Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Biology for Grade 10 > Diffusion
Diffusion | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Some Examples of Diffusion in Biological Systems |

|
| Mixing Particles |

|
| The Rate of Diffusion |

|
| Diffusion, Surface Area and Volume |

|
| Solved Example |

|
Introduction
Particles (molecules and ions) in a liquid and a gas move continuously. Because of this movement, particles will spread themselves evenly throughout a liquid or a gas.
If there is a situation where particles of a substance are in a higher concentration, they will move from this region to where they are in a lower concentration. This is called diffusion.
It is important to remember that the particles:
- will move in both directions, but there will be a net movement from high to low concentration
- will end up evenly spread throughout the liquid or gas, but will continue to move
Some Examples of Diffusion in Biological Systems
Some substances move into and out of living cells by diffusion.
In a leaf
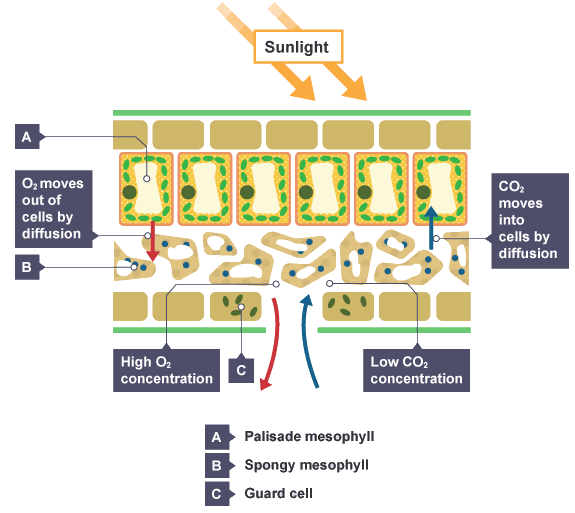
In the lungs
Liver cells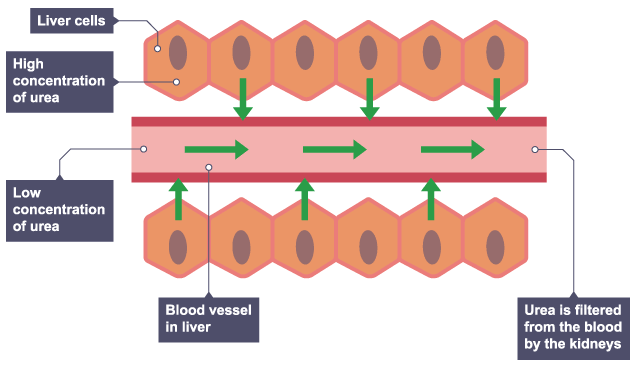
Mixing Particles
If a crystal of a coloured chemical, eg potassium manganate (VII), is placed in water, the particles spread out and mix with the water particles.
- The potassium manganate (VII) is the solute.
- The water is the solvent.
- The potassium manganate (VII) has dissolved.
- The mixture that results is the solution.

The particles have moved from a region of high concentration in the crystal to a low concentration in the water. This difference in concentration is called a concentration gradient. Particles will move down a concentration gradient, from a high concentration to a low concentration.
As well as diffusion occurring between different regions, it also occurs across membranes, between the outside and inside of cells.
The Rate of Diffusion
The rate of diffusion can be affected by a number of factors:
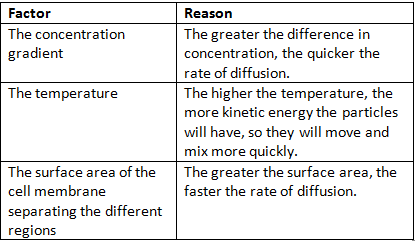
Diffusion, Surface Area and Volume
- For a bacterium, substances diffuse into and out of the bacterial cell across its surface. Once inside, because of the bacterium's size, substances will need to diffuse 1 μm or less to where they are needed, for instance for respiration.
- For simple multicellularorganisms, such as small plants like mosses, substances diffuse into the leaves and roots over their surface. Again, once inside the plant, they don’t need to move far.
- Substances move into and around the moss plants by diffusion and osmosis.
- Simple organisms take in substances over their body surface. Their needs are determined by their volume. As organisms increase in size, their surface area does not increase at the same rate as their volume. For example, the surface area to volume ratio of a puppy is several times greater than that of an adult dog.
Solved Example
Example: Suggest why puppies are more at risk of losing body heat than adult dogs.
Dogs lose heat over their body surface.
Puppies have a larger surface area to volume ratio than adult dogs, so will lose heat more readily.
The document Diffusion | Biology for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Biology for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















