Unit Test (Solutions): Resources & Development | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
(a) Solar energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Fossil fuels
(d) Tidal energy
Ans: (c) Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are non-renewable resources because they are formed over millions of years and cannot be quickly replenished.
Q2: Which type of soil is known as 'black soil' due to its color? (1 Mark)
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Regur soil
Ans: (d) Regur soil
Regur soil, also known as black soil, is dark in color and is found in the Deccan Plateau region of India. It is highly fertile and suitable for growing various crops.
Q3: Which one of the following is a human-made resource? (1 Mark)
(a) Forests
(b) Minerals
(c) Rivers
(d) Dams
Ans: (d)
Dams are human-made structures that harness the power of rivers to generate electricity, store water for irrigation, and control flooding.
Q4: Define the term 'Sustainable Development'. (1 Mark)
Ans: Sustainable Development refers to the balanced and equitable use of resources in a manner that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves economic, social, and environmental considerations to ensure long-term well-being.
Q5: Why is conservation of resources important? (1 Mark)
Ans: Conservation of resources is important to ensure their availability for future generations and to maintain a balanced ecosystem. It helps prevent resource depletion, environmental degradation, and ensures that resources are used efficiently and responsibly.
Q6: Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources. (2 Marks)
Ans: Renewable resources are those that can be naturally replenished over a relatively short period of time, such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass. Non-renewable resources, on the other hand, are finite and cannot be quickly replaced, such as fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and minerals. Renewable resources are sustainable in the long run, while non-renewable resources are exhaustible.
Q7: How can we conserve water resources at the individual level? (2 Marks)
Ans: At the individual level, water conservation can be achieved by adopting simple practices such as fixing leaky faucets, using water-efficient appliances, harvesting rainwater, and avoiding wasteful water practices like leaving taps running. Conserving water in daily activities like bathing, washing, and gardening can collectively make a significant impact on water conservation.
Q8: Explain the term 'land degradation' and mention two human activities responsible for it. (2 Marks)
Ans: Land degradation refers to the deterioration of land quality due to various human activities and natural processes. Two human activities responsible for land degradation are:
- Deforestation: Clearing of forests for agriculture, urbanization, and logging leads to soil erosion and loss of fertile topsoil.
- Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can lead to soil compaction, reduced vegetation cover, and soil erosion, degrading the land's productivity.
Q9: Describe the three types of soil erosion and their causes. (3 Marks)
Ans: The three types of soil erosion are:
- Sheet Erosion: This occurs when a thin layer of topsoil is removed uniformly from a large area due to the impact of raindrops and flowing water. It is mainly caused by heavy rainfall and lack of vegetation cover.
- Rill Erosion: It involves the formation of small channels (rills) on the soil surface due to concentrated runoff. It usually occurs on slopes and is a result of heavy rain and poor land management practices.
- Gully Erosion: Gullies are larger and deeper channels formed by the continuous flow of water through rills. Gully erosion is caused by the accumulation of runoff water and often occurs when rills are left unchecked.
Q10: Explain the concept of 'water scarcity' and suggest three measures to address it. (3 Marks)
Ans: Water scarcity refers to a situation where the demand for water exceeds the available supply. It can result from factors like increasing population, pollution, and unequal distribution of water resources. Measures to address water scarcity include:
- Rainwater Harvesting: Capturing and storing rainwater for later use can help recharge groundwater and supplement water sources.
- Efficient Irrigation Techniques: Promoting techniques like drip irrigation and sprinklers can minimize water wastage in agriculture.
- Water Conservation Awareness: Educating people about the importance of water conservation and encouraging responsible water use can help reduce demand and wastage.
Q11: Three Marks Question: Describe any three methods of soil conservation. (3 Marks)
Ans: Three methods of soil conservation are: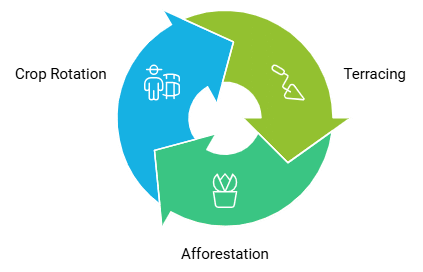
- Terracing: Creating flat platforms on slopes to reduce the speed of water runoff and soil erosion. Terracing also helps retain water and soil nutrients, making it suitable for cultivation.
- Afforestation: Planting trees and vegetation on barren lands helps bind the soil, prevent erosion, and improve soil fertility.
- Crop Rotation: Alternating the types of crops grown in a field over different seasons helps maintain soil fertility, prevent nutrient depletion, and control soil erosion.
Q12: Explain the concept of 'mineral resources' and discuss the importance of conservation of minerals. (5 Marks)
Ans: Mineral resources are naturally occurring substances found in the Earth's crust that have economic value. They are essential for industrial, technological, and economic development. Conservation of minerals is crucial because: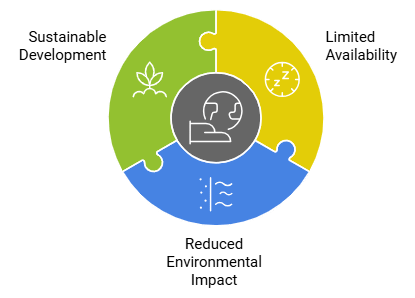
- Limited Availability: Minerals are finite resources that take millions of years to form. Overexploitation can lead to their depletion, affecting industries and future generations.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Extracting minerals often involves destructive methods that harm ecosystems, disrupt habitats, and release pollutants. Conservation helps minimize such impacts.
- Sustainable Development: Conserving minerals ensures their availability for future generations and contributes to sustainable development by preventing resource exhaustion.
Q13: Discuss the challenges of sustainable management of forests in India and suggest measures to overcome them. (5 Marks)
Ans: Sustainable management of forests in India faces several challenges, including: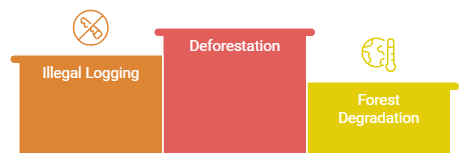
- Deforestation: Due to urbanization, agriculture expansion, and logging, forests are being cleared at an alarming rate, leading to habitat loss, soil erosion, and reduced biodiversity.
- Illegal Logging: Unregulated and illegal logging poses a significant threat to forest ecosystems, depleting valuable timber and disrupting natural habitats.
- Forest Degradation: Overgrazing, encroachment, and unsustainable resource extraction degrade forest quality and reduce their ability to provide ecosystem services.
Measures to overcome these challenges include: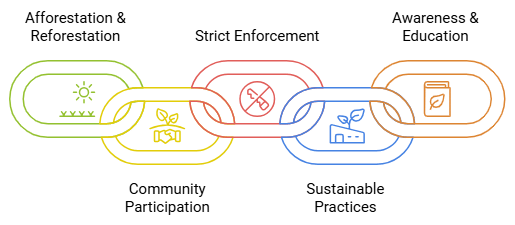
- Afforestation and Reforestation: Planting trees on deforested lands and restoring degraded forests can help restore ecosystem balance and provide habitats for wildlife.
- Community Participation: Involving local communities in forest management and providing them with incentives for sustainable resource use can reduce illegal activities.
- Strict Enforcement: Enforcing laws against illegal logging and encroachment, along with penalties for violations, can deter such activities and protect forests.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable logging practices, eco-tourism, and non-timber forest product collection can provide livelihoods while preserving forests.
- Awareness and Education: Educating people about the importance of forests and their role in climate regulation can foster a sense of responsibility towards forest conservation.
|
90 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Resources & Development - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main types of resources discussed in the Resources & Development chapter? |  |
| 2. How can resources be classified based on their availability? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of sustainable development in resource management? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact the availability of natural resources? |  |
| 5. What role does technology play in the development of resources? |  |






















