Worksheet Solutions: International Organisations | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The United Nations was established in ________ after the Second World War.
Ans: 1945
The UN, founded post-World War II, aims to foster global cooperation, peace, and security, addressing international issues through diplomatic means and collaborative efforts among nations.
Q2: The five permanent members of the UN Security Council have ________ power.
Ans: veto
Permanent Security Council members possess the right to veto, enabling them to block resolutions, showcasing their significant influence in shaping international policies and decisions.
Q3: The body of all employees working for the UN is called ________.
Ans: Secretariat
The Secretariat comprises all UN employees, facilitating communication between UN organs. It plays a vital role in coordinating international efforts and maintaining organizational efficiency.
Q4: The International Court of Justice is located in ________.
Ans: The Hague, Netherlands
The ICJ, situated in The Hague, serves as the principal judicial body of the UN. It adjudicates legal disputes between states, promoting international peace and justice.
Q5: The UN General Assembly meets every ________.
Ans: year
The General Assembly convenes annually, providing member nations a platform to discuss global issues, make decisions, and establish collaborative initiatives, fostering international unity and cooperation.
Q6: The World Bank provides ________ and ________ to member countries, especially developing nations.
Ans: loans, grants
The World Bank extends financial assistance to member nations, supporting development projects through loans and grants. It focuses on fostering economic growth and reducing poverty, especially in developing countries.
Q7: The UN Secretary-General who initiated an inquiry into UN reforms in 1997 was ________.
Ans: Kofi Annan
Kofi Annan, as the UN Secretary-General, initiated a reform inquiry in 1997, aiming to enhance the organization's efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness in addressing global challenges and fostering international cooperation.
Q8: Amnesty International is a ________ organization that campaigns for human rights.
Ans: non-governmental
Amnesty International, a non-governmental organization, advocates for human rights globally. Through campaigns and advocacy, it raises awareness and promotes justice, equality, and dignity for individuals worldwide.
Q9: The UN seeks to prevent international conflicts and facilitate cooperation among ________.
Ans: nations
The UN's primary mission is to prevent conflicts by promoting diplomacy, dialogue, and cooperation among nations. It strives to foster peace, stability, and sustainable development globally.
Q10: The International Atomic Energy Agency promotes the peaceful use of ________ energy.
Ans: nuclear
The IAEA focuses on promoting nuclear energy for peaceful purposes, ensuring its safe use and preventing its military application. It contributes to global energy solutions while prioritizing safety and security.
Match the Column
Q1:
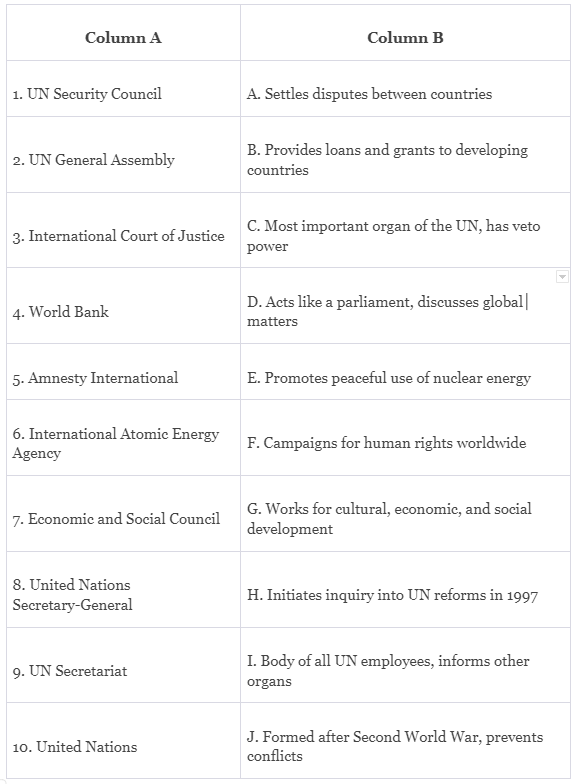
Ans: 1. UN Security Council (A. Settles disputes between countries)
The UN Security Council is the primary body responsible for maintaining international peace and security. It settles disputes between countries through various means, including diplomacy, sanctions, and peacekeeping missions.
2. UN General Assembly (D. Acts like a parliament, discusses global matters)
The UN General Assembly functions as a forum for all member states to discuss and coordinate on a wide array of international issues. It acts akin to a global parliament, allowing nations to voice their concerns, present proposals, and make decisions on global matters through voting.
3. International Court of Justice (C. Most important organ of the UN, has veto power)
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) is the principal judicial organ of the UN. Unlike the Security Council, it does not have veto power. Instead, it settles legal disputes between states and gives advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by the General Assembly, Security Council, or specialized UN agencies.
4. World Bank (B. Provides loans and grants to developing countries)
The World Bank provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries for development projects (e.g., building infrastructure, education, healthcare). It offers loans and grants to help these nations reduce poverty, promote economic growth, and foster sustainable development.
5. Amnesty International (F. Campaigns for human rights worldwide)
Amnesty International is a non-governmental organization that focuses on defending and promoting human rights globally. It campaigns against human rights abuses, conducts research and advocacy, and works to ensure justice, freedom, and dignity for people around the world.
6. International Atomic Energy Agency (E. Promotes peaceful use of nuclear energy)
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) promotes the peaceful use of nuclear energy and prevents its use for military purposes. It establishes international standards, provides technical assistance, and conducts inspections to ensure that nuclear technologies are used for peaceful and safe purposes.
7. Economic and Social Council (G. Works for cultural, economic, and social development)
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) is responsible for promoting international economic and social cooperation and development. It addresses a wide range of issues, including poverty, education, healthcare, and cultural development, to improve living standards and foster social progress worldwide.
8. United Nations Secretary-General (H. Initiates inquiry into UN reforms in 1997)
The UN Secretary-General is the chief administrative officer of the UN. The Secretary-General plays a vital role in initiating reforms within the organization. In 1997, Kofi Annan, the then Secretary-General, initiated an inquiry into how the UN should be reformed, reflecting the commitment to improving the organization's effectiveness.
9. UN Secretariat (I. Body of all UN employees, informs other organs)
The UN Secretariat serves as the executive branch of the UN. It comprises all UN employees worldwide and assists other UN organs in their functions. The Secretariat informs and advises the Security Council, General Assembly, and other UN bodies, keeping an account of their work and facilitating communication among them.
10. United Nations (J. Formed after Second World War, prevents conflicts)
The United Nations, established after the Second World War, is a global organization dedicated to preventing conflicts, fostering cooperation among nations, promoting human rights, providing humanitarian aid, and encouraging socio-economic development. It serves as a platform for dialogue and diplomacy, aiming to maintain international peace and security.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The UN Security Council is the most important organ of the UNO.
Reason: It has veto power, allowing permanent members to limit or withhold decisions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because the UN Security Council is indeed the most important organ of the UNO. It is responsible for maintaining international peace and security, making it a vital component of the United Nations. The reason is also true because the Security Council's significance is partly due to the veto power held by its permanent members. The veto power allows these members (USA, France, UK, China, and Russia) to block any substantive resolution, giving them a unique authority that adds to the Council's importance.
Q2: Assertion: India supports the restructuring of the UN Security Council.
Reason: India is the world's largest democracy and a major contributor to the UN budget.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true as India does support the restructuring of the UN Security Council. India believes that a strengthened and revitalized UN is essential in a changing world. The reason is also true. India's status as the world's largest democracy and its significant contributions to the UN budget justify its support for a more representative and inclusive UN Security Council. India argues that an expanded council will enjoy greater support in the global community, and this reason explains why India supports the restructuring.
Q3: Assertion: The UN can serve as a platform for discussions between the US and other countries in a unipolar world.
Reason: The US is the largest contributor to the UN and holds considerable influence.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true because the UN does serve as a platform for discussions between the US and other countries, even in a unipolar world where the US holds significant power. The UN provides a diplomatic forum for nations to engage in dialogue and negotiations on various global issues. The reason is also true; the US is the largest contributor to the UN in terms of funding, and this financial influence adds to its considerable sway within the organization, enabling it to play a vital role in international discussions.
Q4: Assertion: The UN General Assembly discusses and decides on general matters by a two-thirds majority.
Reason: This ensures that important decisions are made collectively and represent a global consensus.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true as decisions in the UN General Assembly are often made by a two-thirds majority vote. This ensures a collective decision-making process that incorporates the opinions of a majority of member states. The reason is also true because this method promotes inclusivity and represents a global consensus. Requiring a significant majority ensures that important decisions have substantial support from diverse nations, enhancing the legitimacy and representativeness of the resolutions passed.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the purpose of the United Nations?
Ans: The purpose of the United Nations is to prevent international conflict and facilitate cooperation among states.
Q2: Name three permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.
Ans: The three permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the United States, France, and China.
Q3: What is the role of the International Court of Justice?
Ans: The role of the International Court of Justice is to settle disputes between countries.
Q4: How often does the United Nations General Assembly meet and where?
Ans: The United Nations General Assembly meets twice a year - in July in Geneva and in April in New York.
Q5: What is the function of the United Nations Secretariat?
Ans: The United Nations Secretariat informs other UN organs and keeps an account of their work.
Q6: What was the purpose of the UN Trusteeship Council?
Ans: The purpose of the UN Trusteeship Council was to look after areas unable to maintain governance post-WWII until independence.
Q7: When was the World Trade Organization (WTO) established and what is its purpose?
Ans: The World Trade Organization (WTO) was established in 1995 to set rules for global trade.
Q8: What does the veto power of a permanent member of the Security Council mean?
Ans: The veto power of a permanent member allows them to limit or withhold a decision.
Q9: Name two prominent international human rights organizations.
Ans: Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch are two prominent international human rights organizations.
Q10: Why are reforms necessary for the United Nations?
Ans: Reforms are necessary to improve organization performance and address changing global challenges.
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical context leading to the formation of the United Nations after the Second World War.
Ans: The formation of the United Nations (UN) was a response to the devastation caused by World War II. The League of Nations, which was established after World War I, failed to prevent the outbreak of the second global conflict. The UN was established in 1945 with the aim of promoting peace and preventing future wars. It was hoped that through international cooperation and collective security, conflicts could be resolved peacefully.
Q2: Discuss the functions of the UN Security Council and the significance of the veto power held by permanent members.
Ans: The UN Security Council is responsible for maintaining international peace and security. Its functions include identifying threats to peace, taking action to prevent conflicts, and authorizing military interventions if necessary. The Security Council consists of five permanent members - the United States, Russia, China, France, and the United Kingdom - each with veto power. The veto power allows any of these permanent members to block any resolution, even if it has the support of all other members. This power has significant implications as it can lead to the paralysis of the Security Council and hinder its ability to respond effectively to global crises.
Q3: Describe the demands for reform in the UN's structures and processes, and analyze the implications of abolishing the veto power.
Ans: There have been calls for reforming the UN's structures and processes to make them more representative and democratic. Some argue for expanding the number of permanent members in the Security Council, while others advocate for abolishing the veto power altogether. Abolishing the veto power would require a significant overhaul of the UN Charter and would likely face resistance from current permanent members. However, it could lead to a more equitable and inclusive decision-making process within the Security Council, allowing for a greater diversity of voices and potentially preventing abuses of power.
Q4: Explain India's stance on restructuring the UN Security Council and the reasons behind its demand for a permanent seat.
Ans: India has long advocated for the restructuring of the UN Security Council to reflect the realities of the contemporary world. It seeks a permanent seat on the Security Council, arguing that as the world's largest democracy and a major global player, it deserves a seat at the decision-making table. India believes that its inclusion would enhance the Council's representativeness and effectiveness, allowing for better decision-making on issues of global importance.
Q5: Discuss the role of the UN in a unipolar world dominated by the US, considering its influence and financial contributions.
Ans: In a unipolar world dominated by the US, the role of the UN becomes crucial in maintaining a balance of power and ensuring multilateralism. The UN provides a platform for global cooperation, diplomacy, and negotiation. It serves as a forum for member states to address global challenges, such as climate change, terrorism, and nuclear proliferation. However, the influence and financial contributions of the US can sometimes influence the decision-making process within the UN, potentially leading to a concentration of power and undermining the principles of equality and fairness.
Q6: Briefly explain the roles of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and World Trade Organization (WTO) in the global arena.
Ans: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) aims to promote global monetary cooperation, stabilize currencies, and facilitate international trade. It provides financial assistance to member countries facing economic crises and offers policy advice to promote economic stability.
- The World Bank focuses on reducing poverty and promoting sustainable development. It provides loans and grants to developing countries for various projects, such as infrastructure development and poverty alleviation programs.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) seeks to regulate and promote international trade. It establishes rules for trade between member countries, resolves trade disputes, and facilitates negotiations on trade liberalization.
Q7: Compare the objectives and activities of Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch as international human rights organizations.
Ans: Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch are both international human rights organizations, but they have slightly different objectives and activities. Amnesty International focuses on promoting and campaigning for human rights by conducting research, raising awareness, and advocating for policy changes. It mobilizes public support and takes action to prevent and alleviate human rights abuses. Human Rights Watch also conducts research and advocacy to expose and address human rights violations. It investigates and reports on abuses, publishes detailed reports, and engages in direct advocacy with governments, international organizations, and other stakeholders. It seeks to hold perpetrators accountable and provide support to victims.
Q8: Discuss the significance of the UN and other international organizations in promoting global cooperation and preventing conflicts.
Ans: The UN and other international organizations play a crucial role in promoting global cooperation and preventing conflicts. They provide platforms for dialogue, negotiation, and diplomacy, allowing countries to address shared challenges and find peaceful solutions. These organizations facilitate cooperation on issues such as peacekeeping, humanitarian aid, sustainable development, and human rights. They also establish norms and standards that guide international behavior and promote the rule of law. By fostering multilateralism, these organizations help build trust and understanding among nations, reducing the likelihood of conflicts and promoting global stability.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explore the role of the UN Security Council in resolving international conflicts, maintaining peace, and its challenges in a rapidly changing world.
Ans: The UN Security Council plays a crucial role in resolving international conflicts and maintaining peace. It is responsible for the maintenance of international peace and security, and its decisions are binding on all UN member states. The Security Council consists of 15 members, 5 of which are permanent members with veto power (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and 10 non-permanent members elected for a two-year term.
- The Security Council has the authority to take various measures to address conflicts, such as imposing sanctions, authorizing the use of force, or deploying peacekeeping missions. It can also mediate between conflicting parties and facilitate negotiations for peaceful resolutions. By doing so, it aims to prevent the escalation of conflicts and protect civilians from violence and human rights abuses.
- However, the Security Council faces several challenges in a rapidly changing world. One of the main challenges is the veto power held by the permanent members. The use of veto power can hinder the Council's ability to take decisive action, as it requires the consensus of all five permanent members for any resolution to be adopted. This can lead to deadlock and inaction in situations where urgent intervention is needed.
- Another challenge is the evolving nature of conflicts and threats to international peace. In today's world, conflicts are often complex, involving multiple actors and transnational issues such as terrorism, cyber warfare, and organized crime. These challenges require innovative approaches and cooperation among member states, which can be difficult to achieve within the current structure of the Security Council.
- Moreover, the Security Council's effectiveness can be undermined by geopolitical rivalries and conflicting national interests among its members. Political considerations and power dynamics often influence decisions, leading to selective responses or the prioritization of certain conflicts over others. This can erode the credibility and legitimacy of the Security Council as a global peacekeeping body.
- In a rapidly changing world, the Security Council must adapt to address these challenges effectively. Reforming the Security Council has been a topic of debate for many years, with calls for increased representation, removal of veto power, and greater transparency in decision-making processes. However, reaching a consensus on such reforms is a complex task, as it requires the agreement of all member states, each with their own interests and priorities.
Q2: Analyze the challenges faced in implementing reforms within the UN, considering the diverse interests of member countries, and discuss the potential benefits of a restructured UN.
Ans: Implementing reforms within the United Nations (UN) is a complex process due to the diverse interests of member countries. The UN is composed of 193 member states, each with its own political, economic, and social priorities. This diversity often leads to divergent views on reform proposals and challenges the consensus-building process.
- One major challenge is the balance of power among member states. The UN was established after World War II with a structure that reflected the global power dynamics of that time. However, the global landscape has significantly changed since then, with the emergence of new powers and shifts in geopolitical influence. Reform proposals often aim to address this imbalance by increasing the representation and decision-making power of underrepresented regions, such as Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
- However, implementing such reforms requires the consent of the current major powers, who may be hesitant to relinquish their privileged positions. This creates resistance and reluctance to support reform initiatives, as it may result in a dilution of their influence and decision-making power within the UN.
- Another challenge is the divergent priorities and interests of member countries. The UN operates on the principle of sovereign equality, meaning that each member state has an equal say in decision-making processes. This can make it difficult to reach consensus on reforms, as countries have different perspectives on issues such as human rights, development, peace and security, and the role of the UN in global governance.
- Furthermore, financial considerations can pose challenges to implementing reforms. The UN relies on voluntary contributions from member states to fund its operations and programs. Disagreements over funding levels, distribution, and accountability can hinder the implementation of reforms, as countries may be unwilling to allocate additional resources or contribute more to the UN budget.
- Despite these challenges, a restructured UN has the potential to bring several benefits. Firstly, it can enhance the legitimacy and effectiveness of the organization by ensuring a more equitable representation of member states. This can lead to greater trust, cooperation, and inclusivity in decision-making processes, strengthening the UN's ability to address global challenges.
- Secondly, a restructured UN can improve the organization's responsiveness and adaptability to emerging global issues. By streamlining bureaucratic processes and increasing coordination among different UN agencies, a reformed UN can better address complex and interconnected challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and technological advancements. It can also foster innovation and collaboration among member states, enabling more effective and timely responses to evolving global threats.
- Lastly, a restructured UN can promote a more balanced and sustainable approach to global governance. By ensuring the meaningful participation of all member states, including those from the Global South, a reformed UN can foster a more inclusive and representative international order. This can contribute to a more peaceful, just, and prosperous world, where the interests and priorities of all nations are taken into account.
Q3: Examine the influence of major powers, particularly the US, in international organizations like the UN, IMF, and World Bank, and its impact on global decision-making processes.
Ans: Major powers, particularly the United States, exert significant influence in international organizations such as the United Nations (UN), International Monetary Fund (IMF), and World Bank. The influence of major powers stems from their economic, military, and political strength, which allows them to shape global decision-making processes and policy agendas.
- The United States, as the world's largest economy and a superpower, holds considerable influence in these organizations. It often plays a leading role in setting the agenda, mobilizing resources, and influencing outcomes. Its influence is particularly pronounced in the United Nations, where it is one of the five permanent members of the Security Council with veto power.
- The US influence in these organizations has both positive and negative impacts on global decision-making processes. On one hand, the US has the capacity to provide significant financial resources and technical expertise, enabling it to shape policies and programs that align with its national interests. It has the ability to influence the allocation of funds, conditions for financial assistance, and the overall direction of these organizations.
- However, the US's dominant role can also lead to concerns about its unilateralism and the prioritization of its own interests over global cooperation. Critics argue that the US's influence can undermine the principles of multilateralism, equity, and inclusivity. It can result in a concentration of power in the hands of a few, limiting the participation and influence of other member states.
- In addition, major powers like the US can also use their influence to advance their own political and strategic agendas. They may leverage their economic and military power to secure support for their policies, gain access to markets, or secure favorable trade agreements. This can create power imbalances and unequal relationships among member states, impacting the decision-making processes and outcomes of these organizations.
- However, it is important to note that the influence of major powers is not absolute and can be challenged. Other member states, particularly emerging powers, are increasingly asserting their voice and pushing for a more balanced and equitable global governance structure. Efforts are being made to enhance the representation and decision-making power of underrepresented regions and ensure that the interests of all member states are taken into account.
Q4: Predict the future role of international organizations in addressing emerging global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and technological advancements, considering their current functions and limitations.
Ans: International organizations are expected to play a crucial role in addressing emerging global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and technological advancements. These challenges are complex, interconnected, and require collective action at the global level. International organizations provide platforms for cooperation, coordination, and policy development, making them essential actors in addressing these issues.
- In the case of climate change, international organizations like the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have been instrumental in raising awareness, facilitating negotiations, and establishing global agreements such as the Paris Agreement. These organizations provide a forum for countries to come together, share knowledge, and develop strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
- However, international organizations face limitations in addressing climate change, primarily due to the voluntary nature of global agreements and the lack of enforcement mechanisms. The effectiveness of these organizations relies heavily on the willingness of member states to implement commitments and allocate resources. Overcoming these limitations requires stronger political will, increased financial support, and innovative approaches to climate governance.
- In the case of pandemics, international organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) play a central role in coordinating global responses, providing technical expertise, and sharing information. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of international cooperation in addressing health crises. International organizations facilitate the exchange of best practices, support capacity-building in developing countries, and coordinate efforts to ensure equitable access to vaccines and treatments.
- However, the response to the COVID-19 pandemic has also exposed the limitations of international organizations. The WHO, in particular, faced criticism for its handling of the crisis, with calls for reforms to strengthen its mandate, funding, and independence. Addressing these limitations requires greater investment in global health infrastructure, improved coordination among international organizations, and a reevaluation of the global governance framework for health emergencies.
- Regarding technological advancements, international organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) are involved in shaping policies, standards, and regulations in areas such as telecommunications, internet governance, and intellectual property rights. These organizations facilitate global cooperation, promote innovation, and address issues related to digital divide and cybersecurity.
- However, the rapid pace of technological advancements presents challenges for international organizations in keeping up with evolving trends and addressing emerging risks. Issues such as data privacy, artificial intelligence, and cyber warfare require new frameworks and regulations that can adapt to the changing technological landscape. International organizations must foster collaboration with the private sector, academia, and civil society to ensure their policies and approaches remain relevant and effective.
In conclusion, international organizations are expected to continue playing a vital role in addressing emerging global challenges. However, their effectiveness will depend on their ability to adapt to evolving circumstances, overcome limitations, and foster greater cooperation among member states. Strengthening the global governance framework, enhancing inclusivity and representation, and promoting multilateralism will be crucial in ensuring that international organizations can effectively address the complex and interconnected challenges of the future.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: International Organisations - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are some important international organizations in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. What is the role of UNESCO in promoting the humanities/arts? |  |
| 3. How does the International Federation of Arts Councils and Culture Agencies (IFACCA) support the arts sector? |  |
| 4. What initiatives does the International Council of Museums (ICOM) undertake to promote museums worldwide? |  |
| 5. How does the International Theatre Institute (ITI) contribute to the development of performing arts globally? |  |




















