Worksheet Solutions: Contemporary Centres of Power | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the column |

|
| Assertion and Reason based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The European economy was revived after World War II with extensive financial support from ______________ under the Marshall Plan.
Ans: USA
The European economy was revived after World War II with extensive financial support from USA under the Marshall Plan, aiding in post-war reconstruction.
Q2: The Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was founded in ____________ to direct help to West European nations.
Ans: 1948
The Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was founded in 1948 to direct help to West European nations, facilitating economic cooperation and recovery.
Q3: The disintegration of the USSR led to the formation of the ______________ in 1992.
Ans: European Union
The disintegration of the USSR led to the formation of the European Union in 1992, establishing a framework for political and economic integration in Europe.
Q4: ASEAN stands for Association of South East Asian Nations, founded in ____________.
Ans: 1967
ASEAN, which stands for Association of South East Asian Nations, was founded in 1967, fostering regional unity and cooperation among ten Southeast Asian nations.
Q5: The ASEAN emblem consists of ten rice stalks representing ______________ South East Asian nations.
Ans: Ten
The ASEAN emblem consists of ten rice stalks, symbolizing the unity of ten Southeast Asian nations in friendship and cooperation.
Q6: China's "Open Door Policy" was announced by ______________ in 1978.
Ans: Deng Xiaoping
China's "Open Door Policy" was announced by Deng Xiaoping in 1978, encouraging foreign investments and technology to boost China's production and economy.
Q7: India experienced a military setback against China in the year ______________.
Ans: 1962
India experienced a military setback against China in the year 1962, marking a significant conflict in their bilateral relations.
Q8: The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" gained popularity during peaceful relations between ______________ and ______________.
Ans: India, China
The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" gained popularity during peaceful relations between India and China, reflecting the friendly ties between the two nations.
Q9: The ASEAN Economic Community seeks to create a ______________ market and promote regional social and economic development.
Ans: Single
The ASEAN Economic Community seeks to create a single market and promote regional social and economic development, enhancing economic integration among member states.
Q10: The European Union has the largest economy in the world with a GDP exceeding ______________ in 2005.
Ans: $12 trillion
The European Union has the largest economy in the world with a GDP exceeding $12 trillion in 2005, positioning it as a global economic powerhouse.
Match the column
Q1:
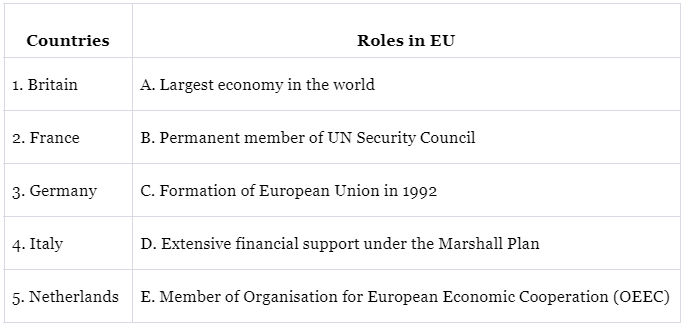 Ans: 1. Britain: C. Formation of European Union in 1992
Ans: 1. Britain: C. Formation of European Union in 1992
Britain was a member when the European Union (EU) was officially formed in 1992 with the signing of the Maastricht Treaty.
2. France: B. Permanent member of UN Security Council
France is one of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, which gives it significant diplomatic and political influence on the global stage.
3. Germany: A. Largest economy in the world
Germany has the largest economy within the EU and is one of the leading economies globally, contributing significantly to the EU's economic strength.
4. Italy: D. Extensive financial support under the Marshall Plan
Italy, like many other European countries, received extensive financial support under the Marshall Plan, which helped rebuild its economy after World War II.
5. Netherlands: E. Member of Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC)
The Netherlands was a member of the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC), which was founded in 1948 to direct economic assistance to Western European nations.
Assertion and Reason based
Q1: Assertion: The disintegration of the USSR led to the formation of the European Union in 1992.
Reason: European nations wanted to establish a common foreign and security policy.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because the disintegration of the USSR did play a significant role in the formation of the European Union. With the end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union, European nations felt the need to strengthen their cooperation and create a united front in the face of changing global dynamics. The reason is also true because one of the key objectives of the European Union was to establish a common foreign and security policy among its member states. The desire for a unified approach to international relations was a driving force behind the formation of the EU in 1992.
Q2: Assertion: China's "Open Door Policy" aimed to boost production through foreign investments.
Reason: Special economic zones were established to attract foreign capital and technology.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because China's "Open Door Policy," initiated by Deng Xiaoping in 1978, was indeed designed to boost production and economic growth by encouraging foreign investments. The reason is also true because special economic zones were created in China to attract foreign capital and technology. These zones offered favorable conditions for foreign companies, leading to increased investments, technology transfer, and overall economic development. The establishment of these zones was a practical step in implementing the Open Door Policy.
Q3: Assertion: ASEAN's emblem represents unity with ten rice stalks.
Reason: ASEAN comprises ten South East Asian nations.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true as the emblem of ASEAN does represent unity with ten rice stalks, symbolizing the ten Southeast Asian nations that are united in friendship and cooperation. The reason is also true because ASEAN does indeed consist of ten member states: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The emblem's symbolism aligns with the actual composition of ASEAN member nations.
Q4: Assertion: India and China had peaceful relations after India's independence.
Reason: The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" symbolized the friendship between the two nations.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because after gaining independence, India and China initially enjoyed peaceful relations. The reason is also true because the slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" (meaning "Indians and Chinese are brothers") was popular during this time, symbolizing the friendly relations and the spirit of brotherhood between the two nations. However, these peaceful relations were later marred by a border dispute and military conflicts, but the assertion and reason are accurate for the specified period in history.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: What was the purpose of the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC)?
Ans: The OEEC was founded in 1948 to provide financial support to West European nations after World War II.
Q2: Name three objectives of ASEAN.
Ans: Accelerate economic growth, promote regional peace and stability, and encourage cultural development.
Q3: Who announced China's "Open Door Policy," and what was its goal?
Ans: Deng Xiaoping announced the policy in 1978 to boost production through foreign investments.
Q4: What does the ASEAN emblem symbolize?
Ans: The emblem represents unity with ten rice stalks, signifying the ten South East Asian nations in ASEAN.
Q5: Which two European countries are permanent members of the UN Security Council?
Ans: Britain and France are permanent members of the UN Security Council.
Q6: What does ASEAN way refer to in the context of interaction?
Ans: ASEAN way signifies an informal, non-confrontationist, and cooperative form of interaction among member states.
Q7: When did India and China experience a military dispute, and what was the cause?
Ans: The dispute occurred in 1962 due to the Chinese takeover of Tibet in 1950.
Q8: What was the slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" associated with?
Ans: The slogan symbolized the peaceful relations and friendship between India and China.
Q9: What are the three pillars of the ASEAN community established in 2003?
Ans: The three pillars are the ASEAN socio-cultural community, the ASEAN economic community, and the ASEAN security community.
Q10: What does China's economy aim to achieve through its Special Economic Zones?
Ans: Special Economic Zones were established to attract foreign capital and technology, boosting China's production and economic growth.
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: How did the Cold War aid the integration of Europe after 1945?
Ans: The extensive financial support provided by the USA under the Marshall Plan revived the European economy, leading to the formation of organizations like the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) and the Council of Europe, fostering political cooperation.
Q2: Explain the objectives of ASEAN's ASEAN Economic Community.
Ans: The ASEAN Economic Community aims to create a single market, promote regional social and economic development, and enhance economic integration among member states. It facilitates the free flow of goods, services, investment, capital, and skilled labor.
Q3: How did China's economic policies change after 1978, leading to its growth as a global economic power?
Ans: China's "Open Door Policy," announced by Deng Xiaoping in 1978, allowed foreign investments in capital and technology, boosting production. Special Economic Zones attracted foreign capital. China's economy shifted from a centrally planned model to one based on internal resources and global engagement.
Q4: Describe the founding principles of ASEAN and its approach to international relations.
Ans: ASEAN was founded on principles of peace, neutrality, cooperation, non-interference, and respect for national differences and sovereign rights. It promotes the ASEAN way, an informal and cooperative form of interaction, in international relations.
Q5: How did the Chinese economy evolve since 1978?
Ans: China's economy, initially modeled on the Soviet model in 1949, shifted focus in 1978. The "Open Door Policy" allowed foreign investments, creating Special Economic Zones. The state played a central role in the economy, leading to China's rapid economic growth. However, not all citizens benefited, leading to issues like poor working conditions and unemployment.
Q6: Discuss the impact of the Chinese economy on the global stage.
Ans: China's economic rise since 1978 positioned it as a major global economic power. By 2040, it's anticipated to surpass the US as the world's largest economy. Its economic policies and global trade have made it a central player in the international market, affecting trade balances and economic strategies of many countries.
Q7: Explain the evolution of the European Union from an economic union to a political entity.
Ans: The European Union began as an economic union, focusing on trade and economic cooperation. Over time, it evolved into a political entity, establishing common policies on foreign affairs, security, and justice. The introduction of a common currency, the Euro, further strengthened its political and economic integration.
Q8: Describe the factors that led to the improvement of relations between India and China in 1988.
Ans: Relations between India and China improved after Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's visit to China in December 1988. Diplomatic efforts and mutual understanding during the visit led to a thaw in tensions, initiating a process of better communication and cooperation between the two nations.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the factors that contributed to the evolution of the European Union from an economic union to a political one. Provide specific examples of this transformation.
Ans: The evolution of the European Union from an economic union to a political one was influenced by several factors.
- Historical Context: The aftermath of World War II and the Cold War led to a desire for regional cooperation to prevent future conflicts. The devastating impact of the war necessitated economic and political integration.
- Marshall Plan and OEEC: The Marshall Plan provided extensive financial support to Europe, reviving its economy. The Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was formed in 1948 to manage this aid, laying the foundation for economic collaboration.
- Political Cooperation: The establishment of the Council of Europe in 1949 marked progress in political cooperation. It emphasized shared democratic values and human rights.
- Formation of the European Union: The collapse of the USSR in 1992 allowed for the formation of the European Union, providing a platform for common foreign and security policies and the introduction of the euro as a single currency.
The EU's evolution was driven by a combination of economic recovery, political cooperation, and the changing geopolitical landscape, ultimately leading to its current status as a significant political and economic power.
Q2: Discuss the founding objectives and principles of ASEAN. How has the ASEAN community evolved over time, and what are its key pillars?
Ans: ASEAN, founded in 1967, aimed to achieve several objectives:
- Economic Growth: Accelerate economic growth and development among member nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Promote regional peace and stability, especially in a region historically marked by conflicts.
- Cultural Development: Foster cultural development and cooperation.
The ASEAN community has evolved with three key pillars:
- ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community: Fosters cultural exchange, social progress, and human development.
- ASEAN Economic Community: Aims to create a single market, promote economic development, and enhance economic integration.
- ASEAN Security Community: Focuses on peace, neutrality, cooperation, non-interference, and respect for national differences and sovereign rights.
These principles and pillars reflect ASEAN's commitment to regional cooperation, mutual respect, and the pursuit of economic and social development, maintaining stability in Southeast Asia.
Q3: Explain the key factors and events that contributed to China's rapid economic growth since 1978. How has this growth positioned China globally?
Ans: China's remarkable economic growth since 1978 can be attributed to various factors and events:
- "Open Door Policy": Deng Xiaoping's announcement of the "Open Door Policy" in 1978 allowed foreign investments in capital and technology, facilitating production and economic growth.
- Special Economic Zones: The establishment of special economic zones created hubs for foreign investments and technology transfer, driving economic development.
- State-Led Development: The Chinese government played a central role in planning and coordinating the nation's economic development.
- Global Engagement: China's diplomatic relations with the USA in the 1970s ended its political and economic isolation, fostering international trade and investment.
- Internal Resources: China shifted from a Soviet-style model to an economy reliant on its vast internal resources.
Globally, China's economic rise has positioned it as a major economic power. By 2040, it is expected to surpass the USA as the world's largest economy, challenging the dominance of the US dollar and playing a pivotal role in global trade and geopolitics.
Q4: Examine the historical trajectory of India-China relations, highlighting key events, conflicts, and turning points. How did the relations between the two countries start improving, and what factors contributed to this improvement?
Ans: The historical trajectory of India-China relations has seen significant ups and downs:
- Early Relations: India and China had cordial relations before both nations' independence, with cultural, economic, and political ties.
- Border Dispute: The border dispute arose due to China's takeover of Tibet in 1950, leading to military conflicts in 1962.
- Deteriorating Relations: Until 1976, India and China faced deteriorating military relations and tensions.
- Improvement: A significant turning point was the visit by Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi to China in December 1988, which marked the beginning of improved relations.
Factors contributing to this improvement include:
- Diplomacy: Both nations engaged in diplomatic dialogues to resolve disputes and build trust.
- Economic Cooperation: Economic ties and trade between India and China grew significantly.
- Focus on Peace: Both countries emphasized peace, non-interference, and respect for sovereignty.
This shift toward improved relations highlights the importance of diplomacy and shared economic interests in fostering peaceful coexistence between two major Asian powers.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Contemporary Centres of Power - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the contemporary centres of power in the field of humanities and arts? |  |
| 2. How do these centres of power impact the art world and cultural landscape? |  |
| 3. What role do universities play as centres of power in humanities and arts? |  |
| 4. How do museums and galleries contribute to the contemporary art scene? |  |
| 5. How are cultural organizations influencing the development of humanities and arts today? |  |















