Mnemonics: Neural Control and Coordination | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Let's memorise our Nervous System and Generation and Conduction of impulses with ease, linking and relating with our daily language and never ever forget it.
Happy mnemonic learning!
1. Parts of a Neuron
Mnemonic: Daisy Nanny Can Now Speak Assamese Marathi Nepali And Sindhi

Mnemonic Explanation: Mnemonic "Daisy Nanny Can Now Speak Assamese, Marathi, Nepali And Sindhi" is a helpful way to remember the parts of a neuron. A neuron is a specialised cell in the nervous system that transmits information in the form of electrical and chemical signals.
2. Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Mnemonic: "Polar Balance NK , Steve Deploarise AP & Nerve Repolarise "
Mnemonic Explanation:
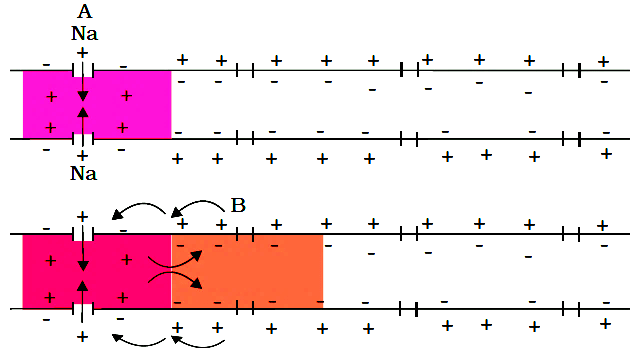 Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
- Polar - Polarisation: Resting state of the neuron with a polarized membrane.
- Balance : Sodium-Potassium Pump maintains balance (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in).
- Steve: Stimulus causes the membrane to become permeable to Na+.
- Depolarise: Depolarisation: Rapid Na+ influx causes depolarization at site A.
- AP : Action potential propagates as current flows to site B.
- Nerve Repolarise: Repolarisation restores resting potential via K+ efflux.
3. Parts of the Brain
Mnemonic:
- Forebrain: HTC Mobiles
- Midbrain: CC to mail
- Hindbrain: PCM subjects
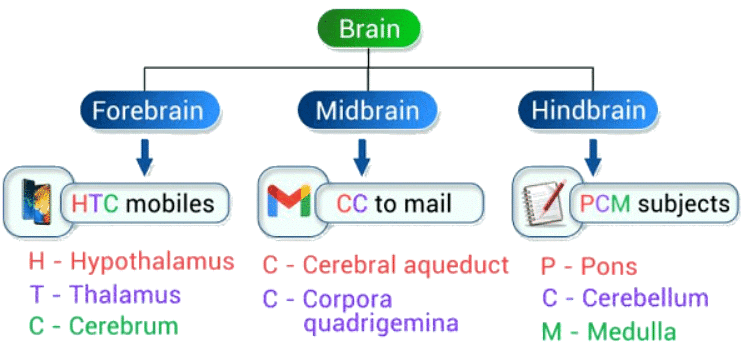
Mnemonic Explanation: Mnemonics "HTC Mobiles," "CC to mail," and "PCM subjects" can help you remember the major parts of the brain.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Neural Control and Coordination - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main parts of a neuron and their functions? |  |
| 2. How is a nerve impulse generated and conducted along a neuron? |  |
| 3. What are the key parts of the brain and their roles? |  |
| 4. What is the role of myelin in nerve impulse conduction? |  |
| 5. How do neurons communicate with each other? |  |
















