Understanding Titration Curves and Equivalence Points | General Chemistry for MCAT PDF Download
Introduction
Before delving into the fascinating world of titration curves and equivalence points, it's essential to have a solid grasp of the concepts of weak and strong acids, as well as weak and strong bases. In this article, we'll explore the fundamentals of titration, define key terminologies, and examine various titration curves. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how titration curves provide valuable insights into acid-base reactions.
Understanding Weak and Strong Acids and Bases
To comprehend titration curves fully, let's start by revisiting the differences between weak and strong acids and bases. Here's a quick recap:
Strong Acids:
- Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and nitric acid (HNO₃), dissociate completely in aqueous solutions, releasing hydronium ions (H₃O⁺).
Weak Acids:
- Weak acids, like acetic acid (CH₃COOH), hydrofluoric acid (HF), and oxalic acid (COOH)₂, only partially dissociate in aqueous solutions, resulting in fewer hydronium ions (H₃O⁺).
Strong Bases:
- Strong bases, including sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and lithium hydroxide (LiOH), dissociate fully in aqueous solutions, producing hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
Weak Bases:
- Weak bases, such as ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) and ammonia (NH₃), do not entirely dissociate in aqueous solutions, leading to a lower concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
Introducing Titration
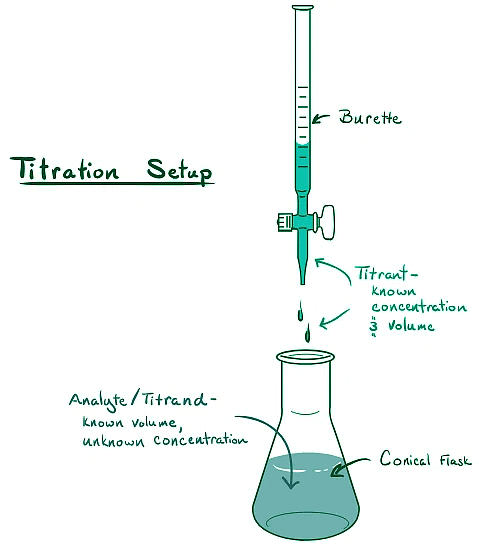
Titration is a powerful technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Titrant and Titrand:
- Titrant: A solution of known concentration added to the solution whose concentration needs to be determined.
- Titrand or analyte: The solution whose concentration is being measured.
Equivalence Point:
- The equivalence point is the stage in the titration where the amount of titrant added is precisely enough to neutralize the analyte solution fully. In acid-base titrations, the moles of the base equal the moles of the acid, resulting in a solution containing only salt and water.
Indicator:
- An indicator, typically a weak acid or base, is added to the analyte solution. It changes color at the endpoint, indicating the completion of the reaction. The addition of an indicator assists in visually identifying the equivalence point in an acid-base titration.
Endpoint:
- The endpoint refers to the point at which the indicator changes color, indicating the completion of the acid-base titration.
Exploring Titration Curves
A titration curve graphically represents the pH of the analyte solution against the volume of titrant added during the titration process. Let's examine some specific examples:
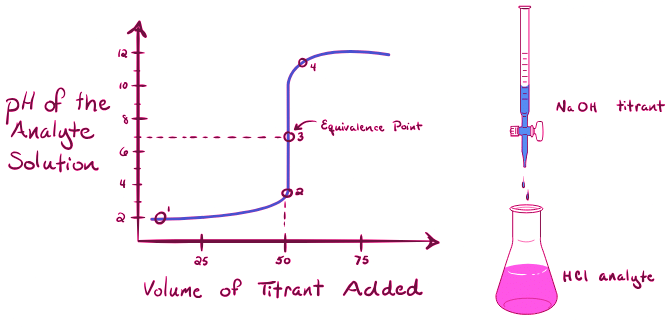
Titration of a Strong Acid with a Strong Base:
When titrating a strong acid (e.g., hydrochloric acid, HCl) with a strong base (e.g., sodium hydroxide, NaOH), the titration curve exhibits the following characteristics:
- Point 1: Initially, with no NaOH added, the pH of the analyte solution is low due to the abundance of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) from the dissociation of HCl.
- Point 2: Just before.
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for MCAT exam
|

|
















