Nervous System - 2 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Fill in the Blanks.
(i) The __________ is the control centre of the nervous system.
Ans: The brain is the control centre of the nervous system.
The brain processes and interprets information received from the sensory organs and sends out commands to the muscles and glands.

(ii) The basic unit of the nervous system is the __________.
Ans: The basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron.
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals, allowing communication within the nervous system.
(iii) The three main parts of the brain are the __________, __________, and __________.
Ans: The three main parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
The cerebrum is responsible for conscious activities, the cerebellum for coordination and balance, and the brainstem controls essential functions like breathing and heartbeat.
(iv) The __________ system controls involuntary actions like breathing and heartbeat.
Ans: The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary actions like breathing and heartbeat.
The autonomic nervous system regulates processes that occur automatically without conscious effort, such as heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.)
(v) The gap between two nerve cells is called the __________.
Ans: The gap between two nerve cells is called the synapse.
At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released from one nerve cell, allowing the signal to pass to the next nerve cell.)
Q2: Match the Column.
Match the parts of the nervous system with their functions by drawing a line to connect them.
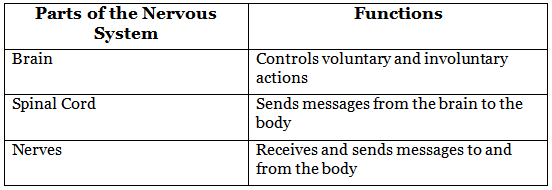 Ans:
Ans:
Brain - Controls voluntary and involuntary actions
Spinal Cord - Sends messages from the brain to the body
Nerves - Receives and sends messages to and from the body
Q3: True or False.
(i) The brain is responsible for controlling all body functions.
Ans: False
While the brain is a vital organ that controls many body functions, it doesn't control all of them. Some functions are regulated by other parts of the nervous system.
(ii) Nerves are the tiny organs inside our body.
Ans: False
Nerves are not organs, but bundles of nerve fibers that transmit signals between different parts of the body and the brain.
(iii) The spinal cord is part of the peripheral nervous system.
Ans: False
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system, along with the brain. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
(iv) The autonomic nervous system controls voluntary actions.
Ans: False
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary actions, not voluntary actions. Voluntary actions are controlled by the somatic nervous system.
(v) Motor nerves send impulses from the brain to the muscles and glands.
Ans: True
Motor nerves send impulses from the brain and spinal cord to different parts of the body.
Q4: Arrange in Correct Order.
Put the following events in the correct order to show how a message travels through the nervous system.
(a) The brain receives and interprets the message.
(b) The nerve cell sends the message.
(c) Brain sends a response message.
(d) Sense organs detect something.
(e) Nerve cell receives the message.
Ans: Sense organs detect something. → Nerve cell sends the message. → Nerve cell receives the message. → Brain receives and interprets the message. → Brain sends a response message.

Q5: Short Answer Questions.
(i) What are the three main parts of the brain?
Ans: The three main parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The cerebrum is responsible for conscious activities and thinking, the cerebellum for coordination and balance, and the brainstem for controlling essential functions like breathing and heartbeat.
(ii) Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary actions.
Ans: Voluntary actions are those that we can control consciously, such as moving our arms or legs. Involuntary actions, on the other hand, are automatic and not under our conscious control, like the beating of the heart or digestion.
(iii) How does the nervous system help us in responding to danger?
Ans: When we sense danger, our nervous system quickly sends signals to the brain, which interprets the threat. The brain then sends signals to the muscles, preparing the body for a fight or flight response, helping us to either confront the danger or escape from it.
(iv) What is the function of the spinal cord?
Ans: The spinal cord serves as a pathway for transmitting messages between the brain and the body. It also controls some reflex actions, which are quick responses to certain stimuli without involving the brain.
(v) Explain how messages travel between nerve cells.
Ans: Messages travel between nerve cells through synapses. When an electrical signal (nerve impulse) reaches the end of a nerve cell, it releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters into the synapse. These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the neighbouring nerve cell, transmitting the signal to the next cell. This process allows communication and coordination within the nervous system.
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Nervous System - 2 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is the main function of the nervous system? |  |
| 2. What are the main parts of the nervous system? |  |
| 3. How does the nervous system communicate with the body? |  |
| 4. What role does the brain play in the nervous system? |  |
| 5. How can we keep our nervous system healthy? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|

















