NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 12 > Mnemonics: Biodiversity and its Conservation
Mnemonics: Biodiversity and its Conservation | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Types of Biodiversity |

|
| 2. Causes of Loss of Biodiversity: The Evil Quartet |

|
| 3. Why Should We Conserve Biodiversity? |

|
| 4. In-Situ Conservation |

|
| 5. Ex-Situ Conservation |

|
Let's make your cramming journey easy to memorise with mnemonics.

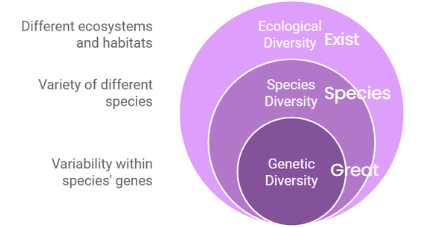
1. Types of Biodiversity
Mnemonic: "Great Species Exist"
Mnemonic Explanation
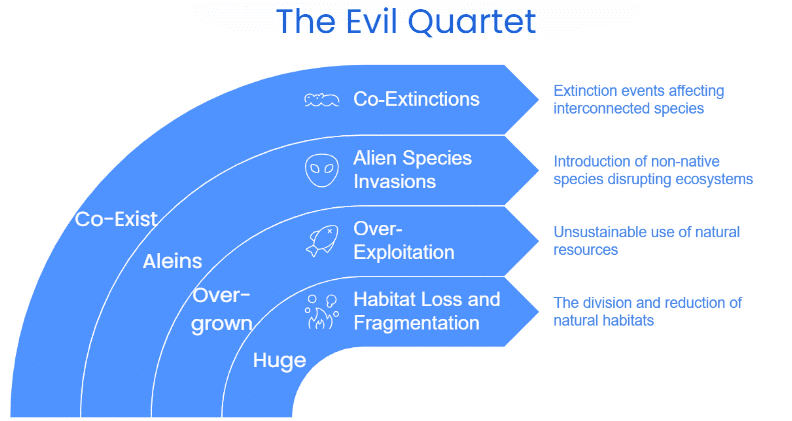
2. Causes of Loss of Biodiversity: The Evil Quartet
Mnemonic: "Huge Overgrown Aliens Coexist"
Mnemonic Explanation
Each word represents a primary cause:
3. Why Should We Conserve Biodiversity?
It is grouped into 3 categories
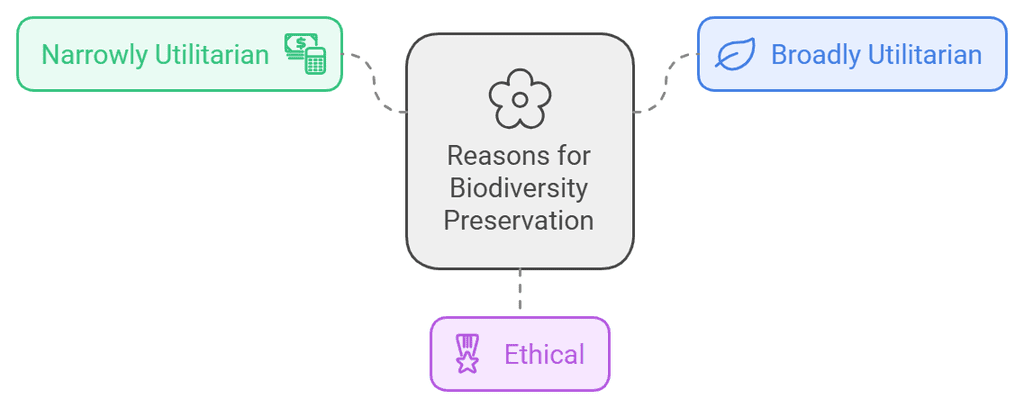
Mnemonic: "Nature Brings Eternal Value"
Mnemonic Explanation
Each word stands for one of the categories:
- Nature - Narrowly utilitarian (direct economic benefits like food, medicines, and materials)
- Brings - Broadly utilitarian (ecosystem services like oxygen production and pollination)
- Eternal - Ethical (moral duty to preserve biodiversity for its intrinsic value)
4. In-Situ Conservation
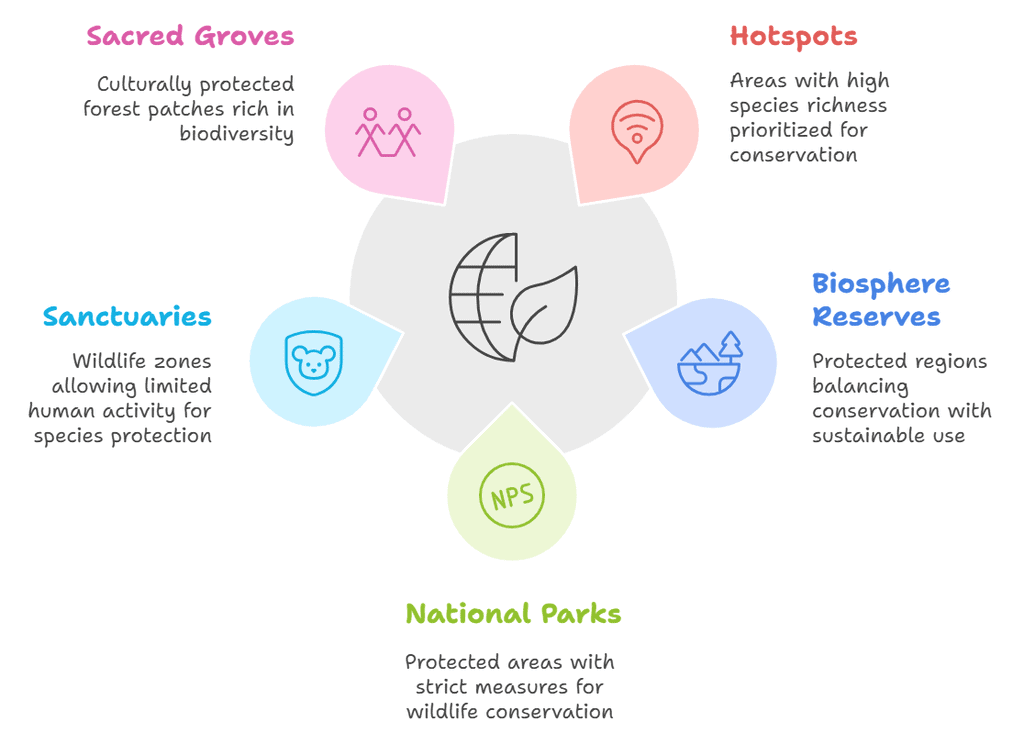 Mnemonic: "Hot Biospheres Naturally Secure Sacred Life"
Mnemonic: "Hot Biospheres Naturally Secure Sacred Life"
Mnemonic Explanation
Each part represents an in situ conservation approach:
- Hot - Hotspots (biodiversity hotspots with high species richness)
- Biospheres - Biosphere reserves
- Naturally - National parks
- Secure - Sanctuaries
- Sacred - Sacred groves
- Life - Reminds us of the goal: to protect biodiversity and life forms.
5. Ex-Situ Conservation
Mnemonic: "Zoo Babies Cry for Seeds"
Mnemonic Explanation
Each word represents a method of ex situ conservation:
- Zoo - Zoological parks
- Babies - Botanical gardens
- Cry - Cryopreservation (preserving gametes)
- Seeds - Seed banks
The document Mnemonics: Biodiversity and its Conservation | Biology Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Biodiversity and its Conservation - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the different types of biodiversity? |  |
Ans. Biodiversity can be categorized into three main types: genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species, which contributes to the adaptability and resilience of populations. Species diversity encompasses the variety of species in a given area, including the number of different species and their relative abundance. Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems in a particular region, including the different habitats, communities, and ecological processes that occur.
| 2. What is "The Evil Quartet" in the context of biodiversity loss? |  |
Ans. "The Evil Quartet" refers to four primary factors contributing to the loss of biodiversity: habitat destruction, overexploitation, invasive species, and climate change. Habitat destruction occurs through activities like deforestation and urbanization, leading to the loss of natural environments. Overexploitation involves the unsustainable use of resources, such as overfishing or poaching. Invasive species are non-native organisms that disrupt local ecosystems and outcompete native species. Climate change alters habitats and affects species survival, leading to shifts in biodiversity.
| 3. Why is it important to conserve biodiversity? |  |
Ans. Conserving biodiversity is crucial for several reasons. It ensures ecosystem stability and resilience, allowing ecosystems to recover from disturbances. Biodiversity also provides essential services to humans, including clean air, water, pollination of crops, and disease regulation. Additionally, genetic diversity is vital for food security and adaptability to changing environmental conditions. The loss of biodiversity can disrupt these services, leading to negative impacts on human health, agriculture, and overall quality of life.
| 4. What is in-situ conservation, and how does it work? |  |
Ans. In-situ conservation refers to the conservation of species in their natural habitats. This approach involves protecting and managing natural ecosystems to maintain their biodiversity. It can include establishing protected areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas. In-situ conservation allows for the natural processes of evolution and adaptation to occur, supporting the survival of species in their native environments. It also involves the sustainable management of resources to ensure that local communities can coexist with wildlife.
| 5. What are some methods of ex-situ conservation? |  |
Ans. Ex-situ conservation involves the preservation of species outside their natural habitats. Common methods include the establishment of botanical gardens, zoos, and seed banks. Botanical gardens cultivate and conserve plant species, often focusing on rare or endangered varieties. Zoos provide a controlled environment for the conservation of animal species, facilitating breeding programs and research. Seed banks store genetic material from various plant species, preserving them for future restoration efforts. These methods help protect species from extinction and support biodiversity conservation efforts.
Related Searches