| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Friedel-Crafts Alkylation |

|
| What are the limitations of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction? |

|
| Friedel-Crafts Acylation |

|
Introduction
The Friedel-Crafts reaction is a chemical process in organic chemistry that involves electrophilic aromatic substitution, enabling the addition of substituents to aromatic rings. It encompasses two main types of reactions: alkylation and acylation. This reaction was first discovered in 1877 by Charles Friedel, a French chemist, and James Crafts, an American chemist.
An illustration describing both the Friedel-Crafts reactions undergone by benzene is provided below.

It is worth noting that both of these reactions involve the substitution of a hydrogen atom, originally attached to the aromatic ring, with an electrophile. In Friedel-Crafts reactions, aluminum trichloride (AlCl3) is commonly employed as a catalyst due to its ability to act as a Lewis acid and coordinate with halogens, thus generating an electrophile.
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the process of replacing an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is achieved through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring facilitated by a carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction serves as a method for producing alkylbenzenes by utilizing alkyl halides as reactants.
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction of benzene is illustrated below.

A Lewis acid catalyst, such as FeCl3 or AlCl3, is utilized in this reaction to facilitate the elimination of the halide and generate a carbocation. The resulting carbocation undergoes rearrangement prior to proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Mechanism:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction follows a three-step mechanism.
- Step 1: The Lewis acid catalyst (AlCl3) reacts with the alkyl halide, leading to the formation of an electrophilic carbocation.
- Step 2: The carbocation attacks the aromatic ring, forming a cyclohexadienyl cation as an intermediate. This process results in a temporary loss of aromaticity in the arene due to the breaking of the carbon-carbon double bond.
- Step 3: Deprotonation of the intermediate occurs, leading to the reestablishment of the carbon-carbon double bond and the restoration of aromaticity in the compound. The proton released in this step combines with a chloride ion to form hydrochloric acid, thus regenerating the AlCl3 catalyst.
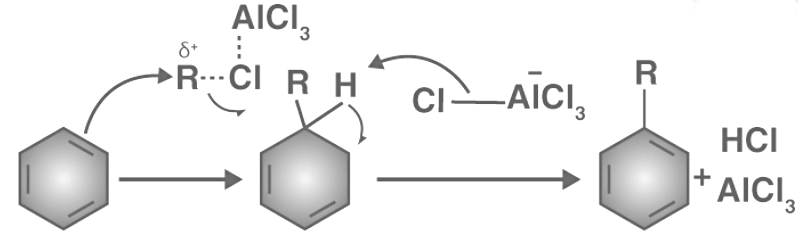
An illustration describing the mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is provided above.
What are the limitations of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction?
Below are some significant limitations of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation:
- Carbocations formed from aryl and vinyl halides are highly unstable and cannot be utilized in this reaction.
- The presence of deactivating groups on the aromatic ring, such as an NH2 group, can lead to catalyst deactivation due to complex formation.
- Excess aromatic compound is required to prevent polyalkylation, which involves the addition of more than one alkyl group to the aromatic compound.
- Aromatic compounds that are less reactive than mono-halobenzenes do not readily participate in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.
- Carbocation rearrangements are common in this reaction, as is the case with any reaction involving carbocations.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction involves the introduction of an acyl group to an aromatic ring. Typically, this is accomplished by utilizing an acid chloride (R-(C=O)-Cl) and a Lewis acid catalyst like AlCl3. In the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, the aromatic ring is converted into a ketone. The reaction between benzene and an acyl chloride under these conditions is demonstrated below.

An acid anhydride can be used as an alternative to the acyl halide in Friedel-Crafts acylations. The halogen belonging to the acyl halide forms a complex with the Lewis acid, generating a highly electrophilic acylium ion, which has a general formula of RCO+ and is stabilized by resonance.
Mechanism
Friedel-Crafts acylations proceed through a four-step mechanism.
- Step 1: A reaction occurs between the Lewis acid catalyst (AlCl3) and the acyl halide. A complex is formed and the acyl halide loses a halide ion, forming an acylium ion which is stabilized by resonance.

- Step 2: The acylium ion (RCO+) goes on to execute an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. The aromaticity of the ring is temporarily lost as a complex is formed.

- Step 3: The intermediate complex is now deprotonated, restoring the aromaticity to the ring. This proton attaches itself to a chloride ion (from the complexed Lewis acid), forming HCl. The AlCl3 catalyst is now regenerated.
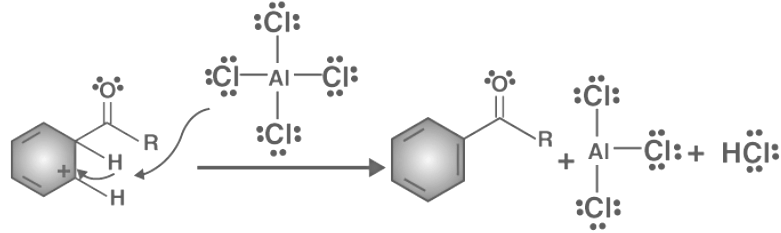
Therefore, the desired product, acyl benzene, is obtained through the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
Limitations
Despite addressing certain limitations of the alkylation reaction, the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction has its own drawbacks.
- The acylation reaction exclusively yields ketones due to the decomposition of formyl chloride (H(C=O)Cl) into CO and HCl under these reaction conditions.
- Aromatic compounds less reactive than mono-halobenzenes do not readily participate in this reaction.
- Aryl amines cannot be utilized in the acylation reaction as they form highly unreactive complexes with the Lewis acid catalyst.
- When amines or alcohols are involved, acylations can occur on the nitrogen or oxygen atoms.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
















