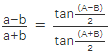Sine Rule | Mathematics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Law of Sines |

|
| What is Law of Sines? |

|
| Law of Sines Formula |

|
| Applications of Sine Law |

|
| Ambiguous Case of Law of Sines |

|
Law of Sines
The law of sines establishes the relationship between the sides and angles of an oblique triangle(non-right triangle). Law of sines and law of cosines in trigonometry are important rules used for "solving a triangle". According to the sine rule, the ratios of the side lengths of a triangle to the sine of their respective opposite angles are equal. Let us understand the sine law formula and its proof using solved examples in the following sections.
What is Law of Sines?
The law of sines relates the ratios of side lengths of triangles to their respective opposite angles. This ratio remains equal for all three sides and opposite angles. We can therefore apply the sine rule to find the missing angle or side of any triangle using the requisite known data.
Law of Sines: Definition
The ratio of the side and the corresponding angle of a triangle is equal to the diameter of the circumcircle of the triangle. The sine law is can therefore be given as,
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC = 2R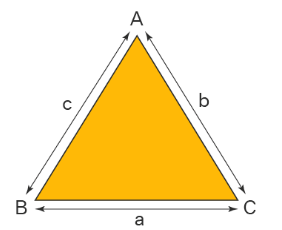
- Here a, b, c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- A, B, and C are the angle of the triangle.
- R is the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle.
Law of Sines Formula
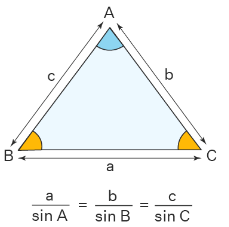
The law of sines formula is used for relating the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of consecutive angles. It is the ratio of the length of the side of the triangle to the sine of the angle thus formed between the other two remaining sides. The law of sines formula is used for any triangle apart from SAS triangle and SSS triangle. It says,
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
where,
- a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle
- A, B, and C are the angles of the triangle.
This formula can be represented in three different forms given as,
- a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
- sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c
- a/b = sinA/sinB; a/c = sinA/sinC; b/c = sinB/sinC
Example: Given a = 20 units c = 25 units and Angle C = 42º. Find the angle A of the triangle.
For the given data, we can use the following formula of sine law: a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
⇒ 20/sin A = 25/sin 42º
⇒ sin A/20 = sin 42º/25
⇒ sin A = (sin 42º/25) × 20
⇒ sin A = (sin 42º/25) × 20
⇒ sin A = (0.6691/5) × 4
⇒ sin A = 0.5353
⇒ A = sin-1(0.5363)
⇒ A = 32.36º
∠A = 32.36º
Proof of Law of Sines Formula
The law of sines is used to compute the remaining sides of a triangle, given two angles and a side. This technique is known as triangulation. It can also be applied when we are given two sides and one of the non-enclosed angles. But, in some such cases, the triangle cannot be uniquely determined by this given data, called the ambiguous case, and we obtain two possible values for the enclosed angle. To prove the sine law, we consider two oblique triangles as shown below.
In the first triangle, we have:
h/b = sinA
⇒ h = b sinA
In the second triangle, we have:
h/a = sinB
⇒ h = a sinB
Also, sin(180º - B) = sinB
Equalizing the h values from the above expressions, we have:
a sinB = b sinA
⇒ a/sinA = b/sinB
Similarly, we can derive a relation for sin A and sin C.
asinC = csinA
⇒ a/sinA = c/sinC
Combining the above two expressions, we have the following sine law.
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
Tips and Tricks on Law of Sines
- The triangulation technique is used to find the sides of a triangle when two angles and one side of a triangle is known. For this the sine law is helpful.
- This sine law of trigonometry should not be confused with the sine law in physics.
- Further deriving from this sine law we can also find the area of an oblique triangle.
- Area of a triangle = (1/2) ab sinC = (1/2) bc sinA = (1/2) ca sinB
- Also sine law provides a relationship with the radius R of the circumcircle,a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC = 2R
- Cosine law: This proves a relationship between the sides and one angle of a triangle, c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab⋅cos C
- Tangent law: This has been derived from the sine law and it gives the relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle.

Applications of Sine Law
The law of sines finds application in finding the missing side or angle of a triangle, given the other requisite data. The sine law can be applied to calculate:
- The length of the side of a triangle using ASA or AAS criteria.
- The unknown angle of a triangle.
- The area of the triangle.
Ambiguous Case of Law of Sines
While applying the law of sines to solve a triangle, there might be a case when there are two possible solutions, which occurs when two different triangles could be created using the given information. Let us understand this ambiguous case while solving a triangle using Sine law using the following example.
Example: If the side lengths of △ABC are a = 18 and b = 20 with ∠A opposite to 'a' measuring 26º, calculate the measure of ∠B opposite to 'b'?
Using the sine rule, we have sinA/a = sinB/b = sin26º/18 = sin B/20.
⇒ sin B = (9/10) sin26º or B ≈ 29.149º.
However, note that sin x = sin(180º - x). ∵ A + B < 180º and A + (180º - B) < 180º, another possible measure of B is approximately 180º - 29.149º = 150.851º.
Solved Example
Example 1: Two angles and an included side is∠A = 47º and ∠B = 78º and c = 12.6 units. Find the value of a.
Given: ∠A = 47º and ∠B = 78º
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180º
⇒ 47º + 78º + ∠C = 180º
⇒ 125º + ∠C = 180º
⇒ ∠C = 180º - 125º
⇒ ∠C = 55º
We shall apply the sine law to find the side of the triangle.
a/sin A = c/sin C
⇒ a/sin 47º = 12.6/sin 55º
⇒ a = 5.62
a = 11.24 units
Example 2: It is given ∠A = 47º, ∠B = 78º, and the side c = 6.3. Find the length a.
To find: Length of a
Given:
∠A = 47º, ∠B = 78º, and c = 6.3.
Since, the sum of all the interior angles of the triangle is 180∘,
Therefore,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C=180º
⇒ 47º + 78º + ∠C = 180º
⇒ ∠C = 55º
Using law of sines formula,
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
⇒ a/sinA = c/sinC
⇒ a/sin47º = 6.3 / sin55º
⇒ a = 6.3 / sin55º × sin47º
⇒ a = 5.6
a = 5.6
Example 3: For a triangle, it is given a = 10 units c = 12.5 units and angle C = 42º. Find the angle A of the triangle.
To find: Angle A
Given:
a = 10, c = 12.5, and angle C = 42º.
Using law of sines formula,
⇒ a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
⇒ 10/sinA = 12.5/sin 42º
⇒ sin A = 0.5353
⇒ ∠A = 32.36º
∠A = 32.36º
|
138 videos|67 docs|41 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|