Class 8 Science Chapter 7 HOTS Questions - Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Q1: One day Seema’s uncle visited her place. Seema prepared dinner for him. When she was about to put rock salt on the salad, her uncle interrupted her and asked to put iodised salt instead of rock salt. He also advised her to prefer iodised salt instead of rock salt. Why do you think Seema’s uncle advised her to have iodised salt instead of rock salt?
Ans: Deficiency of iodine causes goitre disease in our body. This is why Seema’s uncle advised her to have iodised salt.
Q2: It is said that height of a child depends upon the genes inherited from the parents. Are there factors other than genes that causes variation in height?
Ans: Other factors like nutrition, release of growth hormones, exercises, diseases, etc., also have impact on the height of a growing child.
Q3: Is a woman responsible for the birth of a girl child? Explain.
Ans: No, because a woman has eggs of only X chromosomes but a male has sperms of both X and Y chromosomes. It is the type of male chromosome (X or Y) which fuses with the egg and determine the sex of the foetus, i.e., whether it will be male (XY) or female (XX) child.
Q4: John and Radha were classmates since childhood. When Radha became eleven years old, she developed a little swelling on her neck. She visited the doctor who started medication for her. After a few years, John also developed a slight protrusion on his throat. He got worried and went to the doctor. But, the doctor assured him that it was a normal feature in boys while they are growing up. Can you think of any reasons for the difference in diagnoses?
Ans: The swelling on the neck of Radha may be because of insufficient production of thyroxine which results in goitre. However slight protrusion in John’s throat may be due to enlargement of voice box, also known as Adam’s apple, in adolescent boys.
Q5: Why we should not take medicines or drugs unless prescribed by a doctor?
Ans: Certain medicines have specific dosage levels and adverse side effects which if not followed may be proved lethal to us. Drugs can be addictive too and can ruin our health and happiness.
Q6: Salma had a very soft and smooth skin during her childhood. As she entered adolescence, she developed pimples on her face, her body became taller compared to her face. She got worried of all of the sudden changes. Her mother explained that all these changes are normal and advised her to wash her face at regular intervals.
- Why Salma’s mother advised Salma to wash her face at regular intervals?
- What is the reason for appearance of pimples on her face?
- Why Salma experienced disproportionate growth of the body?
- What values do we get from this?
Ans:
- Regular face wash keeps the face clean and dry and helps to reduce the pimples.
- During adolescence, secretion of sweat glands and sebaceous glands increases leading to formation of acne and pimples.
- During adolescence, all parts of the body do not grow at the same rate. Sometimes the arms and legs or hands and feet of adolescents look oversized and out of proportion with the body.
- We must be self-aware, must take proper care and diet during the growing period, not get worried or lose our self-esteem.
Q7: What changes occur in human at puberty?
Ans: There are various changes in human at puberty. They are as follows:
- Change in height: During puberty, there is sudden increase in height in boys and girls. Initially, girls grow faster in height than in boys. But both reach their maximum height at the age of 18 years.
- Change in voice: Boys develop larger voice box or larynx to form protruding part of throat called Adam’s apple making their voice hoarse, girls have high pitched voice.
- Change in body shape: In boys, shoulders broaden and muscles grow more prominently than in girls. In girls the region below the waist becomes wider.
- Secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands (oil glands) in both boys and girls increases and acne or pimples grow on faces of many youths.
- Development of sex organs: In males, testes and penis develop completely. Testes begin producing sperms. In girls, ovaries are enlarged and begin to produce eggs. Both boys and girls reach reproductive maturity.
- In girls, menstruation or periods starts.
- All human beings attain mental, intellectual and emotional maturity at puberty.
- Facial hair like moustache and beard are grown in boys. Hair are grown in armpit and pubic region in both boys and girls. Breasts are developed in girls. These characters are called secondary sexual characters as they distinguish a male from a female.
Q8: Explain the reproductive phase of life in humans.
Ans: Boys and girls become capable of reproduction at puberty because their testes and ovaries begin to release gametes, i.e., sperms and ova respectively. In girls, reproductive phase of life begins at puberty from 10 to 12 years of age and generally lasts till the age of 45 to 50 years. The ova begin to mature with the onset of puberty. The ovum matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in 28 to 30 days. During this period, the wall of the uterus becomes thick so as to receive the egg, in case it is fertilised and begins to develop. This results in pregnancy. If fertilisation does not occur, the released egg, and the thickened lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels are shed off.
This causes menstruation. It occurs once in about 28 to 30 days. The first menstrual flow begin at puberty and is termed as menarche. The menstruation stops at the age of 45 to 50. This stage is known as menopause. In male, the reproductive phase begins at puberty at the ages 14-15 and lasts as long as he is healthy.
Q9: Explain the term reproductive health. What should we do to maintain reproductive health?
Ans: The state of physical, mental and social well being of an individual is regarded as an individual’s health. A healthy person is free from disease, tension and anxiety. Reproductive health refers to a state of physical, mental and social well-being in all matters relating to the reproductive system, at all stages of life. We should take following measures to maintain reproductive health:
- To have a balanced diet: As far as practicable, we should have a balanced diet, i.e., a diet contain
- ing proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. We can have our food which contain these nutrients.
- To take physical exercise: We should take physical exercise like morning walk, running, etc., daily.
- To maintain personal hygiene: We should maintain personal hygiene to stay fit and healthy. We should wash our body especially pubic region, armpit, etc., properly.
- Avoid harmful drugs: We should avoid taking harmful drugs and alcohol.
Q10: Explain sex determination in human.
Ans: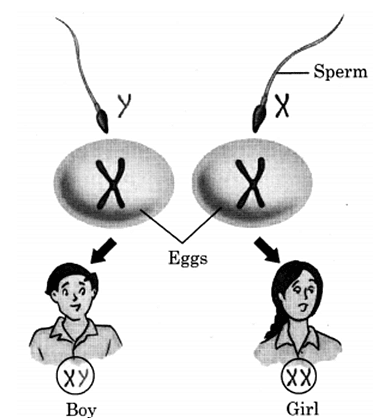
Sex determination of a baby is done at the time of fertilisation when a male gametes fuse with a female gamete. It depends on male partner whether the baby will be a male child or female child. The chances of child to be male or female actually depend on the chromsomes present in the fertilised eggs or ova. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nuclei of all human beings out of which two are sex chromosomes named X and Y. A male has one X and one Y chromosome and a female has two X chromosomes. The gametes (egg and sperm) have only one set of chromosomes. The unfetilised egg always has one X chromosome. But sperms are of two kinds. One kind has an X chromosome, and the other kind has a Y chromosome. When a sperm containing X chromosome fertilises the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes and develop into a female child. If the sperm contributes a Y chromosome to the egg (ovum) at fertilisation, the zygote would develop into a male child. Fig. shows sex determination in humans.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|





















