Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Biology for Grade 10 > Controling the Body Temperature
Controling the Body Temperature | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
Monitoring of Body Temperature
- The human body needs to maintain a temperature at which enzymes work best, around 37°C
- Processes such as respiration release energy as heat; and the body loses heat energy to its surroundings – the energy gained and lost must be regulated to maintain a constant core body temperature
- Body temperature is monitored and controlled by the thermoregulatory centre in the brain
- The thermoregulatory centre contains receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood
- The skin contains temperature receptors and sends nervous impulses to the thermoregulatory centre
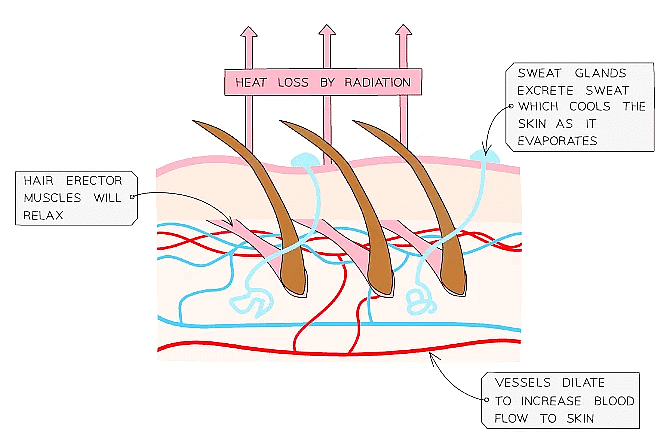
 Human skin contains structures involved in processes that can increase or reduce heat loss to the surroundings
Human skin contains structures involved in processes that can increase or reduce heat loss to the surroundings
Controlling Body Temperature
- If the body temperature is too high, blood vessels dilate (vasodilation) and sweat is produced from the sweat glands
- Both these mechanisms cause a transfer of energy from the skin to the environment, cooling the body down
 Responses in the skin when the body temperature is too high and needs to decrease
Responses in the skin when the body temperature is too high and needs to decrease - If the body temperature is too low, blood vessels constrict (vasoconstriction), sweating stops and skeletal muscles contract (shiver)
These mechanisms reduce heat loss to the surroundings (with skeletal muscle contraction increasing heat released in the body)
 Responses in the skin when body temperature is too low and needs to increase
Responses in the skin when body temperature is too low and needs to increase
Examples of Body Temperature Control
Higher tier only
- The mechanisms described above lower or raise body temperature
- In the exam, you may be given examples of different contexts in which the body temperature needs to decrease (when someone is too hot) or increase (when someone is too cold)
- Learn the following concepts to ensure you can suggest what changes are happening and why:
Body temperature control table
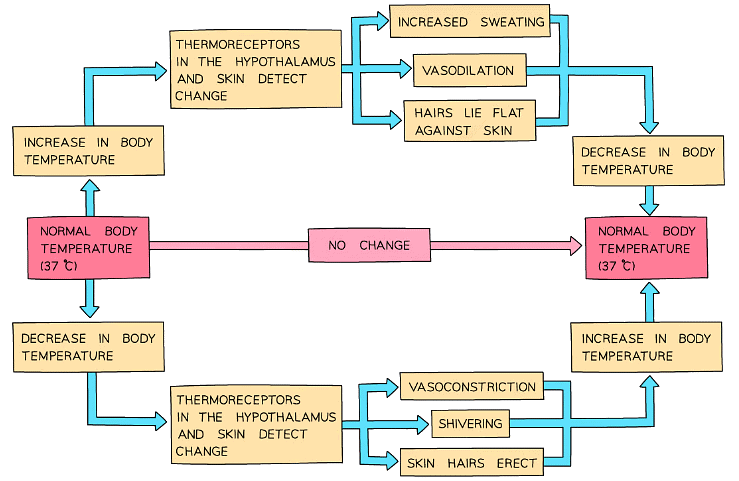 Remember homeostasis involves the maintenance of constant internal environment; temperature control is an example of negative feedback
Remember homeostasis involves the maintenance of constant internal environment; temperature control is an example of negative feedback
The document Controling the Body Temperature | Biology for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Biology for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches