Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > The Process of Electrolysis
The Process of Electrolysis | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Key Terms & Definitions
- When an electric current is passed through a molten ionic compound the compound decomposes or breaks down
- The process also occurs for aqueous solutions of ionic compounds
- Liquids and solutions that are able to conduct electricity are called electrolytes
- Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity hence they do not undergo electrolysis
- An electrolytic cell is the name given to the set-up used in electrolysis and which consists of the following:
- Electrode: a rod of metal or graphite through which an electric current flows into or out of an electrolyte
- Electrolyte: ionic compound in molten or dissolved solution that conducts the electricity
- Anode: the positive electrode of an electrolysis cell
- Anion: negatively charged ion which is attracted to the anode
- Cathode: the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell
- Cation: positively charged ion which is attracted to the cathode
 The basic set-up of an electrolysis cell
The basic set-up of an electrolysis cell
Exam Tip
Use the PANIC mnemonic to remember which electrode is the positive and which is the negative: Positive (is) Anode Negative Is Cathode.
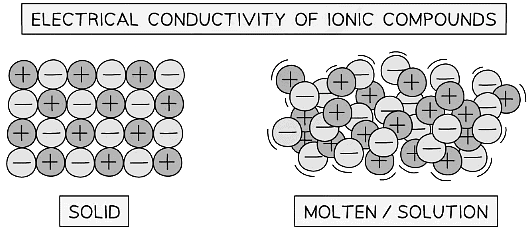
Electrical Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds in the solid state cannot conduct electricity since they have no free ions that can move and carry the charge
- The ions must be able to move and can only do so in the molten state or when dissolved in a solution, usually aqueous
- When the cell is turned on and an electric current is passed through an electrolyte the ions in the solution start to move towards the electrodes
Electrical Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
 Particles in ionic compounds are in fixed position in the solid state but can move around when molten or in solution
Particles in ionic compounds are in fixed position in the solid state but can move around when molten or in solution
Exam Tip
Cations are attracted to the cathode and anions are attracted to the anode. Electron flow in electrochemistry occurs in alphabetical order as electrons flow from the anode to the cathode.
Movement of Ions
- During electrolysis the electrons move from the power supply towards the cathode
- Electron flow in electrochemistry thus occurs in alphabetical order as electrons flow from the anode to the cathode
- Positive ions within the electrolyte migrate towards the negatively charged electrode which is the cathode
- Negative ions within the electrolyte migrate towards the positively charged electrode which is the anode
 Diagram showing the direction of movement of electrons and ions in the electrolysis of NaCl
Diagram showing the direction of movement of electrons and ions in the electrolysis of NaCl
Exam Tip
When a metal conducts it is the electrons that are moving through the metal. When a salt solution conducts it is the ions in the solution that move towards the electrodes while carrying the electrons.
The document The Process of Electrolysis | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
78 videos|87 docs|11 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches