Syllogisms | Decision Making for UCAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Syllogism? |

|
| Method 1: Analytical Method |

|
| Method 2: Venn Diagrams |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
What is Syllogism?
A syllogism is a form of reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn from two or three given propositions or statements. It uses deductive reasoning rather than inductive reasoning.
You have to take the given statements to be true, even if they are at variance from established facts.
Let us see an example of deductive reasoning:
Statements:
(a) All cats are dogs.
(b) All dogs are birds.
Conclusion: All cats are birds.
This conclusion is quite visible. But to solve complex problems we have some standard methods.
Method 1: Analytical Method
Following are the four major types of statements generally asked:
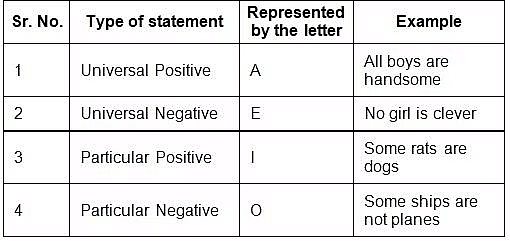
While deriving conclusions, the following points should be kept in mind:
- With two particular statements, no universal conclusion is possible.
- With two positive statements, no negative conclusion is possible.
- With two negative statements, no positive conclusion is possible.
- With two particular statements, no conclusion is possible, except when an 'I' type of statement is given and then by reversing it, an 'I' type of conclusion is given.
Important points related to conclusions drawn from single statements:
- A statement of type 'E' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'E & O'.
- A statement of type 'A' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I'.
- A statement of type 'I' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I.'
- A statement of type 'O' when reversed, does not give a conclusion of any type.
Method 2: Venn Diagrams
- Another method of solving such types of questions is by drawing a Venn diagram representing the statements.
- However, it is important that all possible Venn diagrams be drawn.
- If a conclusion can be deduced from all the possible solutions, then that conclusion is true.
- If the conclusion can be concluded from one of the possible Venn diagrams and not from the other possible Venn diagram, then that conclusion is taken as false.
Solved Examples
Ex.1. In a school, all students wear uniforms. Sarah is a student in the school. Some students in the school are members of the chess club. Sarah is a member of the chess club.
(a) Conclusion 1: Sarah wears a uniform.
(b) Conclusion 2: All members of the chess club wear uniforms.
(c) Conclusion 3: Some members of the chess club are students.
(d) Conclusion 4: All students in the school are members of the chess club.
(e) Conclusion 5: Sarah is the only student in the school.
Correct Answer is Option (a,c)
1st conclusion – Does follow because Sarah is a student in the school, and all students wear uniforms.
2nd conclusion – Does not follow because it is only stated that some students in the school are members of the chess club, not all of them.
3rd conclusion – Does follow because Sarah is mentioned as a member of the chess club.
4th conclusion – Does not follow because it is only stated that some students in the school are members of the chess club, not all of them.
5th conclusion – Does not follow because it is not mentioned that Sarah is the only student in the school.
Ex.2. All dogs like bones. Some cats like fish. All animals like food.
(a) Conclusion 1: Some dogs like fish.
(b) Conclusion 2: Some cats like bones.
(c) Conclusion 3: All dogs are animals.
(d) Conclusion 4: All cats are animals.
(e) Conclusion 5: Some animals like bones.
Correct Answer is Option (c,d)
1st conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all dogs like bones, not fish.
2nd conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that some cats like fish, not bones.
3rd conclusion – Does follow because dogs are a type of animal.
4th conclusion – Does follow because cats are a type of animal.
5th conclusion – Does not follow because it is not mentioned which specific animals like bones.
Ex.3. All cars in the parking lot are red. Some red cars are sedans. Some sedans are hybrid vehicles.
(a) Conclusion 1: All cars in the parking lot are sedans.
(b) Conclusion 2: All hybrid vehicles are sedans.
(c) Conclusion 3: Some sedans are red cars.
(d) Conclusion 4: Some hybrid vehicles are red cars.
(e) Conclusion 5: All red cars are hybrid vehicles.
Correct Answer is Option (c,d)
1st conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all cars in the parking lot are red, not all of them are sedans.
2nd conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that some sedans are hybrid vehicles, not all of them.
3rd conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some red cars are sedans.
4th conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some sedans are hybrid vehicles.
5th conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that some sedans are hybrid vehicles, not all of them are red cars.
Ex.4. All fruits in the basket are apples. Some apples are green. All green things are healthy.
(a) Conclusion 1: All fruits in the basket are green.
(b) Conclusion 2: All healthy things are fruits in the basket.
(c) Conclusion 3: Some green things are fruits in the basket.
(d) Conclusion 4: Some healthy things are apples.
(e) Conclusion 5: Some apples are healthy.
Correct Answer is Option (c,e)
1st conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all fruits in the basket are apples, not all of them are green.
2nd conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all green things are healthy, not all healthy things are fruits in the basket.
3rd conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some apples are green, and all fruits in the basket are apples.
4th conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all green things are healthy, not all healthy things are apples.
5th conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some apples are green, and all green things are healthy.
Ex.5. All flowers in the garden are roses. Some roses are red. Some red things are expensive.
(a) Conclusion 1: All flowers in the garden are red.
(b) Conclusion 2: All expensive things are flowers in the garden.
(c) Conclusion 3: Some red things are flowers in the garden.
(d) Conclusion 4: Some expensive things are roses.
(e) Conclusion 5: Some roses are expensive.
Correct Answer is Option (c,d)
1st conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that all flowers in the garden are roses, not all of them are red.
2nd conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that some red things are expensive, not all expensive things are flowers in the garden.
3rd conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some roses are red, and all flowers in the garden are roses.
4th conclusion – Does not follow because it is only mentioned that some red things are expensive, not all expensive things are roses.
5th conclusion – Does follow because it is stated that some roses are red, and some red things are expensive.
|
17 videos|19 docs|19 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UCAT exam
|

|
















