Important Points: Gravitation | Science Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Gravitation and Gravity |

|
| Centripetal Force |

|
| Universal Law of Gravitation |

|
| Mass and Weight |

|
| Buoyancy and Archimedes' Principle |

|
| Relative Density |

|
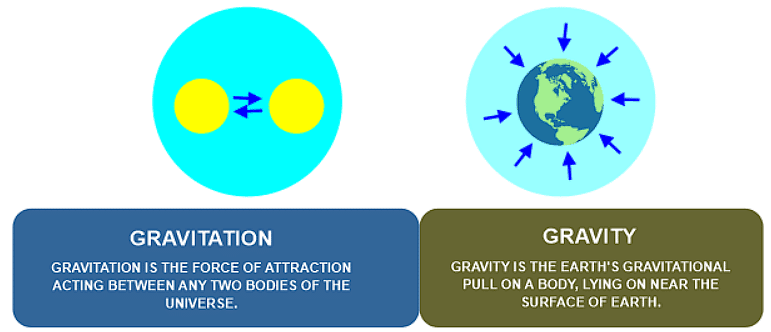
Gravitation and Gravity
Gravitation is a universal phenomenon where every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force called the gravitational force. Gravity is the specific case of gravitation, referring to the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on objects near its surface.
- Gravitation is one of the fundamental forces of nature, alongside electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force. It's the force of attraction between any two objects with mass in the universe.
- This force is responsible for holding planets in orbit around stars, moons around planets, and objects on the Earth's surface.
Gravity specifically refers to the force exerted by Earth on objects near its surface. It's what keeps us anchored to the ground and determines the weight of objects. Without gravity, everything would float off into space.
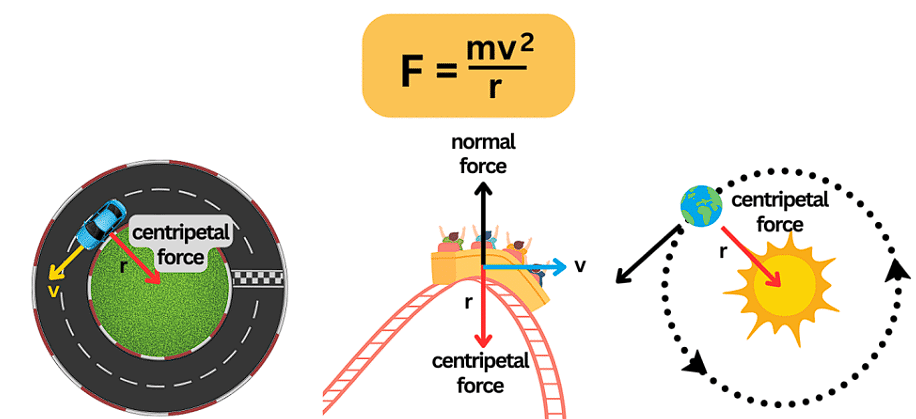
Centripetal Force
Centripetal Force: A force that keeps objects moving in a circular path, directed towards the center of the circle.
- Centripetal force is essential for understanding circular motion. It's the force that keeps objects moving in a circular path by continuously pulling them towards the center of the circle.
- This force allows celestial bodies to maintain their orbits around larger objects like stars and planets.
Tangential Velocity: The speed of an object moving sideways from the circle's center.
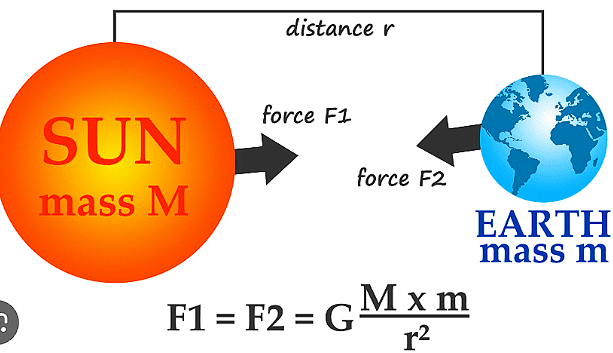
Universal Law of Gravitation
Newton's law of gravitation is a cornerstone of classical physics. It quantifies the gravitational force between two objects based on their masses and the distance between them. This law explains why objects fall to the ground, why planets orbit stars, and why the moon orbits the Earth.
The gravitational constant (G) is a crucial parameter in this equation, determining the strength of the gravitational force.
Importance of the Universal Law of Gravitation
This law has far-reaching implications, explaining a wide range of phenomena: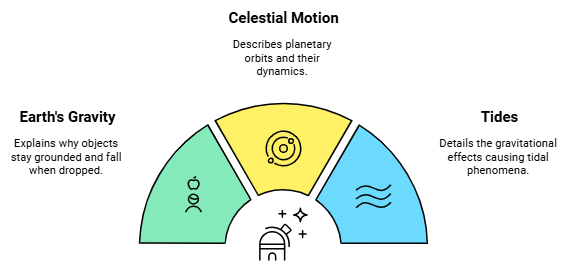
- Earth's Gravity: It elucidates why objects remain grounded and why they fall when dropped.
- Celestial Motion: It describes the dynamics of planetary orbits around stars and moons around planets, providing the foundation for celestial mechanics.
- Tides: The gravitational interaction between celestial bodies, such as the Earth, Moon, and Sun, causes tidal phenomena on Earth's oceans and even affects the planet's crust.
Free Fall and Gravity
Understanding free fall and gravity is essential for predicting the motion of objects under the influence of Earth's gravitational field. The acceleration due to gravity (g) determines the rate at which objects accelerate towards the Earth. This concept is crucial for fields such as engineering, physics, and astronomy.
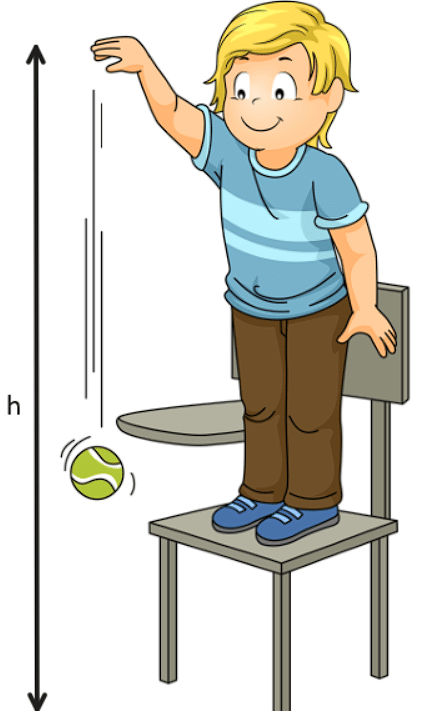
- When an object falls solely under the influence of gravity.
- Acceleration due to Gravity (g): The acceleration experienced by a freely falling object, typically = 9.8 m/s2 on Earth's surface.
- The value of 𝑔 varies by location and decreases with distance from the Earth.
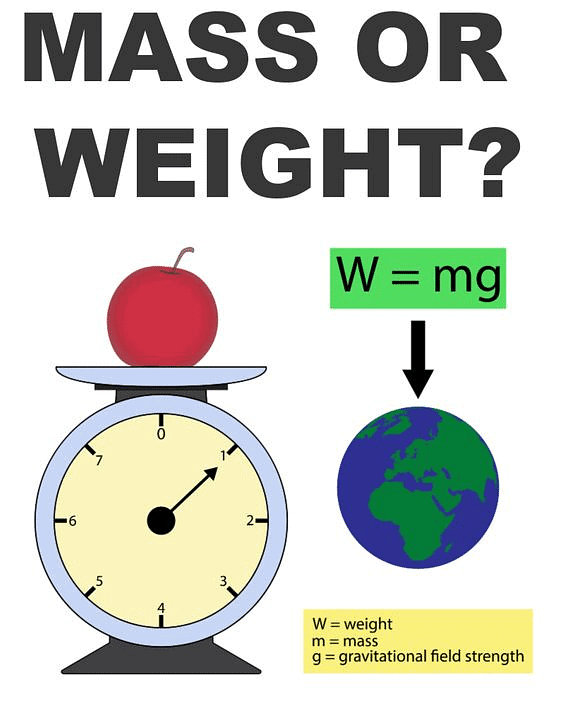
Mass and Weight
Mass: Measure of an object's inertia, constant regardless of location.
Weight: Force with which an object is attracted towards Earth, calculated as 𝑊=𝑚𝑔
Weight changes with location (e.g., 1/6th on the Moon compared to Earth).
Thrust and Pressure
Thrust is like the push an object gives to something it's resting on because of its weight, while pressure is how much force is squeezed into a small area. We need to know about these in building stuff like buildings and bridges, so they can handle different forces without breaking.
- Thrust: The normal force exerted by an object on a surface due to its weight.
- Pressure: Thrust per unit area. Its SI unit is the Pascal (Pa).
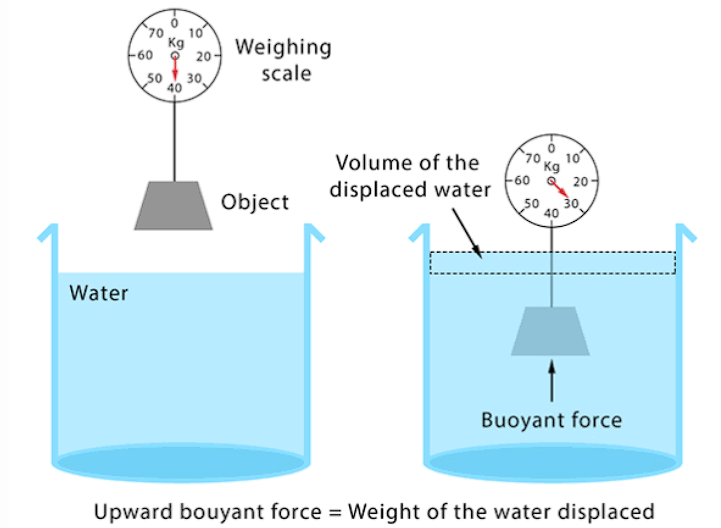
Buoyancy and Archimedes' Principle
When something floats in water, it's because the water pushes it up, balancing out the pull of gravity. Archimedes figured out that the floating force is as strong as the weight of the water the object pushes out of the way. This is really helpful for making things like boats and life jackets that stay afloat.
Relative Density
Relative density is about comparing how heavy something is to how heavy water is. This helps us figure out if something will sink or float. It's super useful for designing things like ships and submarines to make sure they work the way they should in water.
- Density: Mass per unit volume, measured in = kg/m3 or g/cm3
- Relative Density: Ratio of an object's density to the density of water. A unit-less measure that indicates whether an object will float or sink in a fluid.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Important Points: Gravitation - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the difference between gravitation and gravity? |  |
| 2. What is centripetal force and how does it relate to gravity? |  |
| 3. What is the Universal Law of Gravitation? |  |
| 4. How do mass and weight differ? |  |
| 5. What is Archimedes' Principle and how does it relate to buoyancy? |  |
















