Practice extensively to boost your levels of speed and accuracy.
What is EduRev Infinity Package for NEET? What will I get after I purchase it?
The EduRev Infinity Package for NEET is the ultimate package for students aspiring to crack the NEET exam. It provides you with all the resources you need to ace your NEET exams. It's designed to provide comprehensive and up-to-date study material, practice tests, and guidance from experts in the field.
Though EduRev Infinity is more about quality than quantity, if we have to put a number, you would get around 50+ EduRev courses, which includes 1000+ tests, 1500+ docs, and 800+ videos for courses of EduRev Infinity! So you won't have to worry about missing out on anything.
Some of the famous courses in the EduRev Infinity Package include:
- Subject-wise courses for Biology, Chemistry & Physics.
- Topic-wise MCQs for NEET
- NCERTs at Fingertips: NCERT Textbooks, Solutions, Exemplars & NCERT based MCQ Tests
- 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers (Physics, Chemistry & Biology)
- NEET Mock Test Series
- DPPs for each chapter, DC Pandey, HC Verma and Irodov Solutions
And this is just the tip of the iceberg, any new course that is added under EduRev Infinity Package for NEET over the year will also be a part of the package, with detailed solutions with every question, higher preference for questions asked, early access to new features and upcoming deeper analysis are all a part of EduRev Infinity!
All the content offered on EduRev has been curated by the mentors of AIR 17 Priyaz Mishra, Supriya Senapati (360/360 in Biology) & other experts.
You can refer to this video which will help you to understand more about EduRev Infinity Package for NEET. Link to the video: What do you get for NEET under EduRev Infinity?
So don't miss out on this great opportunity - get the EduRev package and get ready to ace the NEET exam!
Why is it important to be familiar with this syllabus?
It is essential to be familiar with the syllabus for NEET 2023 before beginning your preparation in order to ensure you understand the topics well. The following points reflects the importance of knowing the syllabus :-
- It will provide a comprehensive understanding of the topics that will be tested in NEET 2023.
- You will become aware of the essential topics that should be given priority while studying, in order to acquire a high score.
- This will help you comprehend the amount of hard work and commitment that needs to be invested in order to excel in the exam.
- This will enable you to form an effective approach towards the preparation.
- It will also inform you of the topics that can be neglected, so that you can concentrate on the most important ones.
Is it worth buying the EduRev Infinity Package for
NEET
?
The EduRev Infinity Package for NEET is an amazing resource for students studying for the exam. It includes a full set of course materials, including study guides, video lectures, detailed notes, practice tests and mock tests to help you prepare for your exams. All of this makes it a great option for NEET preparation.
"The topic-wise tests of EduRev are really helpful, it gives you a real track of your progress" ~Supriya Senapati (360/360 in Biology)
The EduRev team has interacted with a few students who have been using EduRev while preparing for the NEET exam and here's what these students have to say: Why NEET Aspirants say 'EduRev is just the best app for NEET Preparation'?
With EduRev’s comprehensive resources, you can be sure you're getting the best possible preparation for the exam. So if you're serious about doing well on the NEET, this is definitely a package worth considering.
I’ve purchased the EduRev Infinity Package for NEET but am unable to understand how to use it effectively for NEET Preparation.
No worries, we understand that the NEET exam has a variety of topics to learn, which require a lot of understanding and practice. Our NEET Experts, who’ve mentored AIR 17 Priyaz Mishra, Supriya Senapati (360/360 in Biology), have ensured to create the most structured courses for every section/topic required for NEET Preparation.
They’ve also created a video to help you understand how to use EduRev App effectively: What all do you get & how to use EduRev App effectively to crack NEET Exam?
This comprehensive approach should help you gain a better understanding of the material and gain confidence in your NEET preparation.
What is the fastest way to revise for NEET?
The fastest way to revise for NEET is to focus on the important topics. Make a list of topics you need to cover and focus on them. Make sure you have a good understanding of the concepts and memorize the formulae and equations. Practice questions related to those topics and use mock tests to test your knowledge. Also, make sure to stay organized and have a revision plan in place.
You can refer to NCERT Revision Notes for NEET Preparation: NCERT Exemplar & Revision Notes for NEET















