Worksheet Solutions: Legislature | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Parliament is the center of all democratic ____________ processes.
Ans: political
Parliament is not just about law-making; it's the hub for political processes like debates, discussions, and decisions.
Q2: A genuine democracy is inconceivable without a representative, efficient, and effective ____________.
Ans: legislature
A functioning legislature is crucial for democratic governance as it represents the people's will and enacts laws.
Q3: The Indian Parliament consists of two houses, the Rajya Sabha and the ____________.
Ans: Lok Sabha
These are the two houses of India's bicameral legislature.
Q4: The Constitution allows states to have either a ____________ or bicameral legislature.
Ans: unicameral
States have the option to choose between a single-house legislature or a two-house legislature.
Q5: Rajya Sabha represents the states indirectly, with members elected by State ____________.
Ans: Legislative Assembly
Rajya Sabha members are elected by State Legislative Assembly members, not directly by the people.
Q6: In Rajya Sabha, one-third of the members complete their term every ____________ years.
Ans: two
Rajya Sabha members serve six-year terms, and one-third of them retire every two years, ensuring continuity.
Q7: The Rajya Sabha is also known as the ____________ House of Parliament.
Ans: Permanent
Unlike the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha is a continuing body, and it's always in session.
Q8: Lok Sabha is the lower house and represents the people directly through universal ____________.
Ans: adult suffrage
Lok Sabha members are elected directly by the people, and universal adult suffrage means every adult has the right to vote.
Q9: Parliament plays a crucial role in controlling taxation and government ____________.
Ans: spending
The legislative branch has the power to approve government budgets and taxation, ensuring fiscal responsibility.
Q10: Parliament has the power to discuss and enact changes to the ____________.
Ans: Constitution
This refers to the Parliament's constituent function, where it can amend the Constitution.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the term on the left with its correct definition on the right.
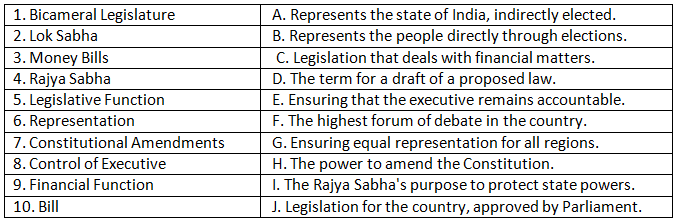 Ans: 1. Bicameral Legislature A. Represents the state of India, indirectly elected.
Ans: 1. Bicameral Legislature A. Represents the state of India, indirectly elected.
Rajya Sabha, as the upper house, represents the states indirectly.
2. Lok Sabha B. Represents the people directly through elections.
Lok Sabha is the lower house, and its members are elected directly by the people.
3. Money Bills C. Legislation that deals with financial matters.
Money bills are specifically about financial matters like taxation and public expenditure.
4. Rajya Sabha D. The term for a draft of a proposed law.
A bill is a proposed law before it becomes an act.
5. Legislative Function E. Ensuring that the executive remains accountable.
The control of the executive branch is one aspect of the legislative function.
6. Representation F. The highest forum of debate in the country.
The Parliament is where debates on national issues take place.
7. Constitutional Amendments G. Ensuring equal representation for all regions.
Representation ensures that all regions have a voice in the legislative process.
8. Control of Executive H. The power to amend the Constitution.
Amending the Constitution is a significant power of Parliament.
9. Financial Function I. The Rajya Sabha's purpose to protect state powers.
One of Rajya Sabha's roles is to protect the interests of the states.
10. Bill J. Legislation for the country, approved by Parliament.
Bills become laws when approved by Parliament.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Parliament is essential for democratic governance.
Reason: It represents the diverse interests of the people and holds the government accountable.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (b)
While both the Assertion and Reason are true, the Reason does not directly explain the Assertion. The importance of Parliament for democratic governance is clear, but the Reason does not explain why it's essential.
Q2: Assertion: The Rajya Sabha represents the states of India and is indirectly elected.
Reason: Members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by residents of the states.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
In this case, the Assertion is true, and the Reason correctly explains why the Rajya Sabha represents the states. Members are indirectly elected by the State Legislative Assembly, which represents the states.
Q3: Assertion: A bicameral legislature ensures a double check on every decision.
Reason: Bills and policies are discussed and voted on in both houses.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The Assertion is accurate, and the Reason provides a correct explanation. In a bicameral system, decisions are subjected to review and scrutiny in both houses, ensuring a double check.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the role of a Parliament in a democracy?
Ans: The role of Parliament in a democracy is to represent the people, make and pass laws, hold the government accountable, and ensure checks and balances in the system. It is the central institution of democratic governance.
Q2: What are the two houses of the Indian Parliament?
Ans: The two houses of the Indian Parliament are the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People).
Q3: What is the purpose of Rajya Sabha?
Ans: The purpose of Rajya Sabha is to represent the states of India and protect their interests. It acts as a revising chamber and ensures that decisions made by the Lok Sabha are reviewed and reconsidered.
Q4: How often do one-third of Rajya Sabha members complete their terms?
Ans: One-third of Rajya Sabha members complete their terms every two years, as members are elected for six-year terms, and their terms are staggered.
Q5: What is the main function of Lok Sabha?
Ans: The main function of Lok Sabha is to represent the people directly and make and pass laws. It is the lower house of Parliament and plays a crucial role in the legislative process.
Q6: What is the significance of financial functions in Parliament?
Ans: The financial functions of Parliament include controlling taxation, government spending, and approving budgets. This ensures that government finances are managed transparently and responsibly.
Q7: Explain the concept of representation in Parliament.
Ans: Representation in Parliament means that elected members (MPs) act as the voice of their constituents. They represent the interests, concerns, and views of the people in the legislative process.
Q8: What is a money bill according to the Constitution?
Ans: According to the Constitution, a money bill is a type of legislation that exclusively deals with financial matters, such as taxation, public expenditure, and the Consolidated Fund of India.
Q9: How can a deadlock be resolved in Parliament?
Ans: A deadlock in Parliament can be resolved by calling a joint session of both houses. In a joint session, members vote to decide the fate of a bill, and if a majority approves it, the bill is passed.
Q10: What happens if the President withholds assent to a bill?
Ans: If the President withholds assent to a bill, it does not become a law. The President may send the bill back to the house for reconsideration or use discretionary powers like a "pocket veto."
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the advantages of having a bicameral legislature in a diverse country like India.
Ans: Having a bicameral legislature in a diverse country like India has several advantages. It allows for better representation of different states and regions, ensures checks and balances, and provides a platform for reconsidering decisions. It also accommodates varying interests and perspectives, leading to more informed and balanced legislation.
Q2: Explain the role of Rajya Sabha in representing the states and protecting their powers.
Ans: Rajya Sabha represents the states by having members elected by State Legislative Assemblies. Its role is to review and revise legislation passed by the Lok Sabha. By doing so, it ensures that the interests of states are safeguarded, and their concerns are addressed in the decision-making process at the national level.
Q3: Detail the legislative functions of Parliament and how laws are enacted.
Ans: The legislative functions of Parliament include drafting, debating, and passing laws. Laws are enacted through a process where a bill is introduced, discussed, amended (if necessary), and voted upon in both houses (Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha). If both houses pass the bill, it goes to the President for assent and becomes a law.
Q4: How does Parliament ensure accountability of the executive branch of government?
Ans: Parliament ensures accountability of the executive branch by allowing members to question government ministers, scrutinize policies, and demand explanations for decisions. It can hold debates and discussions to keep the government in check, making it answerable to the people.
Q5: Discuss the different types of bills and their significance in the legislative process.
Ans: There are different types of bills, including public bills (government and private member's bills), money bills, financial bills, and constitutional amendment bills. Each type serves a specific purpose. Money bills deal with financial matters, while constitutional amendment bills modify the Constitution. Understanding these types is crucial for the legislative process.
Q6: Describe the procedures involved in the enactment of ordinary bills in Parliament.
Ans: Enacting ordinary bills involves several stages: introduction, debate, committee scrutiny, and voting in both houses. If a bill is passed in one house, it goes to the other house for consideration. The second house may pass it as is, with amendments, or reject it. If both houses agree, the bill goes to the President for assent.
Q7: What is the significance of money bills, and how are they processed in Parliament?
Ans: Money bills deal with financial matters and are significant for the government's fiscal management. They can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha and must be approved by both houses. The Rajya Sabha can suggest amendments, but the Lok Sabha has the final say. The President's approval is also required.
Q8: Explain the role of the President in the legislative process, including the use of discretionary powers.
Ans: The President's role in the legislative process is to give assent to bills passed by Parliament. The President can use discretionary powers, such as withholding assent or sending a bill back for reconsideration. These powers ensure that the President acts as a constitutional check on Parliament's decisions.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the essential functions of Parliament, including its role in controlling the executive and ensuring transparency and accountability.
Ans: Parliament is a cornerstone of democratic governance, and it serves several essential functions that are crucial for maintaining the balance of power, accountability, and transparency in a democratic system. These functions play a pivotal role in ensuring the proper functioning of the government and safeguarding the interests of the citizens.
The following are the essential functions of Parliament:
- Legislative Function: Parliament is primarily responsible for the enactment, modification, and repeal of laws. It is the supreme legislative body in a democracy, and it drafts, discusses, amends, and passes legislation. The legislative process includes careful consideration of bills, ensuring that they are in line with the needs and values of the society.
- Control of the Executive and Ensuring Accountability: Parliament acts as a check on the executive branch of government. The executive, including the Prime Minister and Cabinet, derives its authority from Parliament. Members of Parliament (MPs) have the power to question government ministers, scrutinize their policies, and demand explanations for decisions. Through mechanisms like Question Hour, debates, and discussions, the government is held accountable for its actions. This transparency ensures that the government is answerable to the people who elected it.
- Financial Function: In a democratic system, the legislature has significant control over government finances. Parliament approves budgets and has the authority to tax citizens and allocate funds for various programs and expenditures. It reviews government spending and holds the government accountable for the allocation and utilization of public funds.
- Representation: Parliament represents the diverse interests, concerns, and viewpoints of citizens from different regions, social backgrounds, economic strata, and religious beliefs. Elected representatives act as the voice of their constituents in the decision-making process, ensuring that the needs of all sections of society are considered.
- Debating Function: Parliament is the highest forum for open and unrestricted debate. MPs are free to discuss any matter without fear or restrictions. This feature allows Parliament to analyze and evaluate various issues that the nation faces, leading to well-informed decision-making. Debates are at the core of democratic decision-making.
- Constituent Function: Parliament has the power to discuss and enact changes to the Constitution. Constitutional amendments require a special majority in both houses of Parliament. This ensures that changes to the fundamental principles of the nation are made after careful deliberation and consensus.
- Electoral Functions: Parliament plays a significant role in the election of the President and the Vice President of India. These elections are vital components of the democratic process and ensure that the highest constitutional authorities are selected through a representative process.
- Judicial Functions: The Parliament also has judicial functions, including considering proposals for the removal of the President, Vice-President, Judges of High Courts, and the Supreme Court. This mechanism ensures that individuals holding critical positions in the country are held accountable for their actions.
Q2: Explain how Parliament ensures the representation of diverse interests in a democratic society, considering regional, social, economic, and religious factors.
Ans: Parliament, as the supreme legislative body in a democratic society, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the representation of diverse interests. It is essential for Parliament to reflect the complexity and diversity of a nation, taking into account various factors, including regional, social, economic, and religious considerations.
Here's how Parliament ensures such representation:
- Geographical Representation: One of the fundamental ways Parliament ensures diversity is through geographical representation. In the case of India, which is a vast and diverse country, the Parliament is bicameral, with the Lok Sabha (House of the People) representing the people directly. Lok Sabha members are elected from territorial constituencies with approximately equal populations, ensuring that different regions have proportional representation. Additionally, the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) represents the states, with members elected by State Legislative Assemblies, further reinforcing regional representation.
- Social and Economic Diversity: Parliament reflects the social and economic diversity of the country by electing members from different backgrounds. India is a socially and economically diverse nation, with varying groups, castes, and communities. MPs come from various social, economic, and educational backgrounds, which influences the policies and laws they advocate for. This diversity allows Parliament to address the specific needs and concerns of different segments of society.
- Religious Representation: India is a religiously diverse nation with multiple faiths and religious communities. Parliament ensures religious representation by allowing individuals from different religious backgrounds to participate in the political process. MPs may identify with various religions, and they often advocate for policies that respect the secular and pluralistic ethos of the country. This ensures that the religious fabric of the nation is acknowledged and respected in the legislative process.
- Inclusive Electoral System: The inclusive nature of the electoral system is a critical factor in ensuring representation. Universal adult suffrage allows every adult citizen, regardless of their background, to vote and stand for election. This inclusivity ensures that individuals from all walks of life have the opportunity to participate in the democratic process, become potential representatives, and influence policy decisions.
- Political Party System: Political parties play a significant role in ensuring diverse representation. These parties often have specific policy agendas and ideologies, reflecting a wide range of perspectives and interests. Parties nominate candidates from various backgrounds, ensuring that multiple voices are heard in the legislative process. MPs, representing different parties, contribute to the diversity of views and concerns presented in Parliament.
- Special Representation: To address historically disadvantaged and marginalized groups, India has introduced provisions like reserved seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs). These reservations provide specific representation for these groups in both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, ensuring that historically marginalized communities have a voice in the legislative process.
Q3: Describe the powers and functions of both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, highlighting their roles in the legislative process and control of the executive.
Ans: India's Parliament consists of two houses, the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States), each with distinct powers and functions. Both houses play crucial roles in the legislative process and controlling the executive, but they have specific duties and responsibilities.
- Lok Sabha (House of the People): Lok Sabha, as the lower house, is directly elected by the citizens of India. It plays a central role in the legislative process and the functioning of the government.
The key powers and functions of the Lok Sabha include:- Legislative Function: Lok Sabha is primarily responsible for the passage of bills. It introduces, debates, amends, and votes on legislation. Many significant bills, including money bills, must originate in the Lok Sabha.
- Financial Functions: The Lok Sabha controls public finances. It approves the government's annual budget, grants or denies funds, and has the exclusive power to deal with money bills. It scrutinizes government spending, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Executive Control: Lok Sabha exercises significant control over the executive branch. The Council of Ministers, headed by the Prime Minister, must have the confidence of the Lok Sabha. The Prime Minister is usually the leader of the majority party in the Lok Sabha. The Lok Sabha can question the executive, demand explanations, and even pass a vote of no confidence, which can lead to the fall of the government.
- Representation: Lok Sabha represents the will of the people directly. Its members are elected from various constituencies across India. They are responsible for representing the concerns and interests of their constituents in the legislative process.
- Rajya Sabha (Council of States): Rajya Sabha is the upper house of Parliament, and its members are not directly elected but chosen by the State Legislative Assemblies. It plays a distinct but equally important role in the legislative process and controlling the executive.
The key powers and functions of the Rajya Sabha include:- Review and Revising Chamber: Rajya Sabha acts as a revising chamber. It reviews and scrutinizes bills passed by the Lok Sabha. While it cannot veto money bills, it can suggest amendments. This process ensures that bills are thoroughly examined and considered from different perspectives.
- Representation of States: Rajya Sabha represents the interests of the states. Members are elected by State Legislative Assemblies, ensuring that the concerns and aspirations of the states are adequately represented at the national level.
- Expertise and Experience: Rajya Sabha often includes members with expertise and experience in various fields, such as science, arts, literature, and social service. This diversity of knowledge enriches the legislative process and contributes to well-informed decision-making.
- Council of Elders: Rajya Sabha is sometimes referred to as the "Council of Elders" due to its role in providing seasoned and wise counsel on important national issues. It is less subject to the immediate pressures of electoral politics, allowing for more considered deliberations.
- Special Powers: In certain areas, Rajya Sabha has special powers, such as approving constitutional amendments and impeaching the President or other high-ranking officials. These powers ensure a balanced distribution of authority and prevent unilateral decisions.
Q4: Outline the procedures involved in the enactment of constitutional amendment bills and the significance of such amendments in the Indian Constitution.
Ans: The Indian Constitution can be amended to adapt to changing needs and circumstances. However, the procedure for amending the Constitution is more stringent than that for ordinary legislation, reflecting the Constitution's fundamental nature.
The procedures for the enactment of constitutional amendment bills are as follows:
- Introduction: Any amendment to the Constitution can be initiated in either house of Parliament, the Lok Sabha or the Rajya Sabha. The President of India may also propose amendments.
- Passage: The bill must be passed by a special majority in both houses of Parliament. This means that it must be supported by at least two-thirds of the members present and voting, as well as a majority of the total membership in each house. The special majority requirement ensures that constitutional amendments have broad support.
- Approval of States: In some cases, constitutional amendments require approval by a majority of the state legislatures. This is necessary for amendments that affect federal relations, such as changes in the powers of the states or alterations in the representation of states in Parliament. For this purpose, at least half the state legislatures must pass the amendment.
Significance of Constitutional Amendments:
Constitutional amendments are significant for several reasons:
- Flexibility: They allow the Constitution to adapt to changing social, political, and economic realities. Over time, new challenges and issues may emerge that require constitutional adjustments.
- Protection of Fundamental Rights: Amendments can enhance or reinforce fundamental rights and freedoms. For example, the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments empowered local self-government institutions, strengthening democracy at the grassroots level.
- Balancing Federal Relations: Amendments can address imbalances in federal relations, ensuring a fair distribution of powers and resources between the center and the states. The 101st Constitutional Amendment introduced the Goods and Services Tax (GST), transforming India into a single, unified market.
- Adoption of International Agreements: India's international commitments may require constitutional amendments to align domestic laws with international obligations. Amendments may be needed to ratify international treaties or agreements.
- Preservation of Basic Structure: While the Constitution can be amended, it cannot alter its basic structure. The Supreme Court of India has established that certain core features of the Constitution, such as federalism and secularism, are beyond the scope of amendment.
|
43 videos|278 docs|39 tests
|




















