Worksheet: Judiciary | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answers Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The principal role of the judiciary is to protect the __________ of law and ensure the supremacy of law.
Q2: The judiciary must be independent of any __________ pressures.
Q3: The judiciary consists of three main branches: Legislature, Executive, and __________.
Q4: The convention of appointing the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court as the Chief Justice of India was broken twice in ________ and ________.
Q5: To remove a judge, a motion containing charges against the judge must be approved by a special majority in both ________ of Parliament.
Q6: The Supreme Court of India has ________ judges, including the Chief Justice.
Q7: High Courts hear appeals from ________ courts.
Q8: The Supreme Court has exclusive jurisdiction over disputes related to ________ relations.
Q9: PIL stands for ________ and has become an important part of judicial activism.
Q10: The power of judicial review allows the Supreme Court to examine the constitutionality of any law and declare it ________ if it is inconsistent with the Constitution.
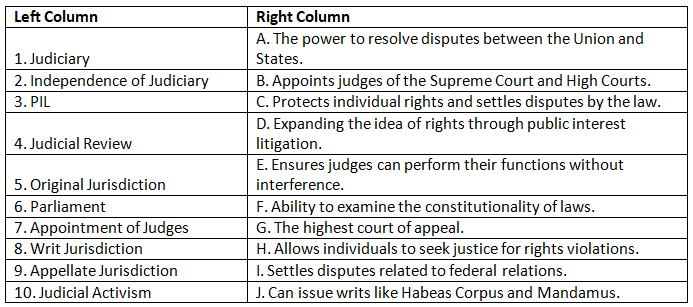
Match the Column
Q1: Match the items in the left column with the appropriate descriptions in the right column.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The independence of the judiciary does not imply arbitrariness.
Reason: The judiciary is accountable to the Constitution and the people.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: The power of judicial review is significant.
Reason: India has a written constitution.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Judicial activism allows the judiciary to consider broader societal implications.
Reason: It restricts the courts to only apply the applicable law.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: The Supreme Court can issue writs to protect fundamental rights.
Reason: High Courts also have the power to issue writs.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q5: Assertion: Parliament has the authority to enact laws limiting fundamental rights while enforcing directive principles.
Reason: The judiciary has no role in interpreting the Constitution.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the importance of an independent judiciary.
Q2: What is the role of the Council of Ministers in the appointment of judges?
Q3: What is the special majority required for the removal of a judge?
Q4: How many judges are there in the Supreme Court at present?
Q5: What are the four types of writs that the Supreme Court can issue?
Q6: What is the original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court?
Q7: Who can directly approach the Supreme Court if their fundamental rights are violated?
Q8: What is judicial activism?
Q9: How does the judiciary protect individual rights?
Q10: What is advisory jurisdiction in the context of the Supreme Court?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of judicial independence and why it's essential for democracy.
Q2: Discuss the controversy surrounding the appointment of judges in India.
Q3: Describe the structure and functions of the Supreme Court.
Q4: Explain the concept of original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court with examples.
Q5: How does the Supreme Court protect individual rights through judicial review?
Q6: What is the significance of Public Interest Litigations (PILs) in judicial activism?
Q7: What powers do High Courts have regarding the issuance of writs?
Q8: Discuss the key issues that have led to disputes between the Parliament and the judiciary.
Long Answers Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the principles of an independent judiciary and its role in upholding the rule of law.
Q2: Analyze the challenges and controversies in the appointment of judges in India and the Supreme Court's recommendations.
Q3: Explain the different types of jurisdiction of the Supreme Court and their significance in upholding justice.
Q4: Elaborate on the concept of judicial activism, its impact on society, and the role of Public Interest Litigations (PILs) in promoting justice.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
44 videos|387 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Judiciary - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the role of the judiciary in a democratic society? |  |
| 2. How are judges appointed in the judicial system? |  |
| 3. What is the hierarchy of courts in the judicial system? |  |
| 4. How are judges ensured to be impartial and independent? |  |
| 5. How can the public hold judges accountable for their actions? |  |




















