Important Diagrams: Anatomy of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Tissues are a group of cells, belonging to a common origin, and they execute a similar type of function. They can be divided as Meristematic Tissue: These tissues consist of cells that possess the capacity to divide. They exist in specific regions in a plant, and they are of three types, apical, lateral, and intercalary meristem. There are some important diagrams that are important for NEET Aspirant.
Plant Tissues
Plant tissue refers to groups of cells with similar structures, functions, and origins that work together to perform specific roles within a plant. These tissues can be categorized into two main types: meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
1. Meristematic tissue
These are rapidly dividing cells responsible for primary growth in plants. They can be categorized into apical, lateral, and intercalary meristems based on their location and function.
(a) Apical meristem: Found at the tips of stems and roots, responsible for increasing plant length.
 Apical Meristem (a) Root (b) Shoot
Apical Meristem (a) Root (b) Shoot
The root apical meristem is found at the tip of a root, while the shoot apical meristem is located at the far end of the stem.
- Root Apical Meristem: Supports root growth by continuously adding new cells at the root tip.
- Shoot Apical Meristem: Enables stem growth and leaf formation by adding new cells at the top of the stem.
- Axillary Buds: Can grow into branches or flowers, contributing to the plant’s ability to branch and reproduce.
(b) Lateral meristem: Located in the stem or root's radial portion, it increases plant thickness.
(c) Intercalary meristem: Found at internodes or base of leaves, it increases internode size.
 Merismatic Tissue
Merismatic Tissue
2. Permanent Tissues
Permanent tissues are comprised of cells that have lost their ability to divide and instead perform specialized functions. There are two main types of permanent tissues: simple and complex.
(a) Simple permanent tissue includes three types: sclerenchyma, collenchyma, and parenchyma.
- Parenchyma cells are living cells with large central vacuoles and serve various functions such as photosynthesis, buoyancy, and storage of starch.

- Collenchyma consists of elongated living cells with flexible cell walls, offering structural support and flexibility.

- Sclerenchyma consists of elongated dead cells with lignin deposits, providing strength to various plant parts.

(b) Complex permanent tissue comprises phloem and xylem, which are responsible for transporting water, solutes, and food throughout the plant.
- The xylem consists of vessels, tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma, conducting water and dissolved substances.

- Phloem, on the other hand, is composed of phloem fibers, sieve tubes, phloem parenchyma, and companion cells, facilitating the transportation of food.

Opening And Closing of Stomata
- Stomata open and close mainly because of changes in the pressure inside the guard cells.
- When these cells swell up with water, the stomata open, and when they lose water and shrink, the stomata close.
- This is like a balloon getting bigger when you blow air into it and smaller when you let the air out.
- There are also other ideas about how stomata open and close, but this is the main one.
 Opening and Closing of Stomato
Opening and Closing of Stomato
The Vascular Tissue System
- The plant vascular system comprises phloem and xylem, forming vascular bundles.
- Dicotyledonous stems possess cambium between phloem and xylem, enabling the formation of secondary tissues, hence termed open vascular bundles.
- Monocotyledonous plants lack cambium in their vascular bundles, thus termed closed, as they cannot produce secondary tissues.
- Radial arrangement of xylem and phloem is observed in roots, where they alternate along different radii.
- In stems and leaves, vascular bundles are typically conjoint, with xylem and phloem positioned together along the same radius, with phloem usually on the outer side of xylem.
 Types of Vascular Bundles
Types of Vascular Bundles
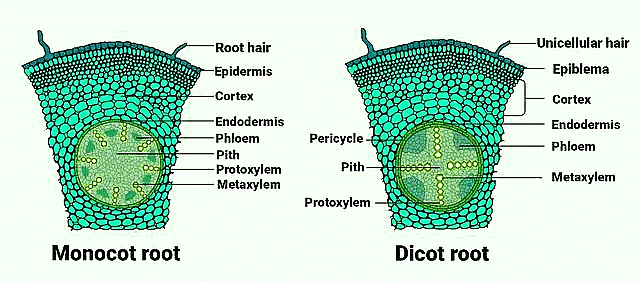
Transverse Section of Monocot and Dicot Roots
Dicotyledonous Root
- Dicotyledonous roots have a distinct structure best observed in transverse sections.
- Epiblema is the outermost layer, with protruding unicellular root hairs.
- Cortex consists of thin-walled parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces.
- Endodermis is a single layer of barrel-shaped cells without intercellular spaces; it has Casparian strips made of suberin.
- Pericycle, adjacent to the endodermis, consists of thick-walled parenchymatous cells where lateral roots and vascular cambium initiate.
- Pith, towards the center, is small or inconspicuous.
- Conjunctive tissue lies between the xylem and phloem; typically two to four patches of each.
- The cambium ring forms between the xylem and phloem.
- All inner tissues, including the pericycle, vascular bundles, and pith, form the stele.
Monocotyledonous Root
- Anatomy similar to dicot root but with some differences.
- Epidermis, Cortex, Endodermis, Pericycle, Vascular Bundles, and Pith present.
- Typically more than six (polyarch) xylem bundles compared to dicots.
- Large and well-developed pith.
- No secondary growth occurs in monocot roots.
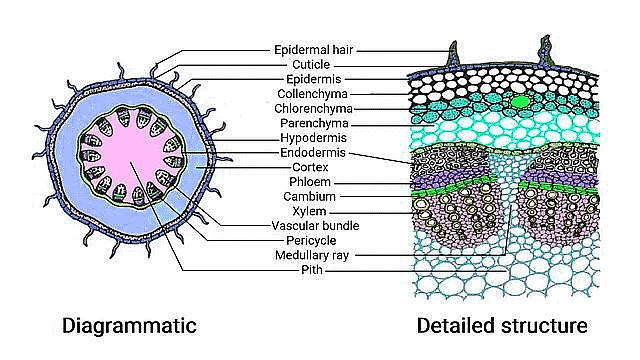
Transverse Section of Monocot & Dicot Stem
Moncotyledonous Root
- Outer layer: Epidermis with a thin protective coating and layers Layers beneath the epidermis:
a. Hypodermis: Provides mechanical support.
b. Parenchyma: Cells with spaces between them.
c. Endodermis: Innermost layer with starch-rich cells. - Pericycle: Sclerenchyma patches above the phloem.
- Medullary rays: Parenchyma cells between vascular bundles.
- Vascular bundles: Arranged in a ring, with open conduits and protoxylem.
- Pith: Central portion with large, space-filled cells.
Monocotyledonous Stem
- Outer layer: Sclerenchymatous hypodermis.
- Vascular bundles: Scattered throughout, surrounded by a bundle sheath.
- Ground tissue: Large, conspicuous parenchyma cells.
- Vascular bundles: Conjoint and closed, with central bundles larger.
- Phloem parenchyma absent, with water-containing cavities within bundles.
Tranverse Section of Monocot & Dicot Leaf
T.S of Monocot Leaf
- Epidermis: Upper and lower surfaces with a cuticle; more stomata on lower surface.
- Mesophyll: Chloroplast-rich parenchyma between epidermis layers.
- Palisade parenchyma: Vertical cells on upper side.
- Spongy parenchyma: Loosely arranged cells with air spaces on lower side.
- Vascular System: Vascular bundles in veins and midrib, surrounded by bundle sheath cells.
- Xylem Position: Locate xylem within vascular bundle

T.S of Dicot Leaf
- Stomata Presence: Stomata are present on both upper and lower surfaces of the epidermis.
- Mesophyll Differentiation: Mesophyll is not differentiated into distinct palisade and spongy parenchyma layers.
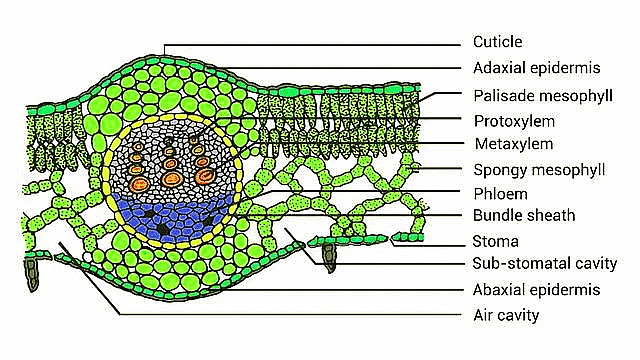
Diagram Based Questions- NEET
Q1: Read the following statements about the vascular bundles:
(a) In roots, the xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii.
(b) Conjoint closed vascular bundles do not possess cambium.
(c) In open vascular bundles, cambium is present in between xylem and phloem
(d) The vascular bundles of dicotyledonous stem possess endarch protoxylem
(e) In the monocotyledonous root, usually there are more than six xylem bundles present
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (b), (c), (d) and (e) Only
(b) (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e)
(c) (a), (c), (d) and (e) Only
(d) (a), (b) and (d) Only
Ans. b
Types of Vascular BundlesThe vascular system consists of complex tissues, the phloem and the xylem. The xylem and phloem together constitute vascular bundles. In roots, xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii the arrangement is called radial. Conjoint closed vascular bundles do not possess cambium. In open vascular bundles, cambium is present in between xylem and phloem. The vascular bundles of dicotyledonous stem possess endarch protoxylem. In monocotyledonous root, usually there are more than six xylem bundles present.
Q2: The transverse section of a plant shows the following anatomical features:
(i) a Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(ii) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(iii) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(iv) Phloem parenchyma absent.
Identify the category of plant and its part:
(a) Dicotyledonous stem
(b) Dicotyledonous root
(c) Monocotyledonous stem
(d) Monocotyledonous root
Ans. c
All these anatomical features are showing that plant is monocotyledonous stem so option 3 is correct. The monocot stem has vascular bundles near the outside edge of the stem. Vascular bundles are scattered in parenchymatous ground tissue. There is no pith region in monocots. The vascular bundles are closed as they do not have cambium in it
|
182 videos|367 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of plant tissues and their functions? |  |
| 2. How do stomata open and close? |  |
| 3. What is the structure and function of vascular tissues in plants? |  |
| 4. How can you differentiate between monocot and dicot roots in a transverse section? |  |
| 5. What are the key differences between monocot and dicot leaves in a transverse section? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















