Important Diagrams: Excretory Products and their Elimination | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Excretory System |

|
| Structure of Kidney |

|
| Structure of Nephron |

|
| Functions of the Tubules |

|
| Counter-Current Mechanism |

|
| Diagram Based Questions NEET PYQs |

|
Excretion is the biological process through which organisms remove waste products generated by their metabolic activities. These waste products include substances like carbon dioxide, urea, ammonia, excess salts, and water. Excretion is crucial for maintaining the internal environment of an organism within optimal conditions for cellular function, a concept known as homeostasis.
Human Excretory System
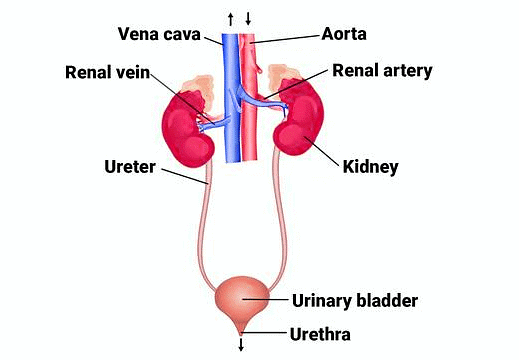
- In humans, the excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, one pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra.
- Kidneys are reddish brown, bean shaped structures situated between the levels of last thoracic and third lumbar vertebra close to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity.
- Each kidney of an adult human measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width, 2-3 cm in thickness with an average weight of 120-170 g.
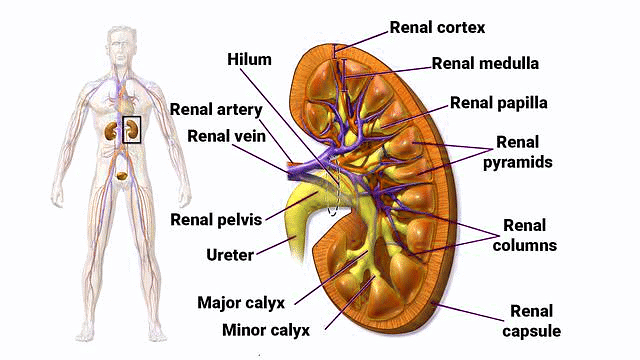
Structure of Kidney
- The kidney has a concave inner surface with a notch called the hilum at its center. The hilum is the entry point for the ureter, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Inside the hilum is the renal pelvis, a broad, funnel-shaped space with projections called calyces. The outer layer of the kidney is a tough protective capsule.
- The kidney is divided into two main zones:
(I)Outer Cortex
(II) Inner Medulla - The medulla contains conical structures known as medullary pyramids, which project into the calyces. The cortex extends between these pyramids, forming renal columns called the Columns of Bertini.
Structure of Nephron
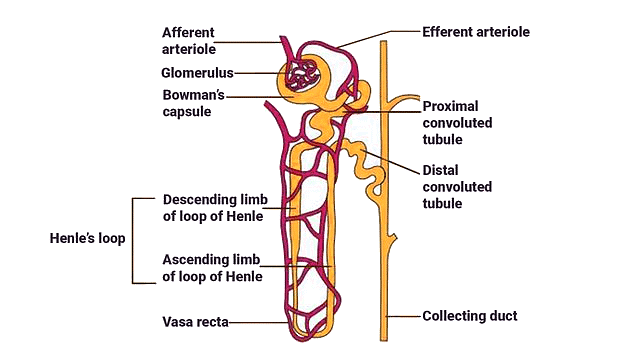
Each kidney contains nearly one million intricate tubular structures known as nephrons, which serve as the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron consists of two main parts: the glomerulus and the renal tubule.
Nephron Structure
- Glomerulus: The glomerulus is a cluster of capillaries formed by the afferent arteriole, a small branch of the renal artery. Blood from the glomerulus is carried away by an efferent arteriole.
- Renal Tubule: The renal tubule begins with Bowman’s capsule, a double-walled cup-like structure that encloses the glomerulus. The glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule together are called the Malpighian body or renal corpuscle.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): After Bowman’s capsule, the tubule continues to form a highly coiled network known as the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
- Loop of Henle: The next part of the tubule is the Loop of Henle, which is hairpin-shaped and consists of a descending and an ascending limb.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): The ascending limb of the Loop of Henle continues as another coiled tubular region called the distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
- Collecting Duct: The DCTs of multiple nephrons open into a straight tube called the collecting duct, which converges and opens into the renal pelvis through medullary pyramids in the calyces.
- Nephron Types:Cortical Nephrons: In the majority of nephrons, the Loop of Henle is short and extends only slightly into the medulla. These are called cortical nephrons. Juxtamedullary Nephrons: In some nephrons, the Loop of Henle is long and runs deep into the medulla, and these are known as juxtamedullary nephrons.
- Peritubular Capillaries: The efferent arteriole emerging from the glomerulus forms a fine capillary network around the renal tubule called the peritubular capillaries. A small vessel of this network runs parallel to the Loop of Henle, forming a ‘U’ shaped structure called the vasa recta. Vasa recta is either absent or highly reduced in cortical nephrons.
Functions of the Tubules
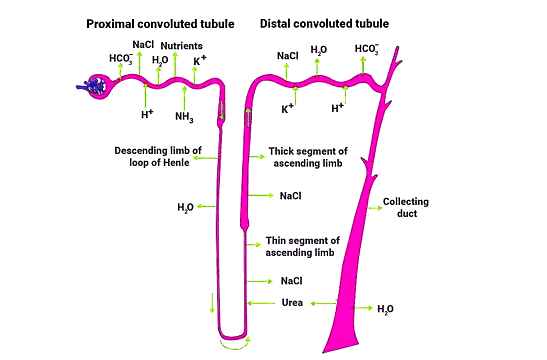
1. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- The PCT is lined with simple cuboidal brush border epithelium, which increases the surface area for reabsorption.
- Nearly all essential nutrients and 70-80% of electrolytes and water are reabsorbed in this segment.
- The PCT also helps maintain the pH and ionic balance of body fluids by selectively secreting hydrogen ions and ammonia into the filtrate and absorbing HCO3 – from it.
2. Loop of Henle
- Descending Limb: This part is permeable to water but nearly impermeable to electrolytes, which concentrates the filtrate as it descends.
- Ascending Limb: This region is impermeable to water but allows the active or passive transport of electrolytes. As the concentrated filtrate ascends, it gets diluted due to the passage of electrolytes into the medullary fluid.
- The ascending limb plays a crucial role in maintaining the high osmolarity of the medullary interstitial fluid.
3. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- The DCT is involved in the conditional reabsorption of Na+ and water.
- It can also reabsorb HCO3 – and selectively secrete hydrogen and potassium ions and ammonia to maintain the pH and sodium-potassium balance in the blood.
4. Collecting Duct
- This long duct extends from the cortex of the kidney to the inner parts of the medulla.
- It allows for the reabsorption of large amounts of water to produce concentrated urine.
- The collecting duct also permits the passage of small amounts of urea into the medullary interstitium to maintain osmolarity.
- Additionally, it helps regulate the pH and ionic balance of blood by selectively secreting H+ and K+ ions.
Counter-Current Mechanism
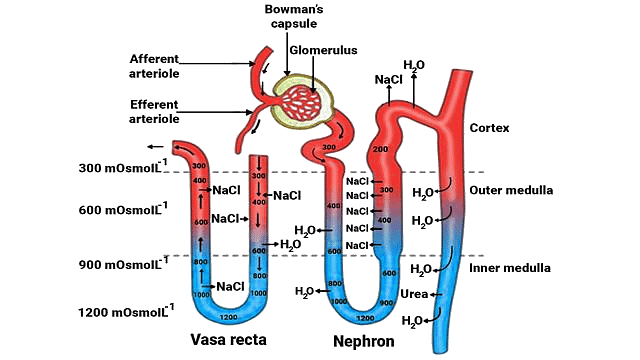
- Mammals can produce highly concentrated urine, aided by the structures of Henle's loop and the vasa recta.
- These structures function in a counter-current system, with the flow of filtrate in Henle's loop and blood in the vasa recta moving in opposite directions.
- This counter-current arrangement helps establish a concentration gradient in the inner medullary interstitium, ranging from 300 mOsmol/L in the cortex to 1200 mOsmol/L in the inner medulla.
- NaCl and urea are primarily responsible for this gradient.
- NaCl is transported by the ascending limb of Henle's loop, exchanged with the descending limb of the vasa recta, and returned to the interstitium.
- Urea enters the ascending limb of Henle's loop and is transported back to the interstitium by the collecting tubule.
- This counter-current mechanism maintains the concentration gradient, allowing for efficient water reabsorption and urine concentration.
- Human kidneys can produce urine up to four times more concentrated than the initial filtrate.
Diagram Based Questions NEET PYQs
Q1. Figure shows a human urinary system with structures labelled A to D. Select option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and/or functions. 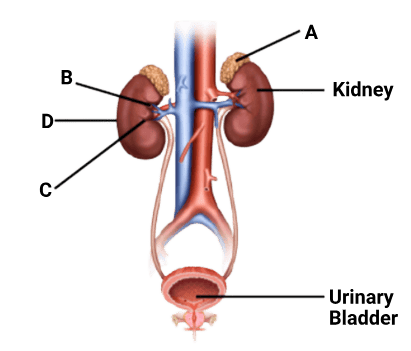
Option A: Adrenal gland-located at the anterior part of Kidney. Secrete catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown
Option B: Pelvis -broad funnel shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loop of Henle.
Option C: Medulla -inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons.
Option D: Cortex -outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons.
Ans: The correct option is A
A - Adrenal gland - is located at the anterior part of Kidney. Secrete catecholamines which helps regulate metabolism and helps body to respond to stress.
B - Renal pelvis - it collects urine from the calyces and funnels it into the ureter.
C - Medulla - it is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids.
D - Cortex - it is the outermost part of the kidney and contains the renal corpuscles and the renal tubules except for parts of the loop of Henle which descend into the renal medulla.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Excretory Products and their Elimination - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the role of the human excretory system in maintaining homeostasis? |  |
| 2. How is the structure of the kidney adapted for its function? |  |
| 3. What are the main parts of a nephron, and what are their functions? |  |
| 4. What is the counter-current mechanism in the nephron, and why is it important? |  |
| 5. What are the common excretory products, and how are they eliminated from the body? |  |
















