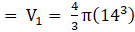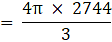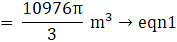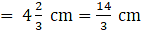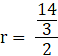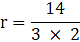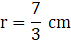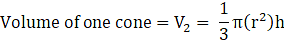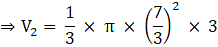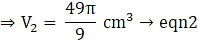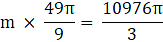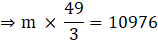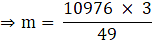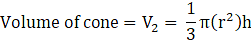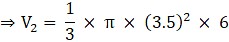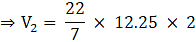RS Aggarwal Solutions: Volume and Surface Area of Solids- 4 | RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics PDF Download
Exercise: 19d
Q.1. A river 1.5 m deep and 36 m wide is flowing at the rate of 3.5 km/hr. Find the amount of water (in cubic metres) that runs into the sea per minute.
Given,
Depth of the river = 1.5 m
Width of the river = 36 m
Flow rate of river = 3.5 km/hr
Now first change the rate of flow of the water in meter/min
As we know,
1 km = 1000 m
1 hour = 60 minutes
So,
River travel in a minute = 350/6 mNow,
The amount of water that runs into sea per minute;
350/6 × 1.5 × 36 = 350 × 1.5 × 6 = 3150
So,
The amount of water that runs into the sea per minute is 3150 m3
Q.2. The volume of a cube is 729 cm3. Find its surface area.
Given,
Volume of the cube = 729 cm3
Let the edge of the cube = a cm
So,
Volume (v) of the cube = a3
a3 = 729
a3 = (9cm)3
a = 9 cm
Lateral surface area of cube = 4a2
= 4 × 92
= 4 × 81
= 324cm2
Total surface area of the cube = 6a2
= 6 × 92
= 6 × 81
= 486 cm2
Q.3. How many cubes of 10 cm edge can be put in a cubical box of 1 m edge?
Given,
Edge of the Cubical Box = 1 m
Volume of the Cubical Box = a3
Edge of the cubes = 10 cm
Volume of the cube = a3
Number of Cubes = Volume of box/volume of the cube
= 100 × 100 × 100/10 × 10 × 10
= 1000000/1000
= 1000 cubes
Q.4. Three cubes of iron whose edges are 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm respectively are melted and formed into a single cube. Find the edge of the new cube formed.
Given,
Edge of the first cube = 6 cm
Volume of the first cube = a3 = (6)3 cm
Edge of the second cube = 8 cm
Volume of the second cube = a3 = (8)3 cm
Edge of the third cube = 10 cm
Volume of the third cube = a3 = (10)3 cm
So,
Volume of the formed cube = Volume of the First + Second + Third Cube
Volume of the formed cube = v1 + v2 + v3= 63 + 83 + 103
= 216 + 512 + 1000
= 1728
Now volume of new cube = a3= 1728
Edge of new cube = a = ∛1728
a = 12
Therefore surface area of new cube = 6a2
= 6 × 122
= 6 × 12 × 12
= 864 cm2
Q.5. Five identical cubes, each of edge 5 cm, are placed adjacent to each other. Find the volume of the resulting cuboid.
Given,
Edge of the given Cube = 5 cm
Now,
Length (l) of the resulting cuboid = Edge × Number of cubes
= 5 x 5 = 25 cm
Breadth (b) of the resulting cuboid = 5 cm
Height (h) of the resulting cuboid = 5 cm
So,
Volume of the resulting cuboid = l × b × h
= 25 x 5 x 5
= 625 cm3
Hence,
The volume of the resulting cube is 625 cm3.
Q.6. The volumes of two cubes are in the ratio 8:27. Find the ratio of their surface areas.
Given,
Ratio of two cube = 8:27
Let the edges of the cubes to x and y
As,
Now,
The ratio of the surface areas of the cubes
⇒ 6x2/6y2
= (x/y)2
= (2/3)2 ….. [Using (i)]
= 4/9
= 4 : 9
So,
The ratio of the surface areas of the given cubes is 4 : 9.
Q.7. The volume of a right circular cylinder with its height equal to the radius is 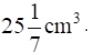 Find the height of the cylinder.
Find the height of the cylinder.
Given,
Radius of the right circular cylinder = 176/7 cm3
Height of the right circular cylinder = Radius of the right circular cylinder
So,
⇒ h = r
As,
Volume of the right circular Cylinder = 176/7 cm3
⇒ πr2h = 176/7
⇒ 22/7 × h2 × h=176/7
⇒ h3 =176 × 7/7 × 22
⇒ h3 = 8
⇒ h = 3√8
Therefore,
h = 2 cm
So,
The height of the right circular cylinder is 2 cm.
Q.8. The ratio between the radius of the base and the height of a cylinder is 2:3. If the volume of the cylinder is 12936 cm3. Find the radius of the base of the cylinder.
Given,
Ratio of the base and the height of a cylinder is 2:3
So,
Let the radius of the base = r
And
The height of the cylinder = h
r : h = 2 : 3
That is,
r/h = 2/3
So,
h = 3r/2 – – – – – – – – – (i)
As,
Volume of the cylinder = 12936 cm3
⇒ πr2h=12936
⇒ 22/7 × r2 × 3r/2=12936 [Using (i)]
⇒ 33/7 × r3=12936
⇒ r3 = 12936 × 7/33
⇒ r3 = 2744
⇒ r = 3√2744
Therefore,
r = 14 cm
So,
The radius of the base of the cylinder is 14 cm.
Q.9. The radii of two cylinder are in the ratio of 2:3 and their height are in the ratio of 5:3. Find the ratio of their volumes.
Let the radus of the first cylinder = r1
And the radus of the second cylinder = r2;
Let the height of first cylinder = h1
And the height of second cylinder = h2
Given,
r1 : r2 = 2 : 3
r1/r2 = 23 ….. (i)
And
h1 : h2 = 5 : 3
h1/h2 = 5/3 … (ii)
Now,
The ratio of the volumes of the cylinders =… [Using (i) and (ii)]
= 20/27
= 20 : 27
So,
The ratio of the volumes of the given cylinders is 20 : 27
Q.10. 66 cubic cm of silver is drawn into a wire 1 mm in diameter. Calculate the length of the wire in metres.
Given,
Volume of the wire = 66 cm3
Diameter of the wire = 1 mm
Radius (r) of wire = 12 = 0.5 mm = 0.05 cm
Let the length of the wire be l
As,
Volume of the wire = 66 cm3
⇒ πr2l = 66
⇒ 227 × 0.05 × 0.05 × l = 66
⇒ l = 66 × 722 × 0.05 × 0.05
Therefore,
l = 8400 cm = 84 m
So,
The length of the wire is 84 m.
Q.11. If the area of the base of a right circular cone is 3850 cm2 and its height is 84 cm, find the slant height of the cone.
Given,
Area of the base of the right circular cone = 3850 cm2
Height of the right circular cone = 84 cm
Let the radius of the cone = r
And the slant height of the cone = l
As,
Area of the base of the cone = 3850 cm2
⇒ πr2 = 3850
⇒ 227 × r2 = 3850
⇒ r2 = 3850 × 722
⇒ r2 = 1225
⇒ r = √1225
Therefore,
r = 35 cm
Now,
length = √h2 + r2
= √(84)2 + (35)2
= √7056 + 1225
= √8281
= 91 cm
So,
The slant height of the given cone is 91 cm.
Q.12. A cylinder with base radius 8 cm and height 2 cm is melted to form a cone of height 6 cm. Calculate the radius of the base of the cone.
Given,
Base radius (r) of the cylinder = 8 cm
Height (h) of the cylinder = 2 cm and
Height (H) of the cone = 6 cm
Let the base radius of the cone = R
Now,
As the cylinder is melted to form the cone,
So,
Volume of the cone = Volume of the cylinder
⇒ 1/3πR2H = πr2h
⇒ R2 = 3r2hH
⇒ R2=3 × 8 × 8 × 26
⇒ R2 = 64
⇒ R = √64
Therefore,
R = 8 cm
So,
The radius of the base of the cone is 8 cm.
Q.13. A right cylindrical vessel is full of water. How many right cones having the same radius and height as those of the right cylinder will be needed to store that water?
Let suppose the radius of the cone = r
And height of the cone = h,
Then,
Radius of the cylindrical vessel = r and
Height of the cylindrical vessel = h
Now,
The required number of cones = Volume of the cylindrical vessel/Volume of a cone
= πr2h/(1/3πr2h)
= 3
So,
The number of the cones that is required to store the water is 3.
Q.14. The volume of a sphere is 4851 cm3. Find its curved surface area.
The volume of the sphere = 4851 cm3
Let the radius of the sphere = r
As,
Volume of the sphere = 4851 cm3
⇒ 4/3πr3 = 4851
⇒ r3 = 92618
⇒ r = 3√92618
⇒ r = 212cm
Now,
The Curved surface area of the sphere = 4πr2
= 4 × 22/7 × 21/2 × 21/2
= 1386 cm2
So,
The curved surface area of the sphere is 1386 cm2.
Q.15. The curved surface area of a sphere is 5544 cm3. Find its volume.
Given,
Curved surface area of the sphere = 5544 cm3
Let the radius of the sphere = r
As we know,
Curved surface area of the sphere = 4πr2
So,
⇒ 4πr2 = 5544
⇒ r2 = 441
⇒ r = √441
⇒ r = 21 cm
Now,
Volume of the sphere = 4/3πr3
= 4/3 × 22/7 × 21 × 21 × 21
= 38808 cm3
So,
The volume of the sphere is 38808 cm3.
Q.16. The surface areas of two sphere are in the ratio of 4:25. Find the ratio of their volumes.
Let suppose the radius of first spheres = r
And the radius of second spheres = R
As per the question,
Surface area of the first sphere /Surface area of the second sphere = 4/25
⇒ 4πr2/4πR2 = 4/25
⇒ (r/R)2 = 4/25
⇒ r/R = √4/25
⇒ r/R = 2/5 …………………(i)
Now,
= (r/R)3
= (2/5)3 …[Using (i)]
= 8/125
= 8 : 125
So,
The ratio of the volumes of the given spheres will be 8 : 125
Q.17. A solid metallic sphere of radius 8 cm is melted and into spherical balls each of radius 2 cm. Find the number of spherical balls obtained.
Given,
Radius (R) of the solid metallic sphere = 8 cm
Radius (r) of the spherical ball = 2 cm
Now,
The number of spherical balls obtained =
= (R/r)3
= (8/2)3
= 43
= 64
So,
The number of spherical balls obtained is 64.
Q.18. How many lead shots each 3 mm in diameter can be made from a cuboid of dimensions 9 cm × 12 cm?
Given,
Diameter of the lead shot = 3 mm
Radius (r) of a lead shot = 3/2 = 1.5 mm = 0.15 cm and
Dimensions of the cuboid = 9 cm x 11 cm x 12 cm
Now,
The number of the lead shots =
= 84000
So,
84000 number of lead shots can be made from the cuboid.
Q.19. A metallic cone of radius 12 cm and height 24 cm is melted and made into spheres of radius 2cm each. How many sphere are formed?
Cone:
Radius = 12cm
Height = 24 cm.
Sphere, radius = 2cm
Volume of cone is given as,
⇒
⇒ V = 3620 cm3
Volume of sphere ,
⇒
⇒ V = 33.52 cm3
∴ the number of squares formed will be: 3620/34 = 106.
Q.20. A hemisphere of lead of radius 6 cm is cast into a right circular cone of height 75 cm. Find the radius of the base of the cone.
Given,
Radius (R) of the hemisphere = 6 cm
Height (h) of the cone = 75 cm
Let the radius of the base of the cone = r
Now,
Volume of the cone = Volume of the hemisphere
⇒
⇒ r2 = 5.76
⇒ r = √5.76
Therefore,
r = 2.4 cm
So,
The radius of the base of the cone is 2.4 cm.
Q.21. A copper sphere of diameter 18 cm is drawn into wire of diameter 4 mm. Find the length of the wire.
The basic concept required to solve any such question is that the volume of the two figures will be same, so here we will equate the volume of sphere to that of wire which is in shape of a cylinder and subsequently will find out the height of the cylinder.
Given diameter of copper sphere = D = 18 cm
∴ Radius of the sphere = R = d/2=18/2 = 9 cm
As we know the wire is cylindrical in shape so,
Let the height of the cylindrical wire be ‘h’ cm
Given diameter of cylindrical wire = d = 4 mm
⇒ Radius of the cylindrical wire = r = d/2= 4/2= 2 mm= 0.2 cm (∵ 1 mm = 0.1 cm)
Volume of a sphere=(where R=radius of sphere)→eqn1
(putting value of R in eqn 1)
⇒ Volume of sphere = 4π × 243= 972π cm3→eqn2
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
Where r = radius of base of cylinder and h = height of cylinder
⇒ Volume of cylindrical wire = π × (0.2)2 × h (putting value of r)
= 0.04π × h cm3→eqn3
Now on equating equation 2 and equation 3, we get,
Volume of sphere = Volume of cylindrical wire
⇒ 972π = 0.04πh
⇒ π(927) = π(0.04h) (taking π common on both sides)
⇒ 927 = 0.04h
∴ h = 24300 cm
The height of cylindrical wire is 24300 cm or 243 m.
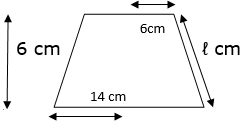
Q.22. The radii of the circular ends of a frustum of height 6 cm are 14 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the slant height of the frustum.
Given height of frustum = h =6 cm
Radius of top = r = 6 cm
Radius of bottom = R = 14 cm
Let the slant height of the frustum be ‘ℓ’ cm
We know in frustum
(Slant height)2 = (height)2 + (R – r)2→eqn1
⇒ ℓ2 = 62 + (14 – 6)2 (putting values of r, R and h in eqn1)
⇒ ℓ2 = 36 + 82
⇒ ℓ2 = 36 + 64
⇒ ℓ2 = 100
⇒ ℓ = √100
∴ ℓ = 10 cm
Slant height of the frustum is 10 cm.
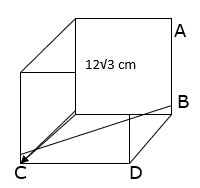
Q.23. Find the ratio of the volume of a cube to that of a sphere which will fit inside it.
Let the radius of the sphere be ‘R’ units
And the cube which will fit inside it be of edge ‘a’ units
Explanation: The longest diagonal of the cube that will fit inside the sphere will be the diameter of the of the sphere.
∴ The longest diagonal of cube = the diameter of the sphere
Consider ΔBCD, ∠BDC = 90°
BD = CD = a units (as they are the edges of cube)
⇒ BC2 = a2 + a2 (putting value of BD and CD)
⇒ BC2 = 2a2
⇒ BC = √(2a2)
∴ BC = a√2 units →eqn1
Now consider ΔABC, ∠ABC = 90°
Here, AB = a units and BC = a√2 units
⇒AC2 = a2 + (a√2)2 (putting values of AB and BC)
⇒ AC2 = a2 + 2a2
⇒AC2 = 3a2
⇒AC = √(3a2)
∴ AC = a√3 units
∴ Diameter of sphere = D = a√3 units
And we know, D = 2 × R
⇒ R = D/2 (put value of D )
Also, Volume of a sphere→eqn2
Put value of R in eqn2
∴ Volume of sphere = πa2 cubic units → eqn3
Volume of cube = (edge)3
∴ Volume of cube = a3 cubic units →eqn4
Ratio of volume of cube to that of sphere(putting values from eqn3 and eqn4)
⇒Ratio of volume of cube to that of sphere
Ratio of volume of cube to that of sphere is a:π
Q.24. Find the ratio of the volumes of a cylinder, a cone and a sphere, if each has the same diameter and same height?
Let the radius of cylinder, cone and sphere be ‘r’ cm
Let the diameter of cylinder, sphere and cone be ‘2r’ units
∴ Height of cylinder, cone, sphere = h = 2r units
Volume of cylinder = π(r2)h
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × r2 × 2r (putting value of h)
∴ Volume of cylinder = 2π × r3→eqn1
Volume of sphere
Volume of cone(put the value of h)
⇒ Volume of cone
∴ Volume of cone
Ratio of volume of cylinder to that of a cone to that of a sphere as:
⇒ Volume of cylinder : Volume of Cone : Volume of sphere(dividing the above relation by (πr3)
(dividing the above ratio by 2)
⇒3 : 1 : 2 (multiplying the above ratio by 3)
Ratio of volume of cylinder to that of cone to that of sphere is 3 : 1 : 2
Q.25. Two cubes each of volume 125 cm3 are joined end to form a solid. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
Given volume of each cube = 125 cm3
Let the edge of each cube be ‘a’ cm
So, Volume of cube = a3
⇒ a3 = 125
⇒ a = ∛(125)
∴ a = 5 cm →eqn1
Now when we join the two cubes then resulting cuboid will be of length twice that of the cube and breadth and height of the resulting cuboid will be same as that of the cube
⇒ length of cuboid = L = 2 × a
⇒ L = 2 × 5 (putting value of a from eqn1)
∴ L = 10 cm
Now, Breadth of cuboid = B = a
⇒ B = 5 cm
Similarly, height of the cuboid = H = 5 cm
Note: Where ever in a question Surface Area is mentioned, it means Total surface area.
Surface area = Total surface area = 2(LB + BH + HL)
⇒ S.A = 2((10 × 5) + (5 × 5) + (10 × 5))
⇒ S.A = 2(50 + 25 + 50)
⇒ S.A = 2 × 125
∴ S.A = 250 cm2
Surface Area of resulting cuboid is 250 cm2.
Q.26. Three metallic cubes whose edges are 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm, are melted and recast into a single large cube. Find the edge of the new cube formed.
Let the edges of cubes be a1, a2 and a3
So, a1 = 3 cm, a2 = 4 cm, and a3 = 5 cm
Explanation: Here the sum of volumes of all three cubes will be equal to the volume of the resulting larger cube as the resulting cube is formed by melting the three cubes.
Volume of cube with edge a1 = v1 = (a1)3
⇒ v1 = (3)3
∴ v1 = 27 cm3→eqn1
Similarly
Volume of cube with edge a2 = v2 = (a2)3
⇒v2 = (4)3
∴ v2 = 64 cm3→eqn2
Volume of cube with edge a3 = v3 = (a3)3
⇒ v3 = (5)3
∴ v3 = 125 cm3→eqn3
Now let the volume of resulting cube be ‘V’ cm3
So, V = v1 + v2 + v3
⇒ V = 27 + 64 + 125 (from eqn1, eqn2 and eqn3)
∴ V = 216 cm3→eqn4
Let the edge of resulting cube be ‘a’ cm
So, volume of the resulting cube = V = a3→eqn5
Equate equation 4 and 5,
⇒ a3 = 216
⇒ a = ∛(216)
∴ a = 6 cm
The edge of new cube formed is 6 cm.
Q.27. A solid metallic sphere of diameter 8 cm is melted and drawn into a cylindrical wire of uniform width. If the length of the wire is 12 m, find its width.
Let the diameter of sphere be ‘D’ and Radius of sphere be ‘R’
∴ D = 8 m
Also, we know
R = D/2
⇒ R = 8/2
∴ R = 4 m
Explanation: Here the volume of sphere will be equal to the volume of the resulting cylinder as the resulting cylinder is formed by melting the sphere.
Volume of the sphere, V1
Let the length/height of the cylinder be ‘H’ and let the radius of the cylinder be ‘r’ and volume of the cylinder be ‘V2’
∴ H = 12 m
Volume of the cylinder = V2 = π(r2)H
⇒ V2 = π(r2) × 12 (putting value of H)
⇒ V2 = 12π × r2 m3→eqn2
Now equate equation 1 and 2,
⇒ V2 = V1
∴ r = 2.66 m
Width of cylinder = diameter of cylinder = 2 × radius
⇒ Width of cylinder = 2 × r
⇒ Width of cylinder = 2 × 2.66
∴ Width of cylinder = 5.32 m
Width of the resulting cylinder is 5.32 m.
Q.28. A 5-m-wide cloth is used to make a conical tent of base diameter 14 m and height 24 m. Find the cost of cloth used, at the rate of Rs 25 per metre.
Let the length of the cloth used be ‘L’ cm
Area of cloth used = 5 × L →eqn1
Also, Given Diameter = d = 14 m and height = h = 24 m
∴ Radius = r = D/2
⇒ r = 14/2
∴ r = 7 m
Let the slant height of the cone be ℓ m
So, (Slant height)2 = (Height)2 + (Radius)2
Put the values in the above relation
⇒ ℓ2 = h2 + r2
⇒ ℓ2 = 242 + 72
⇒ ℓ2 = 576 + 49
⇒ ℓ2 = 625
⇒ ℓ = √(625)
∴ ℓ = 25 cm →eqn1
Also, we know Curved Surface Area of cone = πrℓ
Where r = radius of base, ℓ = slant height
C.S.A = π × 7 × 25
⇒ C.S.A = 22 × 25
⇒ C.S.A = 550 m2→eqn2
Now the Curved surface area of conical tent will be equal to the area of the cloth used to make the tent
⇒ C.S.A = Area of cloth
⇒ 550 = 5 × L (from eqn1 and eqn2)
∴ L = 110 m
So, cost of the cloth used = rate of cloth × Length of the cloth
⇒ Cost of cloth used = 25 × 110
⇒ Cost of cloth = Rs.2750
Cost of the cloth used is Rs. 2750.
Q.29. A wooden toy was made by scooping out a hemisphere of same radius from each end of a solid cylinder. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the volume of wood in the toy.
Given height of cylinder = h = 10 cm
Radius of cylinder = r = 3.5 cm
Radius of hemisphere = R = 3.5 cm
Explanation: In this question the volume of wood in toy can be calculated by subtracting the volume of two hemisphere from the volume of cylinder.
So, volume of cylinder = πr2h
Where r = radius of cylinder and h = height of cylinder
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × (3.5)2 × 10 (from given values)
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × 12.25 × 10
∴ Volume of cylinder = 122.5π cm3→eqn1
Volume of a hemisphere(where R is radius of hemisphere)
∴ Volume of two hemisphere
Volume of wood in toy = eqn1 – eqn2
⇒Volume of wood in toy(taking π common)
∴ Volume of wood in toy = 205.333 cm3
Volume of wood in toy is 205.333 cm3.
Q.30. Three cubes of a metal whose edge are in the ratio 3:4:5 are melted and converted into a single cube whose diagonal is 12 √3 cm. Find the edges of the three cubes.
Let the edges of metal cubes be a1, a2 and a3
And it is given that ratio of edges is 3:4:5
So, let a1 = 3x, a2 = 4x and a3 = 5x
Volume of cube with edge a1 = v1 = (a1)3
⇒ v1 = (3x)3
∴ v1 = 27x3 cm3→ eqn1
Similarly
Volume of cube with edge a2 = v2 = (a2)3
⇒ v2 = (4x)3
∴ v2 = 64x3 cm3→eqn2
Volume of cube with edge a3 = v3 = (a3)3
⇒ v3 = (5x)3
∴ v3 = 125x3 cm3→eqn3
Now let the volume of resulting cube be ‘V’ cm3
So, V = v1 + v2 + v3
⇒ V = 27x3 + 64x3 + 125x3 (from eqn1, eqn2 and eqn3)
∴ V = 216x3 cm3→eqn4
It is given that the diagonal of the resulting cube is 12√3 cm
Let the edge of resulting cube be ‘a’ cm
Consider ΔBCD, ∠BDC = 90°
BD = CD = a cm (as they are the edges of cube)
⇒ BC2 = a2 + a2 (putting value of BD and CD)
⇒ BC2 = 2a2
⇒ BC = √(2a2)
∴ BC = a√2 cm
Now consider ΔABC, ∠ABC = 90°
Here, AB = a cm and BC = a√2 cm and AC = 12√3 cm
⇒ (12√3)2 = a2 + (a√2)2 (putting values of AB, AC and BC)
⇒ 144 × 3 = a2 + 2a2
⇒ 144 × 3 = 3a2
⇒ 144 = a2
⇒ a = √144
∴ a = 12 cm
So, volume of the resulting cube = V = a3
⇒ V = 123 (putting value of a)
∴ V = 1728 cm3 –eqn5
Equate equation 4 and 5
⇒ 216x3 = 1728
⇒ x3 = 1728/216
⇒ x3 = 8
⇒ x = ∛8
∴ x = 2
So a1 = 3x = 3 × 2
⇒ a1 = 6 cm
Similarly a2 = 4x = 4 × 2
∴ a2 = 8 cm
Similarly a3 = 5x = 5 × 2
∴ a3 = 10 cm
The edges of three cubes are 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm.
Q.31. A hollow sphere of external and internal diameter 8 cm and 4 cm respectively is melted into a solid cone of base diameter 8 cm. Find the height of the cone.
External diameter of hollow sphere = D = 8 cm
⇒ External radius of hollow sphere = R = D/2
⇒ R = 8/2
⇒ R = 4 cm
Internal diameter of hollow sphere = d = 4 cm
⇒ Internal radius of hollow sphere = r = d/2
⇒ r = 4/2
⇒ r = 2 cm
Let the height of the resulting cone be ‘h’ cm
Let the volume of External sphere be V1 and that of internal be V2.
Explanation: Here the volume of hollow sphere will be equal to the volume of the resulting cone as the resulting cone is formed by melting the sphere.
Volume of the External sphere=(put the value of R)
Volume of sphere = V = External volume – Internal volume
Given base radius of the resulting cone = r’ = 8 cm
Let the height be ‘h’ and volume of the resulting cone be V’(putting value of r' )
Equate equation 3 and 4,
⇒ V = V’
⇒ 224 = 64h
⇒ h = 224/64
∴ h = 3.5 cm
The height of resulting cone is 3.5 cm.
Q.32. A bucket of height 24 cm is in the form of frustum of a cone whose circular ends are of diameter 28 cm and 42 cm. Find the cost of milk at the rate of Rs 30 per litre, which the bucket can hold.
Upper end radius of frustum = d/2= 28/2 = 14 cm
Lower end radius of frustum = D/2 = 42/2 =21 cm
Height of the frustum = 24 cm
And we know,
The amount of milk that bucket can hold = Volume of the bucket
And, Volume of bucket = Volume of Frustum
∴ Amount of milk that bucket can hold = Volume of frustum
⇒Volume of frustum
Where R = Radius of larger or lower end and r = Radius of smaller or upper end and h = height of frustum π = 22/7
⇒Volume of frustum
= 22 × 8 × 133
∴ Volume of frustum = 23408 cm3
Also we know that 1 litre = 1000 cm3
⇒ Volume of frustum in litre = 23408/1000= 23.408 litre
⇒ Amount of milk that the bucket hold = 23.408 litre
⇒ The cost of milk = Rate of milk × amount of milk bucket holds
⇒ The cost of milk = 30 × 23.408
∴ = Rs. 702.24
The cost of milk is Rs.702.24
Q.33. The interior of a building is in the form of a right circular of diameter 4.2 m and height 4 m surmounted by a cone of same diameter. The height of the cone is 2.8 m. Find the outer surface area of the building.
Here in order to find the outer surface area of building we need to simply add the curved surface areas of cone and cylinder.
Given height of cylinder = h = 4 m
Height of cone = h’ = 2.8 m
Diameter of cylinder = diameter of cone = d = 4.2 m
⇒ Radius of cone = Radius of cylinder = d/2 =4.2m/2 = 2.1 m
Outer surface area of building = C.S.A of cylinder + C.S.A of cone
Now, C.S.A of cylinder = 2πrh →eqn1
Where r = radius of base of cylinder, h = height of cylinder
And C.S.A of cone = πrℓ →eqn2
Where r = radius of base of cone, ℓ = Slant height of cone
We know in a cone
(Slant height)2 = (height)2 + (radius)2 (put the given values)
(ℓ)2 = (2.8)2 + (2.1)2
⇒ (ℓ)2 = 7.84 + 4.41
⇒ (ℓ)2 = 12.25
⇒ ℓ = √(12.25)
∴ ℓ = 3.5 m
Now, C.S.A of cone = π × 2.1 × 3.5 (putting the values in eqn2)
⇒ C.S.A of cone = 7.35π m2→eqn3
C.S.A of cylinder = 2 × π × 2.1 × 4 (putting the values in eqn1)
⇒ C.S.A of cylinder = 2 × π × 4.41 × 4
∴ C.S.A of cylinder = 16.8π m2→eqn4
Outer surface area of building = eqn3 + eqn4
⇒ Outer surface area = 7.35π + 16.8π
= 24.15π
∴ Outer surface area =75.9 m2
The outer surface area of building is 75.9 m2.
Q.34. A metallic solid right circular cone is of height 84 cm and the radius of its base is 21 cm. It is melted and recast into a solid sphere. Find the diameter of the sphere.
Let the Radius of cone be ‘r’ and height of cone be ‘h’
∴ r = 21 cm and h = 84 cm
Explanation: Here the volume of cone will be equal to the volume of the resulting sphere as the resulting sphere is formed by melting the cone.
Volume of cone,
⇒ V1 = π × 441 × 28
∴ V1 = 12348π m3→eqn1
Let the Radius of resulting sphere be ‘R’ cm
Volume of the sphere=
Now equate equation 1 and 2,
⇒ V2 = V1
⇒ R3 = 3087 × 3
⇒ R3 = 9261
⇒ R =∛(9261)
∴ R = 21 cm
Diameter of Sphere = 2 × radius
⇒ Diameter of Sphere = 2 × R = 42 m
Diameter of the resulting Sphere is 42 m.
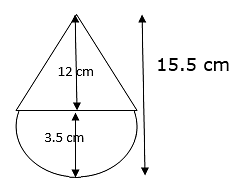
Q.35. A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of same radius. The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
The total surface area of the toy can be calculated by taking the sum of the Curved surface area of cone and that of hemisphere of same radius.
Given total height of toy = H = 15.5 cm
Radius of hemisphere = Radius of cone = r = 3.5 cm
Now the height of cone = h = total height – radius of hemisphere
⇒ Height of cone = h = 15.5 – 3.5
∴ Height of cone = h = 12 cm
Let the slant height of the cone be ‘ℓ’ cm
Also we know that in a cone,
(Slant height)2 = (Height)2 + (Radius)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 122 + 3.52 (putting the values)
⇒ ℓ2 = 144 + 12.25
⇒ ℓ2 = 156.25
⇒ ℓ = √(156.25)
∴ ℓ = 12.5 cm
C.S.A of cone = πrℓ
⇒ C.S.A of cone = π × 3.5 × 12.5 (putting the given values)
∴ C.S.A of cone = 43.75π m2 →eqn1
C.S.A of hemisphere = 2πr2
⇒ C.S.A of hemisphere = 2 × π × 3.52
= 2 × π × 12.25
= 24.5π m2 →eqn2
Now total surface area of toy = eqn1 + eqn2
⇒ Total surface area of toy = 43.75π + 24.5π
= 68.25π
⇒The total surface area of toy(putting π= 22/7)
= 9.75 × 22
= 214.5 m2
The total surface area of the toy is 214.5 m2.
Q.36. If the radii of the circular ends of a bucket 28 cm high, are 28 cm and 7 cm, find its capacity and total surface area.
Here the bucket is in the shape of a frustum. So capacity of bucket will be equal to the volume of the frustum and in order to calculate the total surface area of the bucket we will subtract the top end circular area from the total surface area of the frustum as the bucket is open on top.Upper end radius of frustum/bucket = R = 28 cm
Lower end radius of frustum/bucket =r = 7 cm
Height of the frustum/bucket = 28 cm
And we know,
The capacity of bucket = Volume of the bucket
And, Volume of bucket = Volume of Frustum
∴ Capacity of bucket = Volume of frustum
⇒Volume of frustum
Where R = Radius of larger or upper end and r = Radius of smaller or lower end and h = height of frustum π = 22/7
⇒Volume of frustum
= 22 × 4 × 343
∴ Volume of frustum = 30184 cm3
∴ Capacity of bucket = 30184 cm3
T.S.A of bucket = T.S.A of frustum – Area of upper circle →eqn1
Let the slant height of the frustum be ‘ℓ’ cm
So, ℓ2 = h2 + (R – r)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 282 + (28 – 7)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 784 + (21)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 784 + 441
⇒ ℓ2 = 1225
⇒ ℓ = √(1225)
∴ ℓ = 35 cm
⇒ T.S.A of frustum = π(R + r)ℓ + πR2 + πr2
= π(28 + 7) × 35 + π(28)2 + π(7)2
= 35 × 35π + 784π + 49π
= 1225π + 784π + 49π →eqn2
Area of upper circle = πR2
= π(28)2
= 784π →eqn3
T.S.A of bucket = 1225π + 784π + 49π – 784π (from eqn2 and 3)
⇒ T.S.A of bucket = 1274π
⇒T.S.A of bucket=
⇒ T.S.A of bucket = 182 × 22
∴ T.S.A of bucket = 4004 cm2
The capacity and total surface area of the bucket is 30184 cm3 and 4004 cm2.
Q.37. A bucket is in the form of a frustum of a cone with a capacity of 12308.8 cm3 of water. The radii of the top and bottom circular ends are 20 cm and 12 cm respectively. Find the height of the bucket. (Use π = 3.14.)
Upper end radius of frustum/bucket = R = 20 cm
Lower end radius of frustum/bucket =r = 12 cm
Height of the frustum/bucket be ‘h’ cm
And we know,
The capacity of bucket = Volume of the bucket
And, Volume of bucket = Volume of Frustum
Volume of frustum/bucket = V = 12308.8 cm3
∴ Capacity of bucket = Volume of frustum
⇒Volume of frustum
Where R = Radius of larger or upper end and r = Radius of smaller or lower end and h = height of frustum π = 3.14(putting the values)
⇒ 3.14 × h × (144 + 400 + 240) = 12308.8 × 3
⇒ 3.14 × h × 784 = 36926.4
⇒ 2461.76 × h = 36926.4
⇒ h = 36926.4/2461.76
∴ h = 15 cm
The height of the bucket is 15 cm.
Q.38. A milk container is made of metal sheet in the shape of frustum of a cone whose volume is 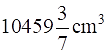 . The radii of its lower and upper circular ends are 8 cm and 20 cm respectively. Find the cost of metal sheet used in making the container at the rate of Rs 1.40 per cm2.
. The radii of its lower and upper circular ends are 8 cm and 20 cm respectively. Find the cost of metal sheet used in making the container at the rate of Rs 1.40 per cm2.
Upper end radius of container = R = 20 cm
Lower end radius of container =r = 8 cm
Height of the container be ‘h’ cm
As container is in shape of frustum
Volume of container = Volume of Frustum
Where R = Radius of larger or upper end and r = Radius of smaller or lower end and h = height of frustum π = 22/7(putting the values)
⇒ 22 × h × 208 = 73216
⇒ 4576 × h = 73216
⇒ h = 73216/4576
∴ h = 16 cm
Let the slant height of the frustum be ‘ℓ’ cm
So, ℓ2 = h2 + (R – r)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 162 + (20 – 8)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 256 + (12)2
⇒ ℓ2 = 256 + 144
⇒ ℓ2 = 400
⇒ ℓ = √(400)
∴ ℓ = 20 cm
Now the Area of sheet used in making the container can be calculated by simply subtracting the area of the upper circular end from the T.S.A of frustum
⇒ T.S.A of frustum = π(R + r)ℓ + πR2 + πr2
= π(20 + 8) × 20 + π(20)2 + π(8)2
= 28 × 20π + 400π + 64π
= 560π + 464π
= 1024π →eqn1
Area of upper circular end = πR2
= π(20)2
= 400π →eqn2
T.S.A of container = 1024π – 400π (from eqn2 and 1)
⇒ T.S.A of container = 624π
⇒ Cost of metal sheet used = T.S.A of container × Rate per cm2
⇒ Cost of metal sheet used
= 13728 × 0.2
= Rs. 2745.6
The cost of the metal sheet used is Rs. 2745.6.
Q.39. A solid metallic sphere of diameter 28 cm is melted and recast into a number of smaller cones, each of diameter 4(2/3)cm and height 3 cm. Find the number of cones so formed.
Here the volume of all the resulting cones will be exactly equal to the volume of the sphere from which they are formed. Son we would find the volume of sphere and then divide the volume of sphere with the volume of one cone to find the number of cones formed.Diameter of the sphere = D = 28 cm
Radius of the sphere = 28/2
Radius of the sphere = R = 14 cm
Volume of the sphere(put the value of R)
⇒Volume of the sphere
Let the number of cones formed out of the sphere be ‘x’
Diameter of each cone
Given the height of each cone = h = 3 cm
Then, radius
Volume of ‘n’ number of cones = n × volume of one cone
Volumes of ‘m’ number of cones = volume of sphere
⇒ m = 224 × 3
∴ m = 672
The number of cones formed out of the sphere is 672.
Q.40. A cylindrical vessel with internal diameter 10 cm and height 10.5 cm is full of water. A solid cone of base diameter 7 cm and height 6 cm is completely immersed in water. Find the volume (i) displaced out of the cylinder (ii) left in the cylinder.
Given internal diameter of cylinder = D = 10 cm
Internal radius of cylinder = R = D/2 = 10/2
Internal radius of cylinder = R = 5 cm
Height of cylinder = H = 10.5 cm
Diameter of solid cone = d = 7 cm
Radius of solid cone = r = d/2 = 7/2
Radius of solid cone = r = 3.5 cm
Height of cone = h = 6 cm
(i) Volume displaced out of cylinder
By Archimedes principle we can easily say that,
Volume displaced out of cylinder = Volume of the solid cone
⇒ V = 22 × 1.75 × 2
∴ V = 77 cm3
The volume displaced out of cylinder is 77 cm3.
(ii)Volume left in cylinder
Volume left in cylinder = Volume of cylinder – Volume displaced out
Volume of cylinder = π(R)2H
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × (5)2 × 10.5 (putting the given values)
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × 25 × 10.5
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × 262.5
⇒ Volume of cylinder = 22 × 37.5
∴ Volume of cylinder = 825 cm3→eqn1
Volume left in cylinder = 825 – 77 (from eqn1 and (i))
∴ Volume left in cylinder = 748 cm3
The volume left in the cylinder is 748 cm3.
|
53 docs|15 tests
|
|
53 docs|15 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
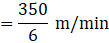
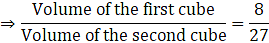
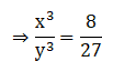
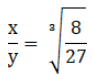
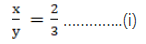
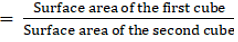
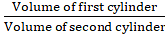
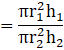
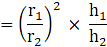
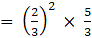 … [Using (i) and (ii)]
… [Using (i) and (ii)]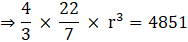
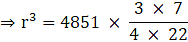
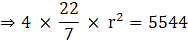
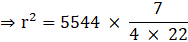
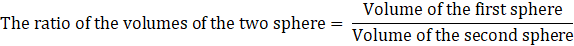
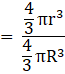
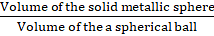
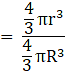
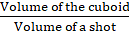
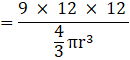
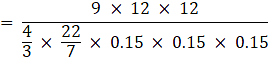
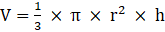
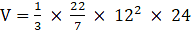
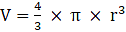
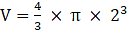
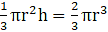
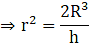
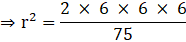
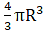 (where R=radius of sphere)→eqn1
(where R=radius of sphere)→eqn1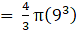 (putting value of R in eqn 1)
(putting value of R in eqn 1)
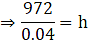
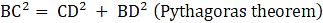
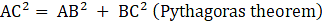
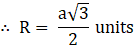
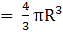 →eqn2
→eqn2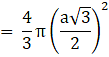
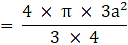
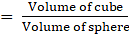
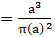 (putting values from eqn3 and eqn4)
(putting values from eqn3 and eqn4)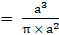
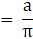
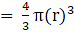
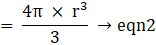
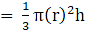 (put the value of h)
(put the value of h)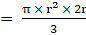
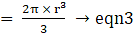
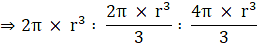
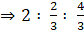 (dividing the above relation by (πr3)
(dividing the above relation by (πr3)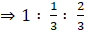 (dividing the above ratio by 2)
(dividing the above ratio by 2)
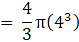
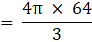
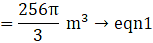
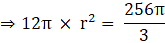
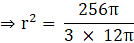
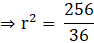
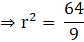
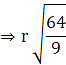
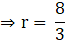
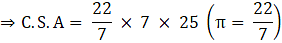
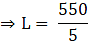
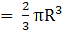 (where R is radius of hemisphere)
(where R is radius of hemisphere)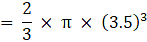
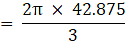
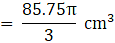
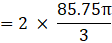
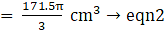
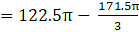
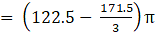 (taking π common)
(taking π common)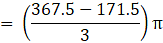
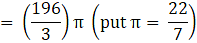
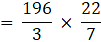
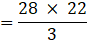
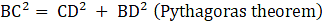
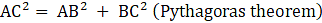
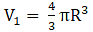 (put the value of R)
(put the value of R)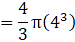
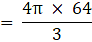
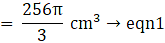
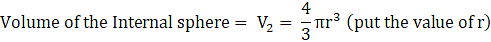
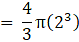
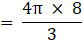

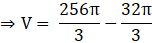
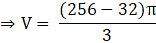
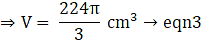
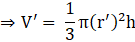
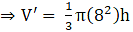 (putting value of r' )
(putting value of r' )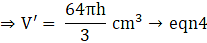
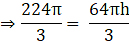
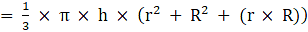
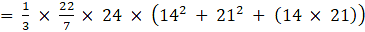
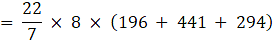
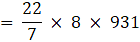
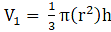
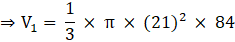
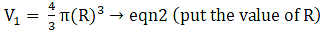
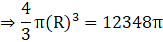
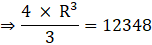
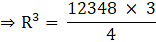
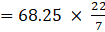 (putting π= 22/7)
(putting π= 22/7)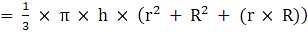
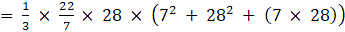
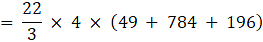
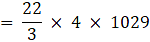
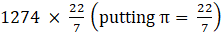
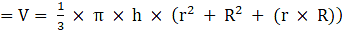
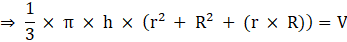
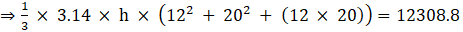 (putting the values)
(putting the values)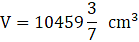
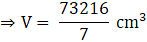
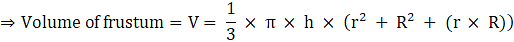
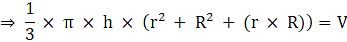
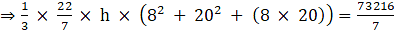 (putting the values)
(putting the values)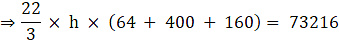
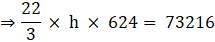
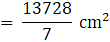
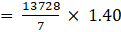
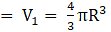 (put the value of R)
(put the value of R)