Worksheet: Election and Representation | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: When did the Election Commission of India get two more Election Commissioners?
Q2: FPTP stands for _______.
Q3: In the FPTP system, the candidate with the _______ number of votes is declared the winner.
Q4: PR stands for _______ _______.
Q5: In India, the FPTP system is used for electing members to the _______ _______ and State Legislative Assemblies.
Q6: The FPTP system is also known as the _______ system.
Q7: Universal Adult Franchise was introduced in India through the _______ Amendment in 1989.
Q8: The Delimitation Commission is responsible for deciding the reservation of _______.
Q9: The Election Commission of India is responsible for conducting elections to _______ _______.
Q10: The Election Commission consists of a Chief Election Commissioner and _______ Election Commissioners.
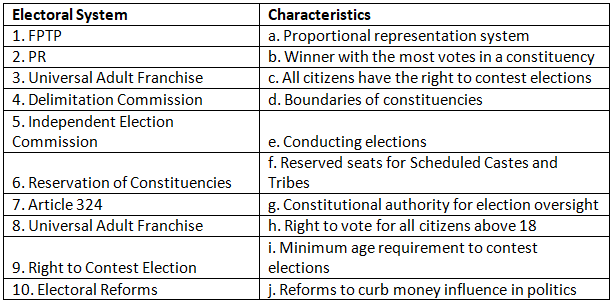
Match the Column
Q1: Match the electoral system with its characteristics:
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Universal Adult Franchise allows all citizens above 21 years to vote.
Reason: It promotes equality and non-discrimination.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q2: Assertion: The FPTP system is popular because of its complexity.
Reason: It ensures proportional representation.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q3: Assertion: The Election Commission conducts local body elections.
Reason: The Election Commission is responsible for all elections in India.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q4: Assertion: Independent Election Commissioners have more powers than the Chief Election Commissioner.
Reason: Independent Election Commissioners are appointed by the President.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain what the FPTP system stands for.
Q2: How is the winning candidate determined in the FPTP system?
Q3: What is Universal Adult Franchise, and when was it introduced in India?
Q4: What is the role of the Delimitation Commission?
Q5: What is the significance of the 61st Amendment in the Indian Constitution?
Q6: What are the minimum age requirements for contesting Lok Sabha or Assembly elections?
Q7: Why was the 42nd Amendment significant regarding the delimitation of seats?
Q8: What is the primary responsibility of the Election Commission of India?
Q9: How are seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the legislature?
Q10: Why are electoral reforms necessary in India?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Compare and contrast the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system and the Proportional Representation (PR) system of elections, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Q2: Explain how the reservation of constituencies for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes is determined in India, and why it is important.
Q3: Describe the composition and functions of the Election Commission of India. How does it ensure free and fair elections?
Q4: Discuss the need for electoral reforms in India, and provide specific suggestions for improving the electoral process and reducing the influence of money in politics.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the advantages of the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system in India, and why it is considered a suitable choice for a stable government.
Q2: Discuss the significance of Universal Adult Franchise in the Indian electoral system and its role in promoting democracy and equality.
Q3: Elaborate on the role and significance of the Delimitation Commission in India, and its impact on fair representation.
Q4: Provide a comprehensive list of electoral reforms that you believe would improve the Indian electoral process, ensuring transparency, fairness, and better representation.
|
44 videos|202 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Election and Representation - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is an election and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How are representatives elected in a democratic system? |  |
| 3. What is the role of political parties in elections? |  |
| 4. How does the concept of representation work in elections? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges or issues faced in elections and representation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|

















