Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Practice Question Answers - Motion
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: A body thrown vertically upwards reaches a maximum height h. It then returns to ground. The distance and the displacement travelled by the body respectively are
(a) 2h , zero
(b) h , zero
(c) zero, 2h
(d) zero, h
Ans: (a)
Distance = h + h = 2h
Displacement = h - h = zero
Q2: In a long distance race, the athletes were expected to take four rounds of the track such that the line of finish was same as the line of start. Suppose the length of the track was 200 m. The what is the displacement of the athletes when they touch the finish line?
(a) zero
(b) 3 m
(c) 5 m
(d) 7 m
Ans : (a)
Displacement = 0 (zero), as athletes finish at the starting line.
Q3: A quantity has a value of -6 0. / m s. It may be the
(a) speed of a particle
(b) velocity of a particle
(c) position of a particle
(d) displacement of a particle
Ans : (b)
If a body travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, how so ever small these intervals may be, then the body is said to be moving with uniform speed. This motion is known as uniform motion.
Q4: Which of the following options is correct for the object having a straight line motion represented by the following graph? (a) The object moves with constantly increasing velocity from O to A and then it moves with constant velocity.
(a) The object moves with constantly increasing velocity from O to A and then it moves with constant velocity.
(b) Velocity of the object increases uniformly.
(c) Average velocity is zero.
(d) The graph shown is impossible.
Ans : (c)
From given, it is clear that the net displacement is zero. So, average velocity will also be zero.
Q5: An object is sliding down an inclined plane. The velocity changes at a constant rate from 10 cm/s to 15 cm/s in two seconds. What is its acceleration? (a) 10 cm/s2
(a) 10 cm/s2
(b) 2.9 cm/s2
(c) 2.5 cm/s2
(d) 40 cm/s2
Ans : (c)
The situation is shown in figure. Let us take BA as the positive direction. The velocity at t = 0 is u =+ 10 cm/s and that at t = 2 s is v =+ 15 cm/s. Thus, The acceleration is positive, which means it is in the direction BA.
The acceleration is positive, which means it is in the direction BA.
Q6: The area under speed-6time graph represents a physical quantity whose unit is equal to the unit of
(a) light year
(b) area
(c) volume
(d) acceleration
Ans: (a)
The area under speed-time graph represents distance and the unit of distance is metre (m), which is same as the unit of light year (1ly = 3.15 × 107 m)
Q7: The graph shows the variation of velocity of a rocket with time. Then, the maximum height attained by the rocket is (a) 1.1 km
(a) 1.1 km
(b) 5 km
(c) 55 km
(d) none of these
Ans: (c)
Q8: If a car at rest accelerates uniformly to a speed of 144 km/h in 20 sec., it covers a distance of
(a) 20 cm
(b) 400 m
(c) 1440 cm
(d) 2980 cm
Ans: (b)
or
∴ 
= 2m/s2
Now
Q9: If a body moves with uniform velocity, then the acceleration is equal to
(a) zero
(b) constant
(c) finite
(d) infinite
Ans: (a)
We know that
When a body moves with a uniform velocity then the value of change in the velocity is zero. Hence acceleration is also zero.
Q10: The displacement of a particle is given by
y = a + bt + ct2 - dt4
The initial velocity and acceleration are respectively
(a) b, -4d
(b) -b, 2c
(c) b, 2c
(d) 2c, -4d
Ans: (c)
Now
∴ a0 = 2x - 12d(0)2 = 2c, (at t = 0)
Q11: Which of the following speed time graphs is not possible ?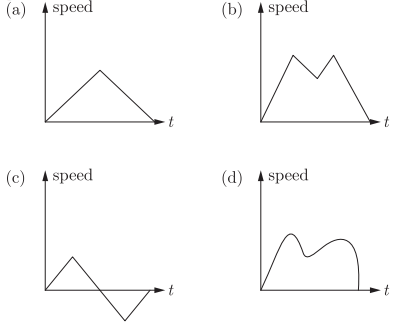 Ans: (c)
Ans: (c)
This is because speed can never be negative.
Q12: If the motion is in straight line without change in direction then
(a) distance ≠ |displacement|
(b) distance > |displacement|
(c) distance < |displacement|
(d) distance = |displacement|
Ans: (d)
In the straight line motion distance is always equal to the displacement.
Q13: A passenger travels along the straight road for half the distance with velocity v1 and the remaining half distance with velocity v2. Then average velocity is given by
(a) v1v2
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (d)
Q14: A particle covers half of the circle of radius r. Then the displacement and distance of the particle are respectively
(a) 2πr, 0
(b) 2r, πr
(c) 
(d) πr, r
Ans: (b) When a particle cover half of circle of radius r , then displacement is AB = 2r
When a particle cover half of circle of radius r , then displacement is AB = 2r
distance = half of circumference of circle = π r
Fill in the blanks.
Q15: The magnitude of average velocity .......... equal to the average speed.
Ans: may or may not be
The magnitude of average velocity may or may not be equal to the average speed because average speed is the total distance covered divided by the total time taken, whereas average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time taken. If the direction of motion changes, the magnitude of average velocity can be different from average speed.
Q16: A body, dropped from a tower with zero velocity, reaches the ground in 4 sec. The height of the tower is about .......... m
Ans: 80
If a body is dropped from a tower with zero velocity and it reaches the ground in 4 seconds, the height of the tower is about 80 m. This is calculated using the second equation of motion, h = 1/2gt2, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (assumed to be 10 m/s2) and t is the time taken (4 seconds).
Q17: When negative acceleration acts on a moving body its velocity ..........
Ans: decreases
When negative acceleration, also known as deceleration, acts on a moving body, its velocity decreases. This is because acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. If the acceleration is negative, this means that the velocity is decreasing over time.
Q18: Distance travelled divided by elapsed time gives ..........
Ans: average speed
When we divide the total distance travelled by the total elapsed time, the value obtained is known as the average speed. This is because average speed is defined as the ratio of the total distance covered to the total time taken.
Q19: A ball thrown vertically upwards return to its starting point in 4s. If g = 10 m/s2, its initial speed was ..........
Ans: 20 m/s
If a ball is thrown vertically upwards and returns to its starting point in 4 seconds, its initial speed was 20 m/s. This is found using the equation of motion, v = u - gt, where v is the final velocity (0 m/s as it returns to the starting point), u is the initial velocity (which we need to find), g is the acceleration due to gravity (10 m/s2) and t is the time taken (4 seconds).
True/False
Q20: A particle is known to be at rest at time t = 0. If its acceleration at t = 0 must be zero.
Ans : False
The statement is false because even if a particle is at rest at a certain time, it doesn't necessarily imply that its acceleration must be zero at that time. The particle could be at the beginning or end of a motion, so it could be at rest but still accelerating or decelerating. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, not the state of motion.
Q21: Magnitude of acceleration is constant in the rotating motion along a circular path.
Ans : True
This statement is true because in a circular path, even though the direction of acceleration (towards the centre of circle) changes, the magnitude of acceleration remains constant. This is because the speed of the rotating object is constant, hence the rate of change of velocity remains constant.
Q22: Magnitude of displacement can be equal to or lesser than distance.
Ans : True
This statement is true because displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final position of a point. Therefore, the magnitude of displacement is either equal to the distance (when the motion is in a straight line) or less than the distance (when the motion is along a curved path).
Q23: In a journey, numerical value of displacement ≤ distance.
Ans : True
This statement is true as it is just a numerical representation of the third statement. Displacement is a vector quantity that considers the shortest path, while distance is a scalar quantity that considers the total path covered. Hence, displacement can be less than or equal to the distance.
Q24: If particle speed is constant, acceleration of the particle must be zero.
Ans : False
This statement is false because even if the speed of a particle is constant, it can still have acceleration. This is because acceleration is not just related to changes in speed, but also changes in direction. For instance, when a particle moves in a circular path at constant speed, it still experiences acceleration due to a continuous change in direction.
Matching Questions
Direction: In the section, each question has two matching lists. Choices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q25: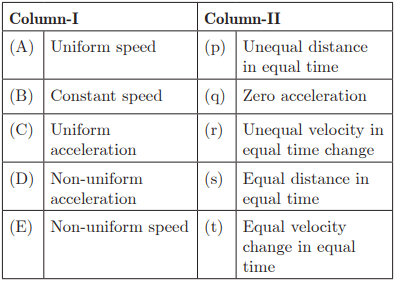 Ans: (A) - (s), (B) - (q), (C) - (t), (D) - (r), (E) - (p)
Ans: (A) - (s), (B) - (q), (C) - (t), (D) - (r), (E) - (p)
Q26: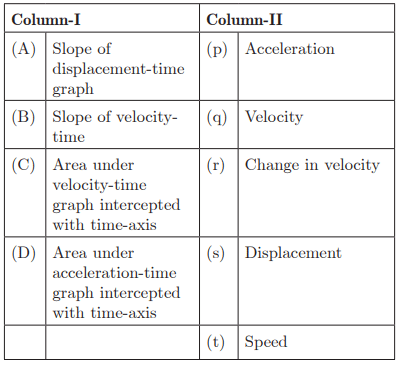 Ans: (A) - (q), (B) - (p), (C) - (s), (D) - (r)
Ans: (A) - (q), (B) - (p), (C) - (s), (D) - (r)
Q27: Ans: (A) - (s), (B) - (p), (C) - (t), (D) - (r), (E) - (q)
Ans: (A) - (s), (B) - (p), (C) - (t), (D) - (r), (E) - (q)
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















