Important Diagrams: Human Health and Diseases | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Structure of Antibody |

|
| 2. Lifecycle of Retrovirus |

|
| 3. Life-cycle of Plasmodium vivax |

|
| Diagram Based Questions- NEET |

|
Human health and sickness are really important parts of being a human. They're closely connected to how our bodies work, where we live, and how we interact with others. Being healthy isn't just about not being sick; it's about feeling good physically, mentally, and socially.
Understanding the basic structures and processes through diagrams is useful for NEET aspirants in solving questions and deeper concept clarity. some of the important diagrams of this chapter are given below.
1. Structure of Antibody
An antibody has a Y-shaped structure with four polypeptide subunits, each containing two identical light and heavy chains.
- The N-terminus of the heavy chains forms antigen-binding domains (Fab), while the C-terminus forms a crystallization domain (Fc) for effector cell interaction.
- Disulfide and non-covalent bonds hold the subunits together.
- Antibodies have two identical antigen-binding sites with variations between them
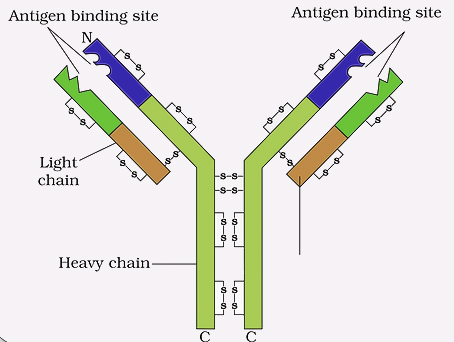 Structure of Antibody
Structure of Antibody
2. Lifecycle of Retrovirus
Retroviruses, a group of viruses within the Retroviridae family, possess RNA as their genetic material. Upon infecting a cell, they undergo reverse transcription, converting their RNA into DNA.
This viral DNA integrates into the host cell's DNA, initiating replication. An example of such a retrovirus is the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
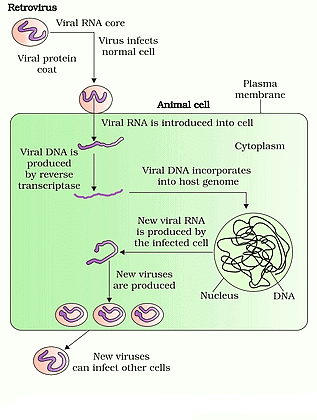 Life Cycle of retrovirus
Life Cycle of retrovirus
3. Life-cycle of Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium is a unicellular parasite that falls under the genus protozoans. The Plasmodium life cycle species includes development within a blood-feeding insect host, which injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal.
- Plasmodium is known to cause malaria, which occurs when a female Anopheles mosquito bites humans or any other mammal. Some other species of Plasmodium are P. malariae, P. ovale, and P. vivax.
- Plasmodium parasite have a complex life cycle consisting of three stages and it alternates between two hosts: humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes. The life cycle of Plasmodium consists of two phases – sexual phase, which occurs in insects and asexual phase that is completed in humans.
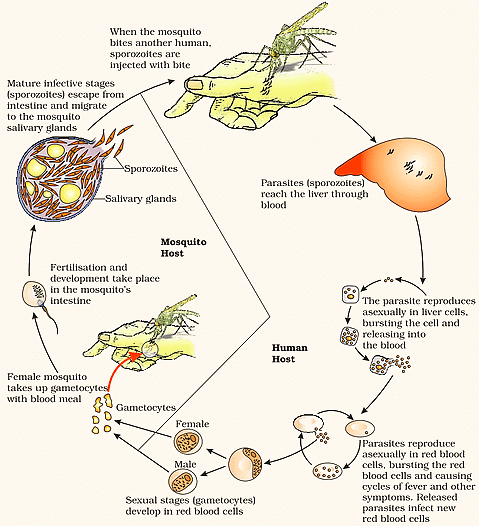
Diagram Based Questions- NEET
Q11: The infectious stage of plasmodium that enters the human body is : (NEET 2020)
(a) Female gametocytes
(b) Male gametocytes
(c) Trophozoites
(d) Sporozoites
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The life cycle of plasmodium that infects humans follows three stages:
Life Cycle of Plasmodium(i) infection of a human with sporozoites
(ii) asexual reproduction
(iii) sexual reproduction.
The two first take place exclusively in the human body, while the third one starts in the human body and is completed into the mosquito organism. The human infection begins when an infected female anopheles mosquito bites a person and injects infected with sporozoites saliva into the blood circulation i.e., the first life stage of plasmodium (stage of infection).
|
78 videos|386 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Human Health and Diseases - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the structure of an antibody? |  |
| 2. What is the lifecycle of a retrovirus? |  |
| 3. What is the life-cycle of Plasmodium vivax? |  |
| 4. How does the immune system respond to antibodies? |  |
| 5. How do antibodies provide immunity against pathogens? |  |















