GATE Life Science Syllabus 2024 PDF Download
Syllabus Of GATE Exam 2024 For Life Sciences (XL)
The syllabus for GATE 2024 Life Sciences (XL) is divided into three sections. The first section is General Aptitude (GA), while the second section, marked as segment P, covers Chemistry and is mandatory for all students. The third section, segments Q to U, comprises Biochemistry (XL-Q), Botany (XL-R), Microbiology (XL-S), Zoology (XL-T), and Food Technology (XL-U), from which applicants must choose any two in addition to the GA segment. Therefore, the Life Sciences (XL) syllabus includes a total of six segments, with Chemistry being the first (P) and the remaining five (Q to U) covering Biochemistry, Botany, Microbiology, Zoology, and Food Technology, from which candidates must select two.
Subjects With Code:
- XL-P – Chemistry
- XL-Q – Biochemistry
- XL-R – Botany
- XL-S – Microbiology
- XL-T – Zoology
- XL-U – Food Technology
GATE 2024 XL-P Chemistry Syllabus (Compulsory)
Section 1: Atomic Structure and Periodicity
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity covers topics such as Planck’s quantum theory, wave-particle duality, uncertainty principle, electronic configuration of atoms and ions, and periodic properties like ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity and atomic size.
Section 2: Structure and Bonding
- Structure and Bonding includes Ionic and covalent bonding, VSEPR theory, hybridization, resonance, dipole moment, structure parameters, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals interactions, among other concepts.
Section 3: s, p and d Block Elements
- s, p and d Block Elements involves oxides, halides, and hydrides of alkali and alkaline earth metals, B, Al, Si, N, P, and S, coordination complexes, and their properties like color, geometry, magnetic properties, and isomerism.
Section 4: Chemical Equilibria
- Chemical Equilibria encompasses concepts like ionic equilibria, solubility product, common ion effect, hydrolysis of salts, pH, buffer and their applications, and equilibrium constants.
Section 5: Electrochemistry
- Electrochemistry includes conductance, Kohlrausch law, cell potentials, EMF, Nernst equation, thermodynamic aspects, and their applications.
Section 6: Reaction Kinetics
- Reaction Kinetics covers topics like rate constant, order of reaction, molecularity, activation energy, and elementary enzyme reactions like reversible and irreversible inhibition.
Section 7: Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics involves qualitative treatment of state and path functions, First and Second laws, internal energy, enthalpy, Kirchoff equation, heat of reaction, Hess’s law, heat of formation, entropy, and free energy.
Section 8: Structure-Reactivity Correlations and Organic Reaction Mechanisms
- Structure-Reactivity Correlations and Organic Reaction Mechanisms includes acids and bases, electronic and steric effects, Stereochemistry, optical and geometrical isomerism, and organic reaction mechanisms like SN1, SN2, E1, E2, radical reactions, addition reactions, and Markownikoff rule.
Section 9: Chemistry of Biomolecules
- Chemistry of Biomolecules covers topics like amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids and nucleotides, carbohydrate, lipids, and principles of biomolecule purification. Also, identification of these biomolecules and Beer-Lambert’s law.
GATE 2024 XL-Q Biochemistry Syllabus
- In Section 1, you will learn about the organization of life, the importance of water, and the structure and function of biomolecules such as amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. You will also study the structure, folding, and function of proteins like myoglobin, hemoglobin, lysozyme, ribonuclease A, carboxypeptidase, and chymotrypsin.
- Section 2 covers enzyme kinetics, including regulation and inhibition, as well as vitamins and coenzymes. You will study metabolism and bioenergetics, the generation and utilization of ATP, and the regulation of metabolic pathways such as glycolysis, the TCA cycle, the pentose phosphate pathway, oxidative phosphorylation, gluconeogenesis, glycogen and fatty acid metabolism. You will also learn about the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds such as nitrogen fixation, amino acids, and nucleotides, as well as the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis.
- In Section 3, you will learn about biochemical separation techniques such as ion exchange, size exclusion, and affinity chromatography. You will also study the characterization of biomolecules using electrophoresis, UV-visible and fluorescence spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry.
- Section 4 covers cell structure and organelles, biological membranes, the action potential, transport across membranes, membrane assembly and protein targeting, signal transduction, receptor-ligand interaction, hormones, and neurotransmitters.
- Section 5 covers DNA replication, transcription, and translation, as well as biochemical regulation of gene expression. You will also learn about recombinant DNA technology and its applications, including PCR, site-directed mutagenesis, DNA microarrays, and next-generation sequencing. Finally, you will study gene silencing and editing.
- In Section 6, you will study the immune system, including innate and adaptive immunity, cells of the immune system, active and passive immunity, the complement system, antibody structure, function, and diversity, B cell and T cell receptors, B cell and T cell activation, the major histocompatibility complex, and immunological techniques such as immuno-diffusion, immune-electrophoresis, RIA and ELISA, flow cytometry, and monoclonal antibodies and their applications.
GATE 2024 XL-R Botany Syllabus
- In the first section, the topics covered include plant systematics, which covers botanical nomenclature, the history of plant taxonomy, diversity and classification of plants, and the APG system of plant classification. Other topics include phylogenetics and cladistics, molecular taxonomy and DNA barcoding, and centers for plant taxonomy and herbaria in India.
- The second section focuses on plant anatomy, covering the anatomy of the root, stem, leaves, floral organs, and young seedlings. It also covers primary and secondary meristems, stellar organization, vascular system and their ontogeny, xylem and phloem structure, secondary growth in plants and wood anatomy, and plant cell structure and differences from animal cells.
- The third section delves into plant development, including topics such as the life cycle of an angiosperm, development of male and female gametophytes, cell fate determination and tissue patterning, embryogenesis, organization and function of shoot and root apical meristems, and the transition to flowering. Other topics covered include Xylem and phloem cell differentiation, photomorphogenesis, and the role of auxin, cytokinin, gibberellins, and brassinosteroids on plant development.
- In the fourth section, plant physiology and biochemistry are discussed, including plant water relations, mechanisms of uptake and transport of water, ions, and solutes from soil to plants, stomatal movements, nitrogen metabolism, photosynthesis, respiration, and plant responses to abiotic stresses. The section also covers the structure and function of biomolecules, enzymes, and major plant secondary metabolites such as alkaloids, terpenes, phenylpropanoids, and flavonoids.
- The fifth section covers genetics and genomics, including the cell cycle and cell division, principles of Mendelian inheritance, genetic mapping, epigenetics, gene silencing, gene expression, gene mutation and repair, and chromosomal aberrations. Other topics covered include model organisms for functional genetics and genomics and an introduction to transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics.
- The sixth section covers plant breeding, genetic modification, and genome editing, including principles and methods of selection, hybridization, male sterility, genetic maps, molecular markers, plant tissue culture, somaclonal variation, marker-assisted selection, gene transfer methods, and genome editing techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9 and the Cre-Lox system.
- The seventh section covers economically and medicinally important plants, including cereals, pulses, fibers, timber, sugar, beverages, oils, rubber, pigments, dyes, gums, drugs, and narcotics. Other topics covered include the economic importance of algae, fungi, lichen, and bacteria, major Indian cash crops, and the effect of industrialization on agricultural botany.
- The eighth section covers plant pathology, including the nature and classification of plant diseases, diseases of important crops caused by fungi, bacteria, nematodes, and viruses, their control measures, and the mechanism of pathogenesis and resistance. The section also covers molecular detection of pathogens, plant-microbe interactions, signaling pathways in plant defense response, and host-parasitic plant interaction.
- The final section covers ecology and the environment, including ecosystems, biogeochemical cycles, ecological succession, food webs, energy flow, vegetation types of the world and India, climate, flora endemism, pollution and global climate change, speciation and extinction, biodiversity and conservation strategies, ecological hotspots, afforestation, habitat restoration, and plant interactions with other organisms such as epiphytes, parasites, and endophytes.
GATE 2024 XL-S Microbiology Syllabus
- Section 1: A Historical Overview of Microbiology – The Discovery of the Microbial World; Key Discoveries Relevant to Microbiology; The Debate Over Spontaneous Generation; The Role of Microorganisms in Organic Matter Transformation and Disease Causation.
- Section 2: Microbiological Methods – Techniques for Pure Culturing; Principles of Microbial Nutrition; Enrichment Culturing for Microbial Isolation; Antigen and Antibody Detection for Microbial Diagnosis; Microscopy Techniques such as Light, Phase Contrast, Fluorescence, and Electron Microscopy; PCR and Real-Time PCR for Microbial Quantitation; Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies for Microbiology.
- Section 3: Microbial Taxonomy and Diversity – Broad Classifications of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotic Microbes such as Yeasts, Molds, and Protozoa; Virus Classification; Molecular Approaches to Microbial Taxonomy and Phylogeny.
- Section 4: Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function – Cell Walls, Cell Membranes and Biosynthesis, Solute Transport Mechanisms, Flagella and Pili, Capsules, Cell Inclusions like Endospores and Gas Vesicles, Bacterial Locomotion including Positive and Negative Chemotaxis.
- Section 5: Microbial Growth – Growth Definition, Growth Curve, Exponential Growth Phase Mathematical Expression, Growth and Growth Yields Measurement, Synchronous Growth, Continuous Culture, Environmental Factors' Effects on Growth, Bacterial Biofilm, and Biofouling.
- Section 6: Microbial Control – Disinfection and Sterilization Principles, Methods, and Efficacy Assessment.
- Section 7: Microbial Metabolism – Redox Reactions and Electron Carriers Energetics, Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation, Glycolysis, Pentose-Phosphate Pathway, Entner-Doudoroff Pathway, Glyoxalate Pathway, Citric Acid Cycle, Fermentation, Aerobic, and Anaerobic Respiration, Chemolithotrophy, Photosynthesis, Calvin Cycle, Biosynthetic Pathway for Fatty Acids Synthesis, Major Metabolic Pathways Regulation.
- Section 8: Microbial Diseases and Host-Pathogen Interaction – Normal Microbiota, Classification of Infectious Diseases, Reservoirs of Infection, Nosocomial Infection, Opportunistic Infections, Emerging Infectious Diseases, Mechanisms of Microbial Pathogenicity, Host's Nonspecific Defense, Antigens and Antibodies, Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity, Vaccines, Passive Immunization, Immune Deficiency, Human Diseases caused by Viruses, Bacteria, and Pathogenic Fungi.
- Section 9: Chemotherapy/Antibiotics – Antimicrobial Drug General Characteristics, Antibiotics Classification, Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Resistance, Antifungal, and Antiviral Drugs.
- Section 10: Microbial Genetics – Mutation Types, UV, and Chemical Mutagens, Selection of Mutants, Ames Test for Mutagenesis, Bacterial Genetic System, DNA Repair, Gene Expression Regulation such as Repression and Induction, Operon Model, E. coli's Bacterial Genome, Phage λ and its Life Cycle, RNA, Virus Genome Mutation, Virus Recombination and Reassortment, Basic Concepts of Microbial Genomics.
- Section 11: Microbial Ecology – Microbial Interactions, Carbon, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Cycles, Soil Microorganisms associated with Vascular Plants, Bioremediation, Uncultivable Microorganisms, Basic Concepts of Metagenomics and Metatranscriptomics.
GATE 2024 XL-T Zoology Syllabus
- Section 1: Animal Diversity – This section covers the distribution, systematics, and classification of animals, as well as their phylogenetic relationships. It uses classical and molecular phylogenetic tools to explore these topics.
- Section 2: Evolution – This section covers the origin and history of life on earth, including theories of evolution, natural selection, adaptation, and speciation.
- Section 3: Genetics – This section covers the basic principles of inheritance, the molecular basis of heredity, sex determination and sex-linked characteristics, cytoplasmic inheritance, linkage, recombination and mapping of genes in eukaryotes, population genetics, genetic disorders, and the roles of model organisms in understanding genetic principles.
- Section 4: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology – This section covers nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates; replication, transcription, and translation; the Krebs cycle; glycolysis; enzyme catalysis; hormones and their actions; and the roles of vitamins and minerals.
- Section 5: Cell Biology – This section covers the basic principles of cellular microscopy, the structure of cells, cytoskeletal organization, cellular organelles and their structure and function, the cell cycle, cell division, and chromosome and chromatin structure.
- Section 6: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes – This section covers eukaryotic genome organization and regulation of gene expression, as well as transposable elements.
- Section 7: Animal Anatomy and Physiology – This section covers comparative physiology, the respiratory system, muscular system, circulatory system, digestive system, nervous system, excretory system, endocrine system, reproductive system, and skeletal system.
- Section 8: Parasitology and Immunology – This section covers the nature of parasites, host-parasite relationships, protozoan and helminthic parasites, and the immune response, including cellular and humoral immune responses.
- Section 9: Developmental Biology – This section covers gametogenesis, embryonic development, cellular differentiation, organogenesis, metamorphosis, model organisms used in developmental biology, the genetic and molecular basis of development, and stem cells.
- Section 10: Ecology – This section covers the ecosystem, animal distribution, ecological niche and its contribution to ecological diversity, the food chain, population dynamics, species diversity, zoogeography, biogeochemical cycles, conservation biology, and ecotoxicology.
- Section 11: Animal Behavior – This section covers the types of behaviors seen in animals, including courtship, mating, and territoriality; instinct, learning, and memory; social behavior across animal taxa; communication, pheromones; and the evolution of behavior in animals.
GATE 2024 XL-U Food Technology Syllabus
- Section 1 focuses on Food Chemistry and Nutrition, covering topics such as carbohydrates (including mono-, oligo-, & poly-saccharides such as starch, cellulose, pectic substances, and dietary fiber), proteins (classification and structure of proteins in food), lipids (classification and structure, rancidity, polymerization, and polymorphism), pigments (carotenoids, chlorophylls, anthocyanins, tannins, and myoglobin), food flavors (terpenes, esters, aldehydes, ketones, and quinones), enzymes (specificity, simple and inhibition kinetics, coenzymes, enzymatic and non-enzymatic browning), nutrition (balanced diet, essential amino acids and essential fatty acids, protein efficiency ratio, water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins, role of minerals in nutrition, co-factors, anti-nutrients, nutraceuticals, nutrient deficiency diseases), and chemical and biochemical changes that occur in foods during processing.
- Section 2 focuses on Food Microbiology, covering characteristics of microorganisms (morphology of bacteria, yeast, mold and actinomycetes, spores, and vegetative cells, gram-staining), microbial growth (growth and death kinetics, serial dilution technique), food spoilage (spoilage microorganisms in different food products including milk, fish, meat, egg, cereals and their products), toxins from microbes (pathogens and non-pathogens including Staphylococcus, Salmonella, Shebelle, Escherichia, Bacillus, Clostridium, and Aspergillums genera), and fermented foods and beverages (curd, yoghurt, cheese, pickles, soya-sauce, sauerkraut, idly, dose, vinegar, alcoholic beverages and sausage).
- Section 3 focuses on Food Products Technology, covering processing principles (thermal processing, chilling, freezing, dehydration, addition of preservatives and food additives, irradiation, fermentation, hurdle technology, intermediate moisture foods), food packaging and storage (packaging materials, aseptic packaging, controlled and modified atmosphere storage), cereal processing and products (milling of rice, wheat, and maize, parboiling of paddy, bread, biscuits, extruded products, and ready-to-eat breakfast cereals), oil processing (expelling, solvent extraction, refining, and hydrogenation), fruits and vegetables processing (extraction, clarification, concentration, and packaging of fruit juice, jam, jelly, marmalade, squash, candies, tomato sauce, ketchup, and puree, potato chips, pickles), plantation crops processing and products (tea, coffee, cocoa, spice, extraction of essential oils, and oleoresins from spices), milk and milk products processing (pasteurization and sterilization, cream, butter, ghee, ice-cream, cheese, and milk powder), processing of animal products (drying, canning, and freezing of fish and meat, production of egg powder), waste utilization (pectin from fruit wastes, uses of by-products from rice milling), and food standards and quality maintenance (FPO, PFA, A-Mark, ISI, HACCP, food plant sanitation, and cleaning in place (CIP)).
- Section 4 focuses on Food Engineering, covering mass and energy balance, momentum transfer (flow rate and pressure drop relationships for Newtonian fluids flowing through pipe, Reynolds number), heat transfer (heat transfer by conduction, convection, radiation, heat exchangers), mass transfer (molecular diffusion and Flick’s law, conduction and convective mass transfer, permeability through single and multilayer films), mechanical operations (size reduction of solids, high pressure homogen.
It is recommended that individuals who plan to take the Gate exam in 2024 refer to the GATE Life Sciences Syllabus 2024 pdf and download it from the provided links for each subject. This will enable them to prepare adequately for the exam.
GATE 2024 Life Sciences Exam Pattern
To ensure success in the GATE exam, it is important for candidates to not only be familiar with the GATE XL syllabus 2024, but also the marking system, mode of exam, and exam pattern. For the convenience of applicants, we have created a table that they can refer to.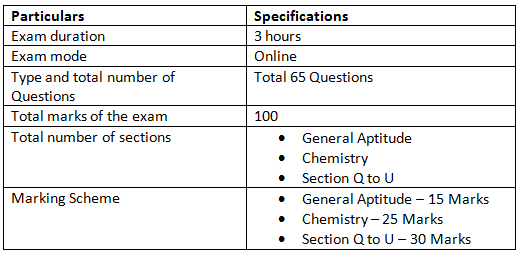
GATE Life Sciences Exam Paper Marking Scheme
- Total marks: 100 marks
- Negative Marking: For MCQs only

FAQs on GATE Life Science Syllabus 2024
| 1. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-P Chemistry? |  |
| 2. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-Q Biochemistry? |  |
| 3. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-R Botany? |  |
| 4. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-S Microbiology? |  |
| 5. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-T Zoology? |  |
| 6. What is the syllabus for GATE 2024 XL-U Food Technology? |  |




















