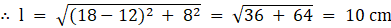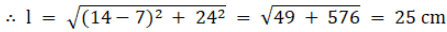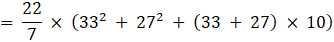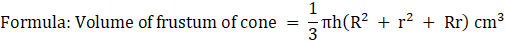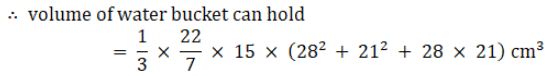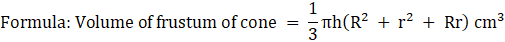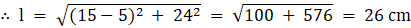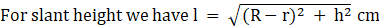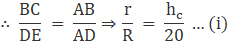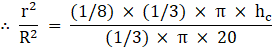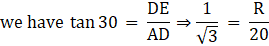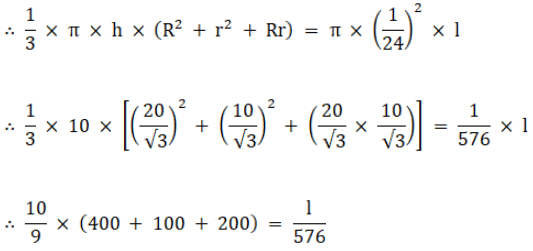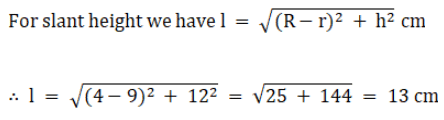RS Aggarwal Solutions: Volume and Surface Area of Solids- 3 | RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics PDF Download
Exercise: 19c
Q.1. A drinking glass is in the shape of a frustum of a cone of height 14 cm. The diameter of its two circular ends are 16 cm and 12 cm. Find the capacity of the glass.
Given: Height of glass = h = 14 cm
Diameter of lower circular end of glass = 12 cm
Diameter of upper circular end of glass = 16 cm
∴ Radius of lower circular end = r = 12/2 = 6 cm
∴ Radius of lower circular end = R = 16/2 = 8 cm
= 44 × 49.33 cm3
= 2170.52 cm3
∴ Capacity of glass = 2170.52 cm3
Q.2. The radii of the circular ends of a solid frustum of a cone are 18 cm and 12 cm and its height is 8 cm. Find its total surface area. [Use π = 3.14.]
Given: Radius of lower circular end = r = 12 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 18 cm
Height of frustum = h = 8 cm
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
For slant height we have
∴ l = 10 cm
∴ total surface area of frustum = π × 122 + π × 182 + π × (18 + 12) × 10 cm2
= 3.14 × (144 + 324 + 300) cm2
= 3.14 × 768 cm2
= 2411.52 cm2
∴ total surface area of frustum = 2411.52 cm2
Q.3. A metallic bucket, open at the top, of height 24 cm is in the form of the frustum of a cone, the radii of whose lower and upper circular ends are 7 cm and 14 cm respectively. Find
(i) the volume of water which can completely fill the bucket;
(ii) the area of the metal sheet used to make the bucket.
Given: Height of bucket = h = 24 cm
Radius of lower circular end = r = 7 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 14 cm
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
∴ l = 25 cm
(i) volume of water which will completely fill the bucket = volume of frustum
= 8 × 22 × 49
= 8722 cm3
∴ volume of water which will completely fill the bucket = 8722 cm3
(ii) area of metal sheet used
Since the top is open we need to subtract the area of top/upper circle from total surface area of frustum because we don’t require a metal plate for top.
Radius of top/upper circle = R
Area of upper circle = πR2
∴ area of metal sheet used = (total surface area of frustum)-πR2
∴ Area of metal sheet used = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l-πR2cm2
= πr2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= 22 × 82 cm2
= 1804 cm2
∴ Area of metal sheet used to make bucket = 1804 cm2
Q.4. A container, open the top, is in the form of a frustum of a cone of height 24 cm with radii of its lower and upper circular ends as 8 cm and 20 cm respectively. Find the cost of milk which can completely fill the container at the rate of Rs 24 per litre.
Given: height of frustum container = h = 24 cm
Radius of lower circular end = r = 8 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 20 cm
Cost of 1 litre milk = 24 Rs
Volume of milk completely fill the container = volume of frustum of cone
= 8 × 3.14 × (400 + 64 + 160) cm3
= 8 × 3.14 × 624 cm3
= 15674.88 cm3
Now, 1 litre is 1000 cm3
∴ 15674.88 cm3 = 15674.88/1000 = 15.67488 litres
∴ Cost of milk which can completely fill the container = 15.67488 × cost of 1 litre milk
= 15.67488 × 24 Rs
= 376.19712 Rs
∴ Cost of milk which can completely fill the container = 376.19712 Rs
Q.5. A container, open at the top and made up of metal sheet, is in the form of a frustum of a cone of height 16 cm with diameters of its lower and upper ends as 16 cm and 14 cm respectively. Find the cost of metal sheet used to make the container, if it costs Rs 10 per 100 cm2.
Given: height of container frustum = h = 16 cm
Diameter of lower circular end = 16 cm
Diameter of upper circular end = 14 cm
∴ Radius of lower circular end = r = 16/2 = 8 cm
∴ Radius of upper circular end = R = 14/2 = 7 cm
Cost of 100 cm2 metal sheet = 10 Rs
∴ Cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet = 10/100 = 0.1 Rs
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
∴ l = 16.0312 cm
Since the top is open we need to subtract the area of top/upper circle from total surface area of frustum because we don’t require a metal plate for top.
Radius of top/upper circle = R
Area of upper circle = πR2
∴ area of metal sheet used = (total surface area of frustum)-πR2
= πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l- πR2 cm2
= πr2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= π × (82 + (7 + 8)16.0312) cm2
= 3.14 × 304.468 cm2
= 956.029 cm2
∴ 956.029 cm2 metal sheet is required to make the container.
∴ Cost of 956.029 cm2 metal sheet = 956.029 × cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet
= 956.029 × 0.1 Rs
= 95.6029 Rs
∴ Cost of metal sheet required to make container = 95.6029 Rs
Q.6. The radii of the circular ends of a solid frustum of a cone are 33 cm and 27 cm, and its slant height is 10 cm. Find its capacity and total surface area. [Take π = 22/7.]
Given: Radius of lower circular end = r = 27 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 33 cm
Slant height = l = 10cm
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Here h height of frustum is not given and we need h to find the volume of frustum therefore we must first calculate the value of h as follows
using formula for slant height and with the help of given data we get
Squaring both sides
∴ 100 = 36 + h2
∴ h2 = 64
∴ h = ±8
As length cannot be negative
∴ h = 8 cm
= 22 × 8 × 129
= 22704 cm3
∴ capacity = volume of frustum = 22704 cm3
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= (22/7) × (1089 + 729 + 600)
= (22/7) × 2418
= 7599.428 cm2
∴ total surface area = 7599.428 cm2
Q.7. A bucket is in the form of a frustum of a cone. Its depts. Is 15 cm and the diameters of the top and the bottom are 56 cm and 42 cm respectively. Find how many litres of water the bucket can hold. [Take π = 22/7.]
Given: Depth of the bucket = height of frustum = h = 15 cm
Diameter of top of bucket = 56 cm
Diameter of bottom of bucket = 42 cm
∴ Radius of top = R = 56/2 = 28 cm
∴ Radius of bottom = r = 42/2 = 21 cm
Volume of water bucket can hold = volume of bucket which is in form of frustum
= (22/7) × 5 × (784 + 441 + 588) cm3
= (22/7) × 5 × 1813 cm3
= 22 × 5 × 259 cm3
= 28490 cm3
Now 1 litre = 1000 cm3
∴ 28490 cm3 = 28490/1000 litres
= 28.49 litres
∴ bucket can hold 28.49 litres of water.
Q.8. A bucket made up of a metal sheet is in the form of frustum of a cone of height 16 cm with radii of its lower and upper ends as 8 cm and 20 cm respectively. Find the cost of the bucket if the cost of metal sheet used is Rs 15 per 100 cm2. [Use π = 3.14.]
Given: height of container frustum = h = 16 cm
Radius of lower circular end = r = 8 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 20 cm
Cost of 100 cm2 metal sheet = 15 Rs
∴ Cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet = 15/100 = 0.15 Rs
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
∴ l = 20 cm
Since it is given that a bucket is to be made hence the top is open we need to subtract the area of top/upper circle from total surface area of frustum because we don’t require a metal plate for top.
Radius of top/upper circle = R
Area of upper circle = πR2
∴ area of metal sheet used = (total surface area of frustum)-πR2
= πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l- πR2 cm2
= πr2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= π × (82 + (20 + 8)20) cm2
= 3.14 × 624 cm2
= 1959.36 cm2
∴ 1959.36 cm2 metal sheet is required to make the container.
∴ Cost of 1959.36 cm2 metal sheet = 1959.36 × cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet
= 1959.36 × 0.15 Rs
= 293.904 Rs
∴ Cost of metal sheet required to make container = 293.904 Rs.
Q.9. A bucket made up of a metal sheet is in the form of frustum of a cone. Its depth is 24 cm and the diameters of the top and bottom are 30 cm and 10 cm respectively. Find the cost of milk which can completely fill the bucket at the rate of Rs 20 per litre and the cost of metal sheet used if it costs Rs 10 per 100 cm2. [Use π = 3.14.]
Given: depth of bucket = height of bucket/frustum = h = 24 cm
Diameter of lower circular end = 10 cm
Diameter of upper circular end = 30 cm
∴ Radius of lower circular end = r = 10/2 = 5 cm
∴ Radius of lower circular end = R = 30/2 = 15 cm
Cost of 100 cm2 metal sheet = 10 Rs
∴ Cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet = 10/100 = 0.1 Rs
Cost of 1 litre milk = 20 Rs
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
∴ l = 26 cm
Since the top is open we need to subtract the area of top/upper circle from total surface area of frustum because we don’t require a metal plate for top.
Radius of top/upper circle = R
Area of upper circle = πR2
∴ area of metal sheet used = (total surface area of frustum)-πR2
= πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l- πR2 cm2
= πr2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= π × (52 + (15 + 5)26) cm2
= 3.14 × 545 cm2
= 1711.3 cm2
∴ 1711.3 cm2 metal sheet is required to make the container.
∴ Cost of 1711.3 cm2 metal sheet = 1711.3 × cost of 1 cm2 metal sheet
= 1711.3 × 0.1 Rs
= 171.13 Rs
∴ Cost of metal sheet required to make container = 171.13 Rs
Now,
Volume of milk which can completely fill the bucket = volume of frustum
= (1/3) × 3.14 × 26 × 325 cm3
= 26533/3 cm3
= 8844.33 cm3
Now 1 litre = 1000 cm3
∴ 8844.33 cm3 = 8844.33/1000 litres
= 8.84433 litres
∴ Volume of milk which can completely fill the bucket = 8.84433 litres
∴ Cost of milk which can completely fill the bucket = volume of milk which can completely
fill the bucket × cost of 1 litre milk Rs
= 8.84433 × 20 Rs
= 176.8866 Rs
Cost of milk which can completely fill the bucket = 176.8866 Rs
Q.10. A container in the shape of a frustum of a cone having diameters of its two circular faces as 35 cm and 30 cm and vertical height 14 cm, is completely filled with oil. If each cm3 of oil has mass 1.2g, then find the cost of oil in the container if it costs Rs 40 per kg.
Given: height of container/frustum = h = 14 cm
Diameter of top of container = 35 cm
Diameter of bottom of container = 30 cm
∴ Radius of top = R = 35/2 = 17.5 cm
∴ Radius of bottom = r = 30/2 = 15 cm
1 cm3 of oil = 1.2g of oil
Cost of 1 kg oil = 40 Rs
Volume of oil in container = volume of container which is in form of frustum
= (22/3) × 2 × (306.25 + 225 + 262.5) cm3
= (22/3) × 2 × 793.75 cm3
= 34925/3 cm3
= 11641.667 cm3
∴ Volume of oil in container = 11641.667 cm3
∴ 11641.667 cm3 of oil = 11641.667 × 1.2 g
= 13970.0004 g
We know 1000 g = 1 kg
∴ 13970.0004 g = 13970.0004/1000 kg
= 13.970 kg
∴ Cost of 13.970 kg oil = 13.970 × cost of 1 kg oil Rs
= 13.970 × 40 Rs
= 558.8 Rs
∴ Cost of oil in container = 558.8 Rs
Q.11. A bucket is in the form of a frustum of a cone and its can hold 28.49 litres of water. If the radii of its circular ends are 28 cm and 21 cm, find the height of the bucket.
Given: volume of bucket = 28.49 litres
1 litre = 1000 cm3
∴ 28.49 litres = 28.49 × 1000 cm3
∴ Volume of bucket = 28490 cm3
Radius of upper circular end = R = 28 cm
Radius of lower circular end = r = 21 cm
Let ‘h’ be the height of the bucket
Volume of bucket = volume of frustum of cone
∴ 28490 × 21 = h × 22 × (784 + 441 + 588)
∴ h = 598290/39886 cm
∴ h = 15 cm
∴ Height of bucket = h = 15 cm
Q.12. The radii of the circular ends of a bucket of height 15 cm are 14 cm and r cm (r < 14). If the volume of the bucket is 5390 cm3, find the value of r.
Given: volume of bucket = 5390 cm3
Radius of upper circular end = R = 14 cm
Radius of lower circular end = r cm & r is less than 14
Height of bucket = h = 15
Volume of bucket = volume of frustum of cone
∴ 5390 × 7 = 22 × 5 × (196 + r2 + 14r)
∴ 37730/110 = 196 + r2 + 14r
∴ 343 = 196 + r2 + 14r
∴ r2 + 14r-147 = 0
∴ r2 + 21r-7r-147 = 0
∴ r(r + 21)-7(r + 21) = 0
∴ (r-7)(r + 21) = 0
∴ r = 7 or r = -21
Since we require r<14 ∴ r = 7 cm
Q.13. The radii of the circular ends of a solid frustum of a cone are 33 cm and 27 cm and its slant height is 10 cm. Find its total surface area. [Use π = 3.14.]
Given: Radius of lower circular end = r = 27 cm
Radius of upper circular end = R = 33 cm
Slant height = l = 10cm
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
= 3.14 × (332 + 272 + (33 + 27) × 10) cm2
= 3.14 × (1089 + 729 + 600) cm2
= 3.14 × 2418 cm2
= 7592.52 cm2
∴ total surface area = 7592.52 cm2
Q.14. A tent is made in the form of a frustum of a cone surmounted by another cone. The diameter of the base and the top of the frustum are 20 m and 6 m respectively, and the height is 24 m. If the height of the tent is 28 m and the radius of the conical part is equal to the radius of the top of the frustum, find the quantity of canvas required. [Take π = 22/7.]
Given: Diameter of base of frustum = 20 m
Diameter of top of frustum = 6 m
∴ Radius of base = R = 20/2 = 10 m
∴ Radius of top = r = 6/2 = 3 m
Height of frustum = hf = 24 m
Height of tent = ht = 28 m
∴ height of cone = hc = ht -hf = 28-24 = 4 m
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)lf m2
Total surface area of cone = πrlc
Where lf = slant height of frustum & lc = slant height of cone
∴ lf = 25 m
For slant height of cone consider right angled ΔABC from figure
AB = hc = 4 m ; BC = r = 3 m ; AC = lc
By pythagoras theorm
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
∴ 42 + 32 = lc2
∴ lc = ±5
Since length cannot be negative lc = 5 m
Since for tent we don’t require the upper circle of frustum and the lower circle of frustum hence we should subtract their area as we don’t require canvas for that.
Surface area of upper circle = πr2
Surface area of lower circle = πR2
∴ Surface area of frustum for which canvas is required = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)lf - πr2-πR2cm2
= π(R + r)lfm2
= (22/7) × (10 + 3) × 25 m2
= (22/7) × 325 m2
= 1021.4285 m2
Surface area of cone = πrlc m2
= (22/7) × 3 × 5 m2
= (22/7) × 15 m2
= 47.1428 m2
∴ Quantity of canvas required = surface area of frustum + surface area of cone
= 1021.4285 + 47.1428 m2
= 1068.5713 m2
∴ Quantity of canvas required = 1068.5713 m2
Q.15. A tent consists of a frustum of a cone, surmounted by a cone. If the diameter of the upper and lower circular ends of the frustum be 14 m and 26 m respectively, the height of the frustum be 8 m and the height of the surmounted conical portion be 12 m, find the area of the canvas required to make the tent. (Assume that the radii of the upper circular end of the frustum and the base of the surmounted conical portion are equal.)
Given: Diameter of base of frustum = 26 m
Diameter of top of frustum = 14 m
∴ Radius of base = R = 26/2 = 13 m
∴ Radius of top = r = 14/2 = 7 m
Height of frustum = hf = 8 m
∴ height of cone = hc = 12 m
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)lf m2
Total surface area of cone = πrlc
Where lf = slant height of frustum & lc = slant height of cone
∴ lf = 10 m
Consider right angled ΔABC from figure
AB = hc = 12 m ; BC = r = 7 m ; AC = lc
By pythagoras theorm
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
∴ 122 + 72 = lc2
∴ lc = ±13.892
Since length cannot be negative lc = 13.892 m
Since for tent we don’t require the upper circle of frustum and the lower circle of frustum hence we should subtract their area as we don’t require canvas for that.
Surface area of upper circle = πr2
Surface area of lower circle = πR2
∴ Surface area of frustum for which canvas is required = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)lf - πr2-πR2cm2
= π(R + r)lfm2
= 3.14 × (13 + 7) × 10 m2
= 3.14 × 200 m2
= 628 m2
Surface area of cone = πrlc m2
= 3.14 × 7 × 13.892 m2
= 3.14 × 97.244 m2
= 305.346 m2
∴ Quantity of canvas required = surface area of frustum + surface area of cone
= 628 + 305.346 m2
= 933.346 m2
∴ Quantity of canvas required = 933.346 m2
Q.16. The perimeters of the two circular ends of a frustum of a cone are 48 cm and 36 cm. If the height of the frustum is 11 cm. find its volume and curved surface area.
Given: perimeter of upper circle = 36 cm
Perimeter of lower circle = 48 cm
Height of frustum = h = 11 cm
Let r: radius of upper circle & R: radius of lower circle
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
Now perimeter of circle = circumference of circle = 2π × radius
∴ Perimeter of upper circle = 2πr
∴ 36 = 2 × 3.14 × r
∴ r = 36/6.28 cm
∴ r = 5.732 cm
∴ Perimeter of lower circle = 2πR
∴ 48 = 2 × 3.14 × R
∴ R = 48/6.28 cm
∴ R = 7.643 cm
∴ l = 11.164 cm
∴ Volume of frustum = (1/3) × 3.14 × 11 × (7.6432 + 5.7322 + 7.643 × 5.732) cm3
= (1/3) × 34.54 × (58.415 + 32.855 + 43.809) cm3
= 11.513 × 135.079 cm3
= 1555.164 cm3
∴ Volume of frustum = 1555.164 cm3
Now we have asked curved surface area so we should subtract the top and bottom surface areas which are flat circles.
Surface area of top = πr2
Surface area of bottom = πR2
∴ Curved surface area = total surface area - πr2 - πR2 cm2
= πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l - πr2 - πR2 cm2
= π(R + r)l cm2
= 3.14 × (7.643 + 5.732) × 11.164 cm2
= 3.14 × 13.375 × 11.164 cm2
= 468.86 cm2
∴ curved surface area = 468.86 cm2
Q.17. A solid cone of base radius 10 cm is cut into two parts through the midpoint of its height, by a plane parallel to its base. Find the ratio of the volumes of the two parts of the cone.
Let ‘H’ be the height of cone ‘R’ be the radius of base of cone.
R = 10 cm
When the cone is cut at midpoint of H by a plane parallel to its base we get a cone of height H/2 and a frustum also of height H/2
Let the radius of the base of the cone which we got after cutting and the radius of upper circle of frustum be ‘r’ as shown in figure
From figure consider ΔABC and ΔADE
∠ABC = ∠ADE = 90˚
∠BAC = ∠DAE …(common angle)
as two angles are equal by AA criteria we can say that
ΔABC∼ΔADE
∴ r = 5 cm
Let Vc be volume of the cone and Vf be the volume of frustum
Volume of cone = (1/3)π(radius)2(height) cm3
∴ Vc = (1/3) × π × r2 × (H/2) cm3
= (1/3) × π × 52 × (H/2) cm3
= (1/3) × π × 25 × (H/2) cm3
Volume of frustum = (1/3)πh(R2 + r2 + Rr) cm3
∴ Vf = (1/3) × π × (H/2)(102 + 52 + 10 × 5) cm3
= (1/3) × π × (H/2) × 175 cm3
∴ The ratio of volumes of two parts after cutting = Vc:Vf = 1:7
Q.18. The height of a right circular cone is 20 cm. A small cone is cut off at the top by a plane parallel to the base. If its volume be 1/8 of the volume of the given cone, at what height above the base is the section made?
Let the cutting plane be passing through points B and C as shown
Height of cone = AD = H = 20 cm
Height of small cone which we get after cutting = AB = hc
Let ‘r’ be the radius of small cone ∴ we have BC = r
‘R’ be radius of original cone which is to be cut ∴ we have DE = R
From figure consider ΔABC and ΔADE
∠ABC = ∠ADE = 90˚
∠BAC = ∠DAE …(common angle)
as two angles are equal by AA criteria we can say that
ΔABC∼ΔADE
Let V1 be the volume of cone to be cut
Let V2 be the volume of small cone which we get after cutting
Volume of cone = (1/3)π(radius)2(height) cm3
∴ V1 = (1/3) × π × R2 × hc
∴ V2 = (1/3) × π × r2 × 20
Given is that the volume of small cone is (1/8) times the original cone
∴ V2 = (1/8) V1
∴ (1/3) × π × r2 × 20 = (1/8) × (1/3) × π × R2 × hc
Using equation (i) we get
∴ hc3 = 203/8 cm
∴ hc = 20/2 cm
∴ hc = 10 cm
But we have to find the height from base i.e. we have to find BD from figure
∴ 20 = BD + hc
∴ 20 = BD + 10
∴ BD = 10 cm
∴ 10 cm above base the section is made.
Q.19. A solid metallic right circular cone 20 cm high and whose vertical angle is 60˚, is cut into two parts at the middle of its height by a plane parallel to its base. If the frustum so obtained be drawn into a wire of diameter 1/12cm, find the length of the wire.
Let ‘R’ be the radius of the base of the cone which is also the base of frustum i.e. lower circular end as shown in the figure
DE = R
Let ‘r’ be the radius of the upper circular end of frustum which we get after cutting the cone
BC = r
The height of the cone is 20 cm and we had cut the cone at midpoint therefore height of the frustum so obtained is 10 cm
Vertical angle as shown in the figure is 60˚
Now a wire of diameter 1/12 (i.e. radius 1/24) is made out of the frustum let ‘l’ be the length of the wire
As we are using the full frustum to make wire therefore volumes of both the frustum and the wire must be equal.
∴ Volume of frustum = volume of wire made …(i)
Consider ΔABC
∠BAC = 30˚ ; AB = 10 cm ; BC = r
∴ r = 10/√3 cm
Consider ΔADE
∠DAE = 30˚ ; AD = 20 cm ; DE = R
∴ R = 20/√3 cm
Now using equation (i)
∴ 7000/9 = l/576
∴ 777.778 = l/576
∴ l = 448000 cmLength of wire = 448000 cm
Q.20. A fez, the cap used by the Turks, is shaped like the frustum of a cone. If its radius on the open side is 10 cm, radius at the upper base is 4 cm and its slant height is 15 cm, find the area of material used for making it. [Use π = 22/7.]
Given: Radius of lower circular end = R = 10 cm
Radius of upper circular end = r = 4 cm
Slant height = l = 15cm
Formula: Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
As the lower circular end is open we need to subtract the area of lower circular end from total surface area since we don’t require material for lower circular end it should be open so that it is wearable.
∴ Total surface area = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l- πR2 cm2
= (22/7) × (42 + (10 + 4) × 15) cm2
= (22/7) × (16 + 210) cm2
= 22 × 226/7 cm2
= 710.285 cm2
∴ total surface area = 710.285 cm2
∴ Area of material used = 710.285 cm2
Q.21. An oil funnel made of tin sheet consist of a 10 cm long cylindrical portion attached to a frustum of a cone. If the total height is 22 cm, diameter of the cylindrical portion is 8 cm and the diameter of the top of the funnel is 18 cm, find the area of the tin sheet required to make the funnel.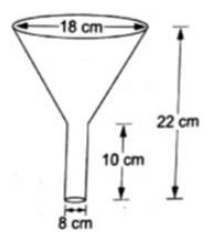
Divide the funnel into two parts frustum and cylinder as shown in the figure
Parameters of frustum:
Diameter of upper circular end = 18 cm
∴ Radius of upper circular end = r = 18/2 = 9 cm
The radius of cylinder is equal to the radius of lower circular end of frustum
∴ radius of lower circular end = R = 4 cm
Height of frustum = total height – height of cylinder
= 22 – 10
= 12 cm
∴ height of frustum = h = 12 cm
Total surface area of frustum = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l cm2
Where l = slant height
∴ l = 13 cm
Since for the frustum part of the funnel we don’t require the upper circular end and the lower circular end hence we need to subtract those areas from total surface area.
Area of upper circular end = πr2
Area of lower circular end = πR2
total surface area = πr2 + πR2 + π(R + r)l- πr2- πR2
= π(R + r)l
= 3.14 × (9 + 4) × 13
= 530.66 cm2
∴ total surface area of frustum for which tin is required = 530.66 cm2
Parameters of cylinder:
Height of cylinder = 10 cm
Radius of cylinder = 4 cm
∴ Area of tin require to make cylinder = 2π × (radius) × (height)
= 2 × 3.14 × 4 × 10
= 251.2 cm2
∴ Area of tin required to make the funnel = area of frustum for which tin is required + area of tin require to make cylinder
∴ area of tin required to make funnel = 530.66 + 251.2
= 781.86 cm2
∴ Area of tin sheet require to make the funnel = 781.86 cm2
|
53 docs|15 tests
|
|
53 docs|15 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|