Worksheet: Modals - 2 | English Grammar for Junior Classes - Class 1 PDF Download

Q1: Fill in the blanks by choosing correct modal verbs inside the box:
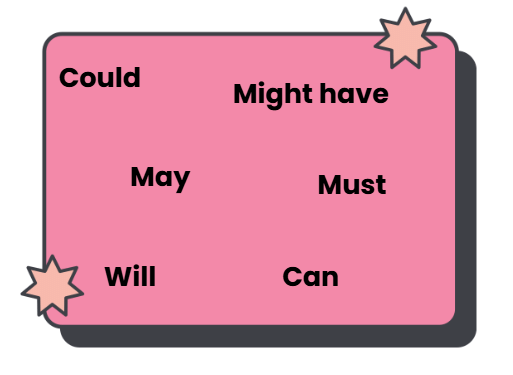
(i) _______ you lend me your computer?
(ii) ________ you come to my home?
(iii) You ______ pay the bill today.
(iv) _______ you drop my letter into the letter box?
(v) I ________ see you if I can find the time.
(vi) I ______ take the bus to the town.
(vii) You _______ succeeded if you had tried a little harder.
(viii) He _______ take rice today.
(ix) You _______ come in.
(x)________ you play ludo?

Q2: Rewrite the sentence using correct modal
I request you to lend me your book. (Use could)
It is possible that he is at home. (Use may)
I advise you to drink more water. (Use should)
It is possible for her to dance well. (Use can)
It is necessary to wash your hands. (Use must)

Q3: Choose the correct modal (MCQ)
1. I ____ swim very well.
(a) should
(b) can
(c) must
(d) will
2. You ____ not be late for school.
(a) can
(b) may
(c) must
(d) could
3. ____ I go outside to play?
(a) Must
(b) Can
(c) Should
(d) Would
4. Students ____ listen to their teacher.
(a) may
(b) could
(c) would
(d) should
5. You ____ wear a helmet while riding a bike.
(a) may
(b) should
(c) would
(d) can
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
18 videos|189 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Modals - 2 - English Grammar for Junior Classes - Class 1
| 1. What are modal verbs and how are they used in English grammar? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between modal verbs and regular verbs? |  |
| 3. Can modal verbs be used in all tenses? |  |
| 4. Are there any exceptions or irregularities in the usage of modal verbs? |  |
| 5. Can modal verbs be used in negative and interrogative forms? |  |
















