Society, Law & Ethics | Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Digital Footprint
- Digital footprint means collection of data or records generated after any activity
- Done by an individual on internet.
- Now a days Digital Footprint plays an important role in making an Individual’s reputation
- Everyone who is connected to internet has Digital Footprint
- Digital Footprints are permanent
- Digital Footprints are also called Digital tattoos.
Types of Digital Footprint
Active Digital Footprint
collection of data or records generated after any activity done intentionally by an individual on internet. Exp-
- Sharing any information on Social Media sites
- Filling Online forms
- login to any type of account such as email, shopping id etc.
- sending and receiving mails
- accepting cookies knowingly
Passive Digital Footprint
Data or records are generated from individual without their knowledge. Exp-
- Turning on Geo location
- cookies installed automatically without concern of user
- like or dislike any activity on social media sites
Digital Society and Netizen
Net Etiquettes
“ Responsible, Safe, positive, legal and ethical use of Internet (digital technology) “

Digital Communication Etiquette
- Don’t respond to junk mails or spam or any unnecessary mail.
- Avoid including large attachments
- Do not use abusive language during communication
- Avoid using sarcasm.
- Be careful and responsible which making any comment
Social Media Etiquette
- Do not use abusive language during communication
- Beware of fake information
- Be careful and responsible which making any comment
- Do not connect with unknowns
- Keep accounts secured with strong password and update regularly
- Do not meet online, no matter how genuine someone is appearing online.
Data Protection
- Security and control on data stored digitally to avoid any inconvenience, harm, loss, embarrassment and unfairness to an individual.
- Each country has its own data protection law to ensure right protection of data from any changes or breach.
Protection measures of data
- Strong data encryption
- do not share sensitive and personal information
- check your data status regularly
- share information on social media carefully and responsibly and avoid oversharing
- ensure proper security measures for your system
- avoid opening unknown and unauthenticated mails
- avoid unexpected verification calls
- take data backups regularly
- take digital breaks occasionally
Intellectual Property Rights
- Intellectual property refers to the products developed by a person or organization by his own intelligence and idea such as any literary works, inventions, artwork, research, software, information etc.
- Intellectual Property Rights stipulates that the creator has full rights over an intellectual property and can protect it.
- IPR also enables the creator or copyright owner to earn recognition or financial benefit by using their creation or invention.
- Intellectual Property is legally protected through
- Copyrights
- Patents
- Trademarks
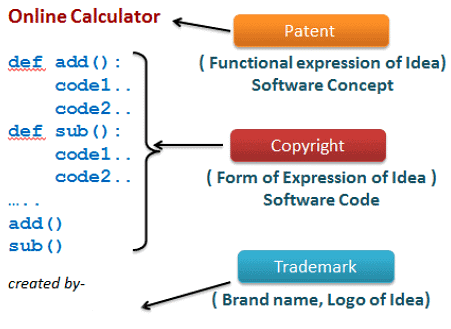
Copyright
- It protects form of expression of Idea.
- It protects any original literary, artistic, dramatic, musical, creative work.
- Copyright lasts for 60 years.
- It is automatically granted to creator or authors.
Patent
- It protects functional expression of Idea.
- It protects inventions
- It is applied in Industries, Machines, Processes, manufactures etc.
- It is registered right, which means one need to legally register and get patent from govt agencies.
Trademark
- A trademark is a word, symbol, design, label or phrase that identifies specific product and distinguish it from similar products.
- It should be unique
IPR Violations
It may happen in following ways:
- Plagiarism
- Copyright Infringement
- Trademark Infringement
Plagiarism
- Copying or stealing Intellectual properties without giving credit to its creator or owner.
- Presenting someone else’s idea or work as one’s own idea or work
- Using someone else’s work without giving credit to him/her
- providing incorrect source of information
- using someone else’s work wrongly intended originally something else
- modifying someone else’s work without attributing to creator
How to avoid Plagiarism
- Give credit to creator or owner of intellectual property being used.
- Preset quote of others as it is.
- Paraphrase quotes
- Create own Intellectual properties.
Copyright Infringement
Unauthorized use of copyright protected property without the permission of copyright holder. for example
- using copyright images in your document
- using someone’s song as background in your work
- download movie from unauthorized source
- record TV program and distributing with others
Trademark Infringement
- Unauthorized use of Trademark of others in any product or service.
Licensing
- Legal contract or agreement between user and creator permitting to use original creation with limitations
- License provide rules and guidelines for others to use the existing work
- user can get license of copyrighted material by paying some price
Software Licensing
- Legal contract or agreement between user and software developer permitting to use and distribute software
- It’s a legal text document defines that outlines
- responsibilities of parties to use software with imposed restrictions
- end user rights such as installation, warranties etc
- protection of developer’s intellectual property
- it ensures source code availability to user or not
Open Source Software
Common Features
- Provides authority to use, distribute, code modification
- Provide source code that can rebuild new version of software
- encourage developers to improve the design, performance of software so that whole community benefited.
- Public licenses (GNU GPL and CC) also referred as open source license allows users to contribute to existing project without seeking permission from anyone.
GNU General Public License
- GNU GPL is free software license, which provides end users the freedom to run, study, share and modify the software, besides getting regular updates.
- Agencies who distribute GPL license may or may not charge a fee for copies.
- It forces to provide Source code with the software being licensed.
Creative Common
- Creative Common is non-profit organization provides public CC license free of charge.
- CC license is governed by Copyright law.
- CC is used for all kind of creative works like websites, music, film, literature, etc. CC enables the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work.
- There are six different Creative Commons licenses: CC BY, CC BY-SA, CC BY-NC, CC BY-ND, CC BY-NC-SA, CC BY-NC-ND.
- CC BY is the most open license.
Cyber Crime
- Any Criminal offence involves the use of computer, Internet ,communication System or digital technology in any which ways.
- Cyber crime can be categorized in two ways
- Crime that targets computer or technology. For exp – Hacking, Phishing, Virus, DoS etc.
- Crime that uses computer or technology. for exp – Identity theft, Cyber bullying, Illegal downloads, Spamming etc.
Types of Cyber Crime
- Hacking
- Phishing
- Identity theft
- Cyber Bullying
- Cyber Stacking
- Illegal Download
- Dos Attack
- Online Scam
- Plagiarism
- Spamming
Hacking
- Gaining unauthorized and illegal access of any computer information system with the intention of stealing or damaging that information system.
- Hacking with positive intent is called ethical hacking
- Ethical hackers are also known as White hat hackers
- Hackers practice hacking with negative intentions (Non-ethical) are known as Black hat hackers.
Preventing Hacking
- Install Antivirus in System
- Update System regularly
- Use Secure Wi-Fi
- Keep strong password for accounts and change it frequently
- Avoid clicking and opening unknown and suspicious mails
- Must use authorized software and applications
- Do safe browsing
Phishing
- The illegal process of obtaining sensitive information of a user by impersonating as a legitimate entity is called phishing.
- Phishing is carried out using emails, text messages or phone calls. most commonly email is involved in such illegal activities
- Phishing is practiced to get
- User Credentials
- Social ID
- Bank Details
- Debit/Credit card details
- Personal Info
Prevent Phishing
- Ignore unknown and suspicious mail
- Do not open Unwanted and unknown attachments
- Do not click on suspicious links
- use anti phishing toolbar
- check email timings
Identity Theft
Stealing personal information such as Bank details, Voter ID, email ID, Passport, PAN etc of a person illegally by criminals and misuse it in various illegal and criminal activities.
Identity Theft are of following types-
- Financial Identity Theft
- Medical Identity Theft
- Criminal Identity Theft
Preventing Cyber Crime
- Install Antivirus in System
- Update System regularly
- Use Secure Wi-Fi
- Keep strong password for accounts and change it frequently
- Avoid clicking and opening unknown and suspicious mails
- Must use authorized software and applications
- Do safe browsing
- Do not open Unwanted and unknown attachments
- Do not click on suspicious links
- use anti phishing toolbar
- Do not share your personal info with anyone
- do not browse untrusted websites
- ignore cookies of unknown sites
- do online transaction with secured and authentic websites
Indian IT Act
- In India Cyber Law is implemented through Information Technology Act 2000 (IT Act 2000).
- Indian IT Act is related to cyber crime and e-commerce that provide legal infrastructure For e-commerce in India. It came into force in October 27, 2009 onwards.
- Following are some amendment of IT ACT included
- Digital Signature
- Electronic Governance
- Offences and Penalties
E-Waste
- E-waste is all about Electronic waste that includes all electrical and electronic gadgets and components that are n longer of use
- Globally, e-waste constitutes more than 5 percent of the municipal solid waste.
- Electronic waste generally contains deadly elements like cadmium, beryllium, mercury etc.
E-Waste Hazard
- Our Environment
- Acidification of soil
- Air pollution
- ground water pollution
- landfills with lead and heavy metals
- Our Health
- Lung Cancer
- Asthma
- Damage of heart, kidney
- Break central nervous system
- DNA damage
E-Waste Management
The most popular way to manage e-waste is RRR that is
- Reduce- Try to reduce the consumption of electronic and electrical gadgets as much as possible. Purchase only when needed
- Reuse – it refers to reusing electronic goods instead of throwing it. donate or resell to someone willing to use it
- Recycle – Recycling is the process of conversion of electronic devices into something that can be used again and again in some or the other manner
|
20 videos|20 docs|5 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|
















