Taxonomical Hierarchy | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
Taxonomic Categories
Classification is the process of grouping organisms that are genetically similar. The groups that share characteristics are combined to form larger groups.The various grouping levels or ranks in classification are known as taxonomic categories.
Example: Insects represent a group of organisms sharing common features like three pairs of jointed legs.
There are seven main taxonomic categories:
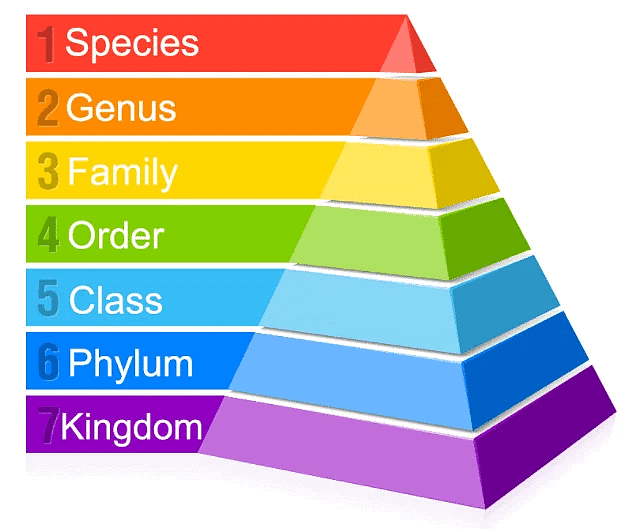
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in a decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and vice versa.
Organisms are classified into similar categories namely kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
1. Species
- Species (used both as singular and plural) is a natural population of individuals or groups of populations that resemble one another in all essential morphological and reproductive characters so that they are able to interbreed freely and produce fertile offspring. It has the lowest taxonomic characteristics. Individuals can be distinguished due to distinct morphological features.
- For example, the scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica, where "Mangifera" is the genus and "indica" is the species. The scientific name of potato is Solanum tuberosum, where “Solanum” is the genus and “tuberosum” is the species.
2. Genus
- It is a group or assemblage of related species that share certain associated characteristics. Correlated Characters are those similar or common features used to classify a taxon above the rank of species.
- All the species of a genus are presumed to have evolved from a common ancestor.
- Among animals, for example, the species of horses and zebras form the genus Equus, lion and tiger are placed under the genus Panthera.
3. Family
- It is a taxonomic category that contains one or more related genera.
- All the genera of a family have some common features or correlated characters.
- They are separable from the genera of a related family by important and characteristic differences in both vegetative and reproductive features.
- Example: The genera of cats (Felis) and leopards (Panthera) are included in the family Felidae.
4. Order
- Order is a more specific rank than class. The category includes one or more related families.
- Plant families such as Convolvulaceae and Solanaceae are classified in the order Polymoniales based on their floral characteristics.
- In the animal family, Felidae and Canidae are included in the same order Carnivora.
5. Class
- A class is a group of one or more related orders.
- Example: The class dicotyledonous (Dicotyledonae, dicotyledons) of flowering plants contains all dicots which are grouped into several orders.
- For example order Primata comprising monkeys, gorillas and gibbons are placed in Class Mammalia along with order Carnivora which includes animals like tiger, cat, and dog all having a common feature that is hair on skin and milk glands.
6. Division/Phylum
- It is a category of related animals of classes.
- The term phylum is used for animals, while division is commonly used for plants.
- A division of phylum is formed of one or more classes.
- For example, Chordata is a phylum that includes organisms that share characteristics such as a notochord and a dorsal hollow neural system , so based on this characteristics phylum chordate of animals contains not only class mammalian but also Aves (birds), reptilian (reptiles), amphibians (amphibians), Cyclostomata, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes (fishes), etc.
7. Kingdom
- It is the highest taxonomic category of biological classification.
- For example, all plants are included in kingdom Plantae while all animals belong to kingdom Animalia.
- There are some extra categories, like subdivision, suborder, subfamily, tribe, sub-tribe, etc. They are not regularly used. They are used only when they are needed.
Note:
As we go higher from species to kingdom, the number of common characters decreases. Lower the taxa more are the characteristics that the members within the taxon share. Higher the category, greater is the difficulty of determining the relationship to other taxa at the same level.
Note:
These taxonomic categories/groups are distinct biological entities and not merely morphological aggregates.

 Examples of Taxonomic Categories
Examples of Taxonomic Categories
Taxonomical Aids
Techniques, procedures and stored Information that are useful in the identification and classification of organisms are called taxonomic aids. They are required because the taxonomic study of plants, animals and other organisms is basic to almost all biological studies branches for their proper identification and finding their relationships with others.
- Herbarium, botanical gardens, museums, zoological parks (zoos) and keys are important tools used in the identification of plants and animals.

1. Herbarium
 A Herbarium
A Herbarium
- The herbarium is a reference collection of carefully selected and dried and pressed plant specimens, mounted on sheets and are kept systematically according to a widely accepted system of classification.
- The herbarium is a repository or storehouse for future use. Every institute, school, college, university teaching botany has a small or large herbarium. Very large herbaria are maintained by botanical gardens and institutes connected with plant systematics.
- The herbarium sheets also include a label with information such as the date and location of collection, English, local, and botanical names, family, collector's name, and so on.
- Every student of botany is required to collect plant specimens and prepare herbarium sheets.
- Equipment: Digger and pruning knife, a sickle with a long handle, vasculum, polythene bags, magazines or newspapers, blotting papers, plant press, field notebook, herbarium sheets, glue, labels, small transparent polythene bags.
 Herbarium Sheet
Herbarium Sheet
Method of Specimen Collection and Mounting

- An area is selected for the botanical excursion. It is preferable to visit the same site in different seasons.
- For herbaceous species, the entire plant with the intact part is collected. For others, shoots having flowers, leaves and fruits are selected and cut with the help of a pruning knife.
- A sickle with a long handle is used if the desired twigs are present at a height. Diggers are used to obtain underground parts like a root system, tuber, bulb, corm, rhizome, etc.
- The collected materials are pressed, dried, mounted on the herbarium sheets, labelled and- can be placed in polythene bags or vacuum.
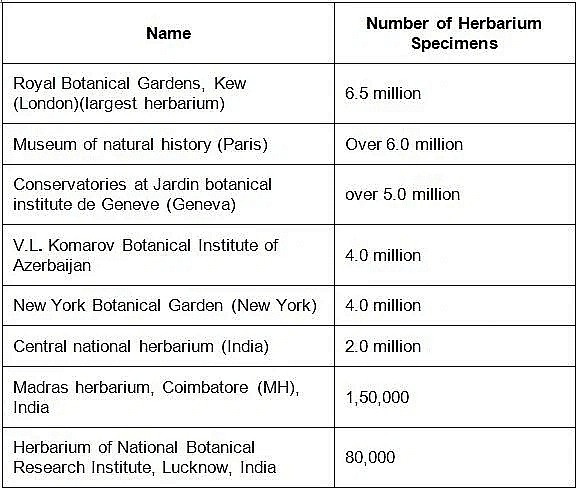
Important Herbaria
2. Botanical Gardens
 Botanical gardens
Botanical gardens
- Botanical gardens are efficiently large size tracts where plants of different types and areas are grown for scientific and educational purposes.
- Botanical gardens are usually run by universities or other scientific research organisations, and they often include herbaria and research projects in plant taxonomy or another aspect of botanical science.
- The first real mechanical garden was developed by Theophrastus (370-285 B.C.). Of course, the garden was part of Indian Chinese and Roman cultures. “Hanging Garden” of Babylon was considered to be a wonder of ancient time.
- Modern-day Botanical Gardens contain outdoor plants, a greenhouse, library, research laboratory, herbarium with documented collections of various taxa.
- There is an international association of botanical gardens (established in 1962) that coordinates research and exchange of plant materials.
The Important Functions of Botanical Gardens
- Plant species are grown in these gardens for identification purposes labelled with its botanical/scientific name and family.
- Growing important plants of local flora.
- Keeping a record of local flora.
- Providing living plant material for systematic work.
- Supplying seeds and materials for different aspects of Botanical research.
- Growing and maintaining rare and endangered plants.
Some Major Botanical Gardens of the World
- Main botanical garden Moscow: The largest botanical garden spread over an area of 900 acres.
- Bunde's garden, Vienna: It is spread over an area of 400 acres.
- Royal Botanical Garden, Kew London: It has an area of 300 acres but grows a very large number of plants.
- Kebun Raya (Botanical Garden)Bojor Java: Spread over an area of 200 acres, the garden has a section with virgin rainforest.
- Indian Botanical Garden Shibpur, Kolkata: It is the largest botanical garden of Asia spread over 273 acres, which is famous for its Great Banyan tree, Palm house, Succulent Plants, Indian Grasses etc.
3. Museum

- The word museum comes from the Greek word mouseion. In ancient Greek mouseion was the temple of Muses. The goddess of arts and sciences.
- Museums have collections of preserved plant and animal specimens for study and reference.
- The materials available in the exhibition for study are called collections. A Collection may include scientific specimens, works of art and exhibits and information on the history of technology.
- Specimens are preserved in preservative solutions in containers or jars.
- Plant and animal specimens can be preserved as dry specimens as well. After collecting, killing, and pinning, insects are stored in insect boxes. Larger animals, such as birds and mammals are stuffed and preserved.
Museums Perform Various Functions
Acquisition of materials: Every new object that a museum adds to its collection is called Acquisition. Museums acquire objects in several ways, of which field collection is the most useful. The scientists and technicians go outside to gather specimens and data on a particular subject, which is with the scope of the museum.
Recording of Materials: Each acquisition is listed carefully by specialist staff. As soon as objects are received, the data, the source, the method of acquisition and other available information are entered into the record register.
Preservation of Materials: The primary purpose of the museum is to preserve selected objects that are received. Curators (the person in charge of the museum) are incharge of it.
Preservation in a museum consists of two steps:
(i) Specimens must be put into a condition that checks deterioration.
(ii) The specimens must be protected.Research: One important use of the museum is to extract as much knowledge as possible. Many museums published scholarly journals, series of papers and books to make available results of research on collections.
Exhibitions of Materials: Various members of museum staff prepare acquisitions for exhibitions. The specimens selected for the exhibition are put on view in numerous ways.
Education: A Number of universities conduct some courses in certain subjects as museum. Universities take advantage of such collections. Thus museums help in spreading education.
4. Zoological Parks (Zoos)
 Tigers at Zoo
Tigers at Zoo
- Zoological parks are the places where wild animals are kept in safe environments under human supervision where we can learn about their eating habits and behaviour.
- Many threatened species on the verge of extinction are saved in zoological parks. Zoological parks or zoological gardens are established where a high standard of care is observed and the animals live under more natural conditions.
- The animals provide better recreation to visitors.
- For example: Nehru Zoological Park (also known as Hyderabad Zoo or Zoo Park) is a zoo located in Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
The Role of Zoological Parks in Wildlife Conservation
- The regular zoo movement in India began in the year 1885 when the first zoo was set up in Chennai.
- In the Zoological Park, animals enjoy protection, fine sunshine, fresh air and above all, ample open space to play around.
- They have now become repositories of threatened wildlife and a storehouse of the knowledge on animal behaviour, breeding habits, etc.
- Zoological Park is the place where they are assured of food, medical care and treatment and where they also feel safe from their natural enemies.
- Zoological Parks are very useful in spreading knowledge of the wildlife wealth of the country.
5. Key
- Another taxonomic aid used for plant and animal identification based on similarities and differences is the key.
- For identification purposes, separate taxonomic keys are required for each taxonomic category such as family, genus, and species.
- Each statement in the key is called a lead.
- The keys are based on the contrasting characters in a pair known as a couplet. It represents the choice between two contrasting choices.
- The key is made up of a series of choices based on the observed characteristics of the plant specimen. It is also known as a dichotomous key.
Role of taxonomic keys
- A taxonomic key helps in the identification of unknown organism species based on contrasting characteristics.
- It provides basic characters on the basis of which one can get the taxonomic position of an unknown organism.
- It is of two types, indented key and bracketed key. Indented key gives a number of choices between two or more characteristics of a species. The correct choice is essential for identification.
- For example: wings absent, body covered by furs, etc.

How to use the keys
- Keys should be carefully chosen from manuals, floras, handbooks, monographs, and so on. For example, cultivated plants are not typically included in floras; in this case, manuals are used.
- Before making a decision, carefully read and understand both leads. At times, it appears that the second lead is more appropriate than the first.
- With the help of a glossary, check the meaning of unknown terms.
- Refrain from making decisions on the basis of a single observation.
- After reading the description, verify and validate the results by equating the specimens with the illustration or with an authentic herbarium specimen.
In this document you have learnt
- Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in a decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and vice versa.
- As we go higher from species to kingdom, the number of common characters decreases. Lower the taxa more are the characteristics that the members within the taxon share. Higher the category, greater is the difficulty of determining the relationship to other taxa at the same level.
- Indian Botanical Garden Shibpur, Kolkata: It is the largest botanical garden of Asia spread over 273 acres, which is famous for its Great Banyan tree, Palm house, Succulent Plants, Indian Grasses etc.
- The first real mechanical garden was developed by Theophrastus (370-285 B.C.). Of course, the garden was part of Indian Chinese and Roman cultures. “Hanging Garden” of Babylon was considered to be a wonder of ancient time.
- The first real mechanical garden was developed by Theophrastus (370-285 B.C.). Of course, the garden was part of Indian Chinese and Roman cultures. “Hanging Garden” of Babylon was considered to be a wonder of ancient time.
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JAMB exam
|

|

















