Important Questions: Human Capital Formation in India | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What do you mean by human capital formation?
Ans: Human capital formation refers to the process of changing a country's people into workers who are capable of creating commodities and services. Relatively unskilled individuals are given the tools they need to contribute to the economy during this process.
Q2: Name the movement started by the national literacy mission.
Ans: ‘Education for all' is a movement begun by the National Literacy Mission.
Q3: What is meant by OJT?
Ans: On-the-job training refers to the instruction given to employees by their employers at the workplace which will enable them to master their particular abilities. It increases their efficiency and productivity.
Q4: What is the literacy rate of India?
Ans: India's literacy rate is 77.7% as of 2020.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q5: What is meant by financial capital? Explain with examples.
Ans: Financial capital is any monetary economic resource utilised largely by entrepreneurs and firms to purchase the resources required to make their goods or deliver services to the economy. Retail, corporate, and investment banking are a few examples. The most common categories include equity, debt, sweat equity etc.
Q6: What is the difference between literacy and education?
Ans: The difference between literacy and education is given below: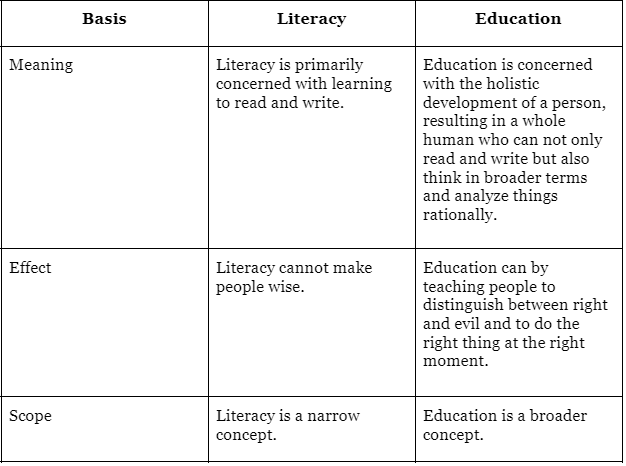
Q7: Write three differences between physical capital and human capital?
Ans: Three differences between physical capital and human capital are: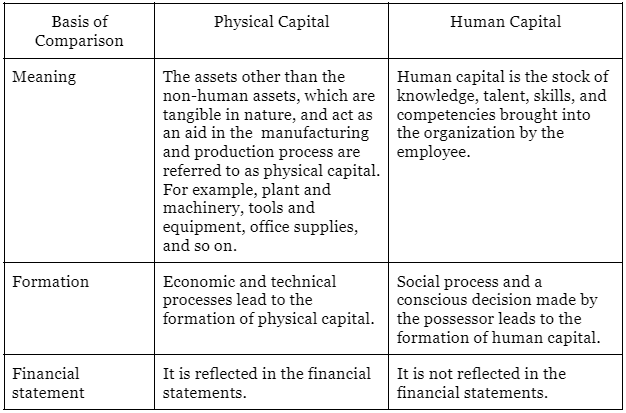
Q8: How does human capital formation improve quality of life?
Ans: Human capital formation is influenced by factors such as investment in education, healthcare, on-the-job training, migration, and so on. People who are literate, healthy, skilled, and trained are valuable assets to an economy. As a result, higher population quality indicates higher economic growth. Human capital formation is linked to investment in man and his growth as a creative and productive resource. Also, human capital formation will make people capable of performing skilled work, thus increasing their employability, which will further raise their standard of living and quality of life through improved income.
Q9: What do you mean by investment in education?
Ans: The investment in education is an investment in the acquisition of skills and knowledge of an individual that will boost income or bring long-term advantages such as literary appreciation. It is critical to remember that when a person performs in his chosen sector and increases his income, he also contributes to the nation's economic progress. Hence, investment in education encourages economic growth.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q10: Discuss the educational achievements of India and what are the future prospects in education?
Ans: After the ideas were put into action, efforts were undertaken to promote education. In order to streamline education, the government implemented the Kothari Commission's recommendations under the "National Policy on Education" in 1968. The key recommendations were universal primary education and universal secondary education. Introduction of a new educational pattern, three-language formula, inclusion of regional languages in higher education, advancement of agricultural and industrial education, and adult education. The following points describe the evolution of education in India post-independence:
- Expansion of General Education: During the planning period, general education was expanded. Primary education has always been free and mandatory. Since 1995, schools have served a midday meal to reduce dropout rates.
- Technical Education Development: Technical education, in addition to general education, plays a significant role in the building of human capital. The government has built several Industrial Training Institutes, Polytechnics, Engineering colleges, Medical and Dental colleges, Management institutes, and so on. Examples include IITs, IIMs, and NITs.
- Women's Literacy: In India, women's literacy was extremely poor, and was 52% as per 2011 Census. Men had a literacy rate of 75.8 percent. Women's education was prioritized in the National Policy on Education.
- Vocational Education: The National Education Policy of 1986 strives for vocational secondary education. Since 1988, the federal government has provided subsidies to state governments to help them carry out the program.
- Adult Education: Simply put, adult education refers to education for illiterate adults between the ages of 15 and 35. The First Five Year Plan established the National Board of Adult Education.
- Education for All: The 93rd Amendment makes obligatory education for all. Elementary education is a fundamental entitlement of all children aged 6 to 14 years. It's also completely free, and for the fulfilment of this purpose, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan has been launched.
Q11: What is the role of human capital formation in an economy?
OR
State the importance of human capital formation in a country.
Ans: Human capital is the primary driver of economic progress. It is a source of both increasing output and technological advancement. The main distinction between industrialized and developing countries is the rate of human capital advancement.
Human capital is required in developing countries to staff new and expanding government services, to implement new land-use systems and agricultural practices, develop new modes of communication, advance industry, and strengthen the education system.
- To be more specific, a country's citizens are said to have greater human capital if they are well educated, well-nourished, skilled, and healthy.
- Underdeveloped countries around the world are investing in people in order to improve their programming skills, social abilities, ideas, and health.
- These investments are intended to boost productivity. Their economies' success is dependent on growing human capacities.
- Human capital, on the other hand, does not exist in a vacuum.
- To have a better understanding of this complex subject, we must evaluate the physical/passive variables that relate to a country's ability to make these investments.
- Human capital formation is the act of enhancing the productive qualities of the labor force by giving more education and boosting the working population's skills, health, and notarization level.
- It is the process of changing a country's inhabitants into employees capable of generating goods and services.
- Relatively unskilled individuals are given the tools they need to contribute to the economy during this process.
- It is vital to a country's long-term economic progress and offers the same advantages as new technology or more efficient industrial equipment.
- While this process takes time, it frequently results in a higher quality of life for the population of a country within a few generations, if not sooner.
- This procedure can be accomplished through the use of public health policy, education, or training opportunities.
Methods for Creating Human Capital:
- The provision of health-care services that affect people's life expectancy, strength, energy, and vitality.
- Provision of on-the-job training to improve labor force skills.
- Organizing education at the elementary, intermediate, and tertiary levels.
- Adult education and training programs.
- Adequate migration facilities for families to adapt to changing job possibilities.
Human capital is inextricably linked to economic growth. The amount of money put into people's education might be used to gauge the relationship. Many nations, for example, provide free higher education to citizens. These governments recognize that the information gained through education contributes to the development of an economy and leads to economic progress.
Q12: ‘School dropouts are giving way to child labour.’ Discuss how this is a loss to human capital?
Ans: School dropout and child labor are related to the low socioeconomic position since parents want to send their children to work in order to raise household income.
Reasons for School Dropout:
- Poverty.
- Migration.
- Child marriage.
- Child labour.
Out of all the above reasons, child labour and poverty are the major ones.
- Due to the gruesome situation of poverty, children are forced to leave their education, and work as labourers.
- Child labor deprives children of their childhood and is harmful to the emotional, physical and mental health of these children.
- School dropouts prevent children from acquiring literacy skills and pave the way for child labor.
- These children are typically employed in dhabas, houses, construction sites, and other menial jobs.
- Being illiterate accelerates the poverty cycle and, as a result, the process of human capital formation is incomplete.
- Had these children remained in school, they would have gotten education, thus paving their way for a better earning job where they could employ their skills and knowledge. But working in menial jobs, neither adds to the skills, nor their income, thus leading to a loss of human capital.
The Following Economic Impact of Child Labor are Examined:
- Child labor's effects at the microfamily level, particularly on family poverty in the short and long term.
- Child labor's impact on long-run growth and social development via various transmission mechanisms.
- The international economic implications of child labor, particularly the effects on foreign direct investment.
- Child labor's impact on the adult labor market.
Findings at the Micro Family Level:
- Child labor, in the long run, reinforces household poverty by lowering human capital.
- Child labor and education are not always mutually exclusive.
- Child labor in most wage-employment non-agricultural industries does not result in skill development.
- Child labor, in the long run, exacerbates poverty through increasing fertility.
Findings at the Macro Family Level:
- Child labor can impair long-run growth and social development by reducing human capital accumulation.
- Child labor can be commonly seen in the unorganized and tiny sectors of the economy.
- The influence on adult pay determines whether lowering child labor would accelerate capital investment and technological advancement.
- Child labor may harm more girls than boys, contributing to gender disparities in education.
- Child labor does not attract foreign direct investment.
- Both children and adults can work as substitutes for one another.
- It is unclear whether children truly substitute for adult employees, hence increasing adult unemployment and/or lowering adult wage rates.
Hence, the above explanation clarifies that school dropouts adds to the child labour in the economy, and creates a loss to human capital.
Q13: What do you think about India’s current situation on gender equality?
Ans: Gender equality indicates that men and women's different behaviors, desires, and needs are evaluated, respected, and favored equally. It does not imply that men and women must become the same, but that their rights, duties, and opportunities will not be determined by whether they are born male or female.
For ages, gender inequality has been a major societal concern in India. In India, the child sex ratio among children aged 0 to 6 years is 918 girls for every 1000 boys, according to Census 2011. This figure speaks for itself, indicating the need for immediate and effective measures to address the root causes of gender disparity.
The inequality between a girl and boy begins even before they are born. In many cases, she is not allowed to be born. The girl kid is regarded as a liability. She is frequently denied fundamental rights and equitable chances to have a healthy childhood and adult life.
Girls account for 48 percent of India's overall child population, according to Census 2011, and many of them are involved in child labour, child trafficking, and child marriage. As evidenced by the following figures, the future of many females appears to be bleak:
- In India, 12.15 million children are married, with 8.9 million of them being females; married girls outnumber boys three to one. (According to the 2011 Census)
- Children made up 51% of all victims of human trafficking, with more than 80% of them being females. (National Cancer Research Board, 2018).
- In India, there are 223 million child brides, 102 million of whom were married before the age of 15. (UNICEF)
Efforts to Modify the Situation Include the Following:
- Education to assist people change their minds on gender prejudice, as well as initiatives to raise awareness.
- Continual efforts to dispel gender preconceptions and misconceptions.
- Assuring the state's accountability for different plans, policies, laws, constitutional guarantees, and international obligations.
- Gender-sensitive procedures are becoming institutionalised in different institutions, such as law and programmes.
- Promoting community responsibility in the prevention of gender discrimination breaches.
All girls deserve equal chances and an empowering environment to grow, whether it's in terms of education, health, protection, or involvement.
|
64 videos|275 docs|52 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|

















