Conjugate in Math | Advance Learner Course: Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Introduction
The term "conjugate" signifies a pairing of two elements. For instance, consider two smileys, one depicting a smile and the other a sad expression, which are almost identical except for their opposite facial features. In mathematics, "conjugate" refers to the transformation of a surd or a complex number, involving a sign change based on specific conditions.
What is Conjugate in Math?
In mathematics, a conjugate is created by altering the sign between the two terms in a binomial, following the condition that the sum and product of the binomial and its conjugate result in rational numbers. This applies to binomials containing either surds or complex numbers. Let's examine some examples of binomials and their corresponding conjugates.
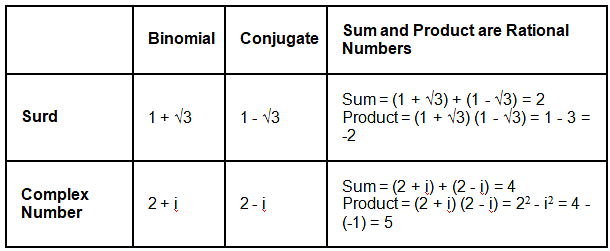
We study two types of conjugates in math.
- Conjugate of a Surd
- Conjugate of a Complex Number
Let us study each of these in detail
Conjugate of a Surd
The conjugate of a surd x + y√z is always x - y√z and vice versa. This is because the sum is (x + y√z) + (x - y√z) = 2x, and the product = (x + y√z) (x - y√z) = x2 - (y√z)2 = x2 - y2z (by the formula of a2 - b2) are rational numbers. For example, for the surd 3 + √2, the conjugate surd is 3 - √2, this is because:
Their sum = (3 + √2) + (3 - √2) = 6 and
Their product = (3 + √2) (3 - √2) = 9 - 2 = 7
Here, both 6 and 7 are rational numbers. Note that to find the conjugate of a surd, just change the sign of the surd (irrational part), but it is not changing the middle sign always. For example, the conjugate of the surd √2 + 3 is -√2 + 3, but NOT √2 - 3. Because, if we assume that √2 - 3 is the conjugate of √2 + 3, then their sum is 2√2, which is NOT a rational number. Here are some more examples of conjugates of surds in math.
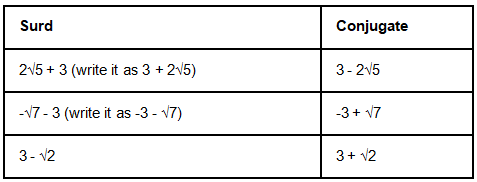
The easiest way of writing conjugate surd is to find the conjugate is just to write the given number in the order of rational part first and irrational part next and then change the middle sign.
Conjugate of a Complex Number
The complex conjugate of a complex number z = x + iy is x - iy (and vice versa) and it is represented by 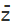 as their sum (2x) and the product x2 + y2 both are rational numbers. To write the complex conjugate,
as their sum (2x) and the product x2 + y2 both are rational numbers. To write the complex conjugate,
- Write the given complex number in the form of x + iy (real part first and then the imaginary part)
- Change the middle sign. Then the complex conjugate of x + iy is x - iy.
Here are some examples of conjugates of complex numbers.
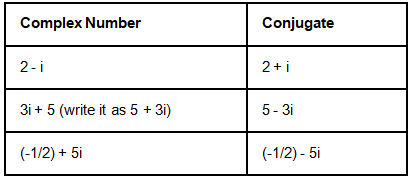
Conjugate and Rational Factor
If the product of two surds is a rational number, then each one of them is called the rational factor of the other. For example, the rational factors of 2 + √3 are each of 2 - √3 and -2 + √3. This is because by multiplying 2 + √3 with each of their conjugates result in a rational number as shown below.
- (2 + √3) (2 - √3) = 4 - 3 = 1
- (2 + √3) (-2 + √3) = -4 + 3 = -1
Note that -2 + √3 is NOT a conjugate of 2 + √3, its only a rational factor.
Sometimes, rational factor and conjugate of a number are referred to as the same but there is one minor difference between them. The sum of a binomial and its rational factor does NOT need to be a rational number, but the sum of a binomial and its conjugate SHOULD be a rational number. On the other hand, the product of a binomial with each of its rational factor and conjugate should be a rational number.
Conjugates and Rationalization
Rationalization of the denominator is the process of multiplying a fraction (with an irrational or complex denominator) by its rational factor or conjugate to make the denominator a rational number. This is because it is very convenient to have rational numbers in the denominators to compare or make some calculations in math. Here are two examples to understand how to rationalize the denominators by using conjugates.
Rationalization of Surds Example:
Q. Rationalize the denominator of 1 / (3 + √2).
Sol: The conjugate of 3 + √2 is 3 - √2. Multiplying and dividing the given fraction by 3 - √2,
1 / (3 + √2) × (3 - √2) / (3 - √2)
= (3 - √2) / (32 - (√2)2)
= (3 - √2) / (9 - 4)
= (3 - √2) / 5
Rationalization of Complex Numbers Example:
Q. Rationalize the denominator of 1 / (1 + i).
Sol: The complex conjugate of 1 + i is 1 - i.
1 / (1 + i) × (1 - i) / (1 - i)
= (1 - i) / (12 - i2)
= (1 - i) / (1 + 1) (Because by powers of iota, i2 = -1)
= (1 - i) / 2
Important Notes on Conjugate in Math
- If z = x + √y and its conjugate is

- If z = x + iy and its conjugate is

- For a complex number z, if
 then z is purely imaginary.
then z is purely imaginary. - The modulus of a complex number and its conjugate are always the same. i.e.,
 for any complex number z.
for any complex number z. - The conjugates are very useful in rationalization.
Examples
Q1. If x = 2 + √3, then find 1/x.
Ans: 2 - √3.
Sol:
1/x = 1 / (2 + √3). The conjugate of 2 + √3 is 2 - √3. Multiplying and dividing 1/x by the conjugate,
1/x = (2 - √3) / [ (2 + √3) (2 - √3)]
= (2 - √3) / (4 - 3)
= (2 - √3) / 1
= 2 - √3
Q2. For the value of x given in Example 1, compute the value of x2 + 1/x2.
Ans: 10
Sol:
x2 = (2 + √3)2
= 2 + 2(2) √3 + (√3)2 (Using (a+b)2 Formula)
= 2 + 4√3 + 3
= 5 + 4√3
1/x2 = (1/x)2 = (2 - √3)2
= 2 - 2(2) √3 + (√3)2 (Using (a-b)2 Formula)
= 2 - 4√3 + 3
= 5 - 4√3
Now, x2 + 1/x2 = (5 + 4√3) + (5 - 4√3) = 10.
Q3. Find the values of a and b if (3 + √7) / (3 - √7) = a + b√7.
Ans: a = 8 and b = 3.
Sol:
It is given that (3 + √7) / (3 - √7) = a + b√7.
Here the conjugate of the denominator 3 - √7 is 3 + √7. So, we get
= (3 + √7) / (3 - √7) × (3 + √7) / (3 + √7)
= (9 + 6√7 + 7) / (9 - 7)
= (16 + 6√7) / 2
= 8 + 3√7
= a + b√7
Comparing the rational and irrational parts, a = 8 and b = 3.
|
5 videos|57 docs|20 tests
|
|
5 videos|57 docs|20 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
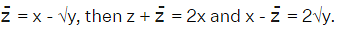
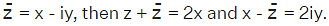
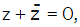 then z is purely imaginary.
then z is purely imaginary.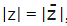 for any complex number z.
for any complex number z.















