Important Questions: Executive | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the different types of Executives?
Ans: There are two main types of executives:
- Political Executive: This includes leaders like the President, Prime Minister, ministers, and monarchs. They are responsible for making key decisions and setting government policies.
- Permanent Executive: This consists of civil servants and administrative staff who implement government policies and programmes. They ensure that the decisions made by the political executive are carried out effectively.
Q2: Write four features of Presidential executive.
Ans: The following are the main features of the Presidential executive:
- Direct Election: The President is typically elected directly by the people, ensuring a strong mandate.
- Separation of Powers: The President operates independently from the legislature, reducing the risk of conflicts of interest.
- Fixed Term: The President serves for a fixed term, providing stability and continuity in leadership.
- Executive Authority: The President holds significant executive powers, often overseeing the administration and implementation of laws.
Q3: How the President of India is elected?
Ans: The President of India is elected indirectly by an electoral college comprising elected MPs and MLAs through proportional representation using a single transferable vote.
Q4: How the Prime Minister of India is appointed?
Ans: The Prime minister is the real head of India. He is a leader of ministers. He is appointed by the President of India. The person who is elected leader of the majority party in the election is appointed as Prime-Minister by the President of India. Q5: Name the services in India?
Q5: Name the services in India?
Ans: The following are three types of services in India
- All India Government Service
- Central Services
- State Services
Q6: Explain the functions of the Vice-President of India?
Ans: The Vice President of India is given two responsibilities. Firstly he acts’ as ex-office Chairman of Rajya Sabha. In this capacity, he conducts the proceedings of Rajya Sabha. Secondary he acts as President in the absence of the President due to leave, resignation or death.
Q7: What is the State Public Service Commission?
Ans: Almost every state is given a state public service commission like that of UPSC at the centre. The members of Public Service Commissions are appointed for a fixed period. PSCS conduct recruitment for the state Service. PSCS also conducts interviews and exams and set all conditions related to services.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q8: Why India adopted a Parliamentary system?
Ans: During the drafting of the Constitution of India, there was a discussion about whether to adopt a Parliamentary or a Presidential system of government. The decision was made in favour of the Parliamentary system due to prior experience with it under the Government of India Acts of 1919 and 1935. This experience revealed several key points:
- The executive can be effectively controlled by the legislature, ensuring accountability.
- The Constitution makers aimed for a government that is responsive to the people's needs.
- The Parliamentary system has mechanisms to check the power of the executive, preventing the rise of a personality cult.
In this system, the President serves as the formal Head of State, while the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers manage the government
Q9: How the President can be removed.
Ans: The President of India serves a term of five years but can be removed through a process called impeachment. This process involves the following steps:
- Charges are brought against the President in one house of Parliament.
- These charges are then examined by the second house.
- The President is given a notice of 14 days to respond to the charges.
- If the charges are upheld by a two-thirds majority of the members present and voting, the President is impeached.
- Upon impeachment, the President must vacate the office.
Q10: Write the Executive functions of Indian President.
Ans: The President of India serves as the Chief Executive of the country, with all executive powers formally vested in their name. These powers can be summarised as follows:
- The President acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers, led by the Prime Minister.
- They are responsible for appointing the Prime Minister and other ministers.
- The President represents India in international forums and affairs.
- They have the authority to summon and prorogue Parliament sessions.
- The President can grant pardons, reprieves, respites, or remissions of punishment under Article 72 of the Constitution.
- They play a crucial role in the legislative process, including giving assent to bills.
The President is elected for a term of five years through an indirect election process, involving elected members of the legislative assemblies and Parliament. They can only be removed through impeachment by Parliament.
Q11: Write the main functions of Indian Prime-minister.
Ans: The Indian Prime Minister holds a significant position with various important functions, which can be summarised as follows:
- Acts as the head of the Council of Ministers, leading the executive branch of the government.
- Communicates all decisions regarding the administration to the President.
- Involved in crucial government decisions and policy formulation.
- Leads the majority party in the Lok Sabha, influencing legislative processes.
- Commands the bureaucratic machinery and oversees its operations.
- Engages with the media and represents India in international forums.
- His power may vary based on the political landscape, especially during coalition governments.
Q12: What are the functions of the council of ministers?
Ans: The Council of Ministers plays a crucial role in the governance of the country. Its main functions include:
- Acting as the real political executive, overseeing the administration across various sectors.
- Formulating and implementing government policies.
- Advising the President, whose decisions are largely based on their recommendations.
- Ensuring collective responsibility, meaning all ministers must support cabinet decisions.
Q13: How the Chief Minister is appointed and what are his main functions?
Ans: The Chief Minister serves as the real executive head at the state level and leads the Council of Ministers. His appointment is made by the Governor, similar to how the Prime Minister is appointed by the President of India. Here are the key points regarding his appointment and functions:
- The Governor appoints the Chief Minister from the leader of the majority party in the state assembly.
- If no party achieves a clear majority, the Governor has the discretion to explore various options to form a government.
- The Chief Minister's main functions include:
- Formulating policies and decisions for the state.
- Leading the Council of Ministers in executing government functions.
- Representing the state in interactions with the central government.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q14: Discuss the increasing role of Executive in the modern state.
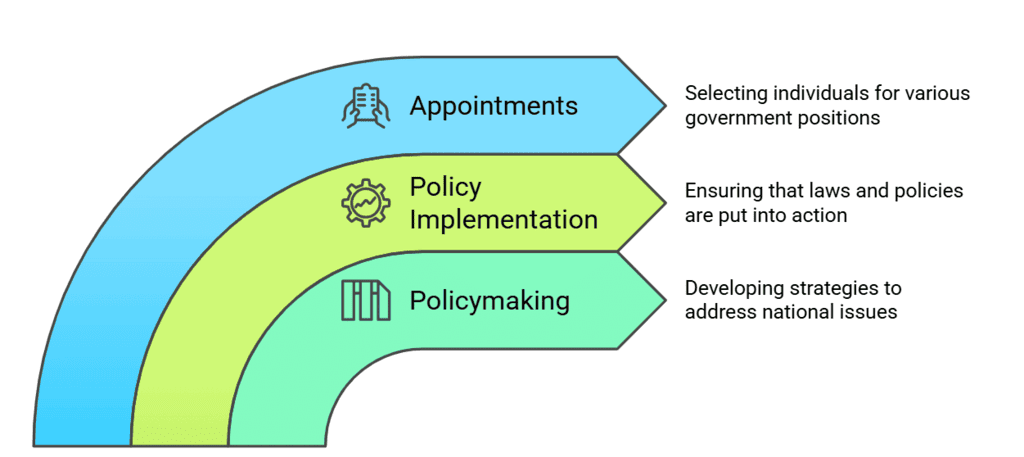
Ans: The executive is a crucial part of government, responsible for key functions such as:
- Policymaking: Developing strategies to address national issues.
- Policy Implementation: Ensuring that laws and policies are put into action.
- Appointments: Selecting individuals for various government positions.
There are different types of executives:
- Civil or military
- Hereditary (like a monarchy) or elected (like a republic)
- Political (such as a cabinet) or permanent (like the civil service)
- Parliamentary or Presidential
In the modern state, the role of the executive has significantly increased due to its welfare responsibilities. Key points include:
- The executive influences nearly every aspect of national life.
- As societies evolve, the demands on the executive grow.
- The executive plays a vital role not only in policy areas but also in legislative, financial, and judicial matters.
- With globalisation and internationalism, the executive's responsibilities continue to expand.
Overall, the modern executive is a powerful institution that requires effective democratic control to ensure accountability and responsiveness.
Q15: Write the legislative Functions of Indian President.
Ans: Legislative Functions of the President of India:
- The President summons and prorogues Parliament sessions.
- They give assent to bills passed by Parliament, allowing them to become law.
- The President can withhold assent or return a bill for reconsideration, except for Money Bills.
- They have the power to dissolve the Lok Sabha.
- The President addresses both Houses of Parliament at the beginning of the first session after each general election and the first session of each year.
- They can also summon a joint sitting of both Houses to resolve disagreements on a bill.
Q16: How the Prime-minister of India is appointed?
Ans: The Prime Minister of India is appointed by the President. The process is as follows:
- After the Lok Sabha elections, the leader of the party or coalition with a majority is invited by the President to form the government.
- If this leader agrees, the President administers the oath of office to them.
- If no party has a clear majority, the President uses their discretion to choose a leader they believe can form a stable government.
- In cases where a party has a clear majority, the President must invite the leader of that party to form the government.
This process ensures that the Prime Minister has the support of the majority in the Lok Sabha, which is essential for effective governance.
Q17: How the council of ministers is constituted?
Ans: The Council of Ministers is the key political executive in India, functioning under the leadership of the Prime Minister. Here’s how it is constituted:
- The President of India appoints the ministers based on the advice of the Prime Minister.
- Ministers hold office at the pleasure of the President.
- The Prime Minister decides which members of their party will be included in the Council.
- Once selected, the Prime Minister submits the list to the President, who administers the oath of secrecy to the ministers.
- Ministers can be removed from the Council on the Prime Minister's advice.
- To become a minister, one must be a member of either house of Parliament.
Q18: Compare the powers and position of Prime-minister of India with the powers and position of US president.
Ans: India has a Parliamentary system where the Prime Minister is the actual executive, carrying out all powers and responsibilities assigned to the Indian President in the Constitution. In contrast, the President of the USA is the real head of state, exercising powers defined in the US Constitution. Both positions have their strengths and weaknesses. Here are some key comparisons:
- Executive Power: The Indian Prime Minister leads the government and is accountable to the Parliament, while the President of USA has significant authority but operates independently.
- Legislative Role: The Prime Minister must maintain the confidence of the legislature, whereas the President does not require legislative approval for their position.
- Decision-Making: The Prime Minister's decisions are often influenced by party politics, while the President has more unilateral decision-making power.
- Tenure: The Prime Minister can be removed by a vote of no confidence, while the President serves a fixed term unless impeached.
Q19: How the Governor is appointed? What are its functions?
Ans: The Governor is appointed as the nominal head of state by the President of India. This appointment is essential in a state with a parliamentary system of government. As the head of state, the Governor has several important functions:
- Performs formal duties in the legislative field.
- Engages in executive functions.
- Participates in judicial activities.
- Acts as an agent of the central government.
- Serves as a watchdog for national and central interests within the state.
Q20: Discuss the composition and functions of UPSC and SPSCS. (State Public Service Commission).
Ans: The Constitution establishes the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) at the central level and the State Public Service Commissions (SPSCs) at the state level. Their primary roles include:
- Recruitment: Both UPSC and SPSCs are responsible for recruiting civil servants for the Government of India and state governments, respectively.
- Appointments: The Chairman and members of the UPSC are appointed by the President, while those of the SPSCs are appointed by the respective state governors.
- Removal: Members can be removed through an inquiry conducted by a judge from the Supreme Court or High Court.

The UPSC conducts exams and interviews for various central services, while the SPSCs manage appointments for state services. Additionally, the Constitution ensures that recruitment is based on merit, with provisions for reservations for:
- Scheduled Castes (SC)
- Scheduled Tribes (ST)
- Women
- Other Backward Classes (OBC)
- Economically Weaker Sections (EWS)
These measures aim to create a more representative bureaucracy and reduce social inequalities in public service recruitment.
|
44 videos|387 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Executive - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the importance of Executive Humanities/Arts in education? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the Executive Humanities/Arts exam? |  |
| 3. What are the main topics covered in the Executive Humanities/Arts syllabus? |  |
| 4. Are there any recommended books or resources for studying Executive Humanities/Arts? |  |
| 5. How do Executive Humanities/Arts skills apply in the workplace? |  |

















